💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
使用遗传算法解决机器人路径规划问题在机器人领域,路径规划是一项关键任务,旨在为机器人找到从起始位置到目标位置的最优或接近最优路径。遗传算法作为一种强大的优化算法,在解决机器人路径规划问题上具有显著优势。 遗传算法通过模拟自然进化过程来搜索最优解。在机器人路径规划中,首先需要将路径问题进行编码,通常可以将路径表示为一系列的坐标点或者特定的数据结构。然后,初始化一个包含多个潜在路径的种群。 适应度函数在遗传算法中起着核心作用。对于机器人路径规划,适应度函数可以根据路径的长度、安全性、平滑度等因素来评估每个路径的优劣。路径越短、避开障碍物的能力越强、运动越平滑,其适应度就越高。 通过遗传操作,如选择、交叉和变异,不断地改进种群中的路径。选择操作根据适应度挑选出较优的路径作为父代,交叉操作将父代路径进行组合以产生新的路径,变异操作则对路径进行随机的改变,增加种群的多样性。 随着迭代的进行,种群中的路径逐渐优化,最终收敛到一个较好的解决方案,即机器人的最优或接近最优路径。遗传算法能够处理复杂的环境,包括存在多个障碍物、动态变化的环境等情况,为机器人在不同场景下的路径规划提供了一种有效的方法。
📚2 运行结果
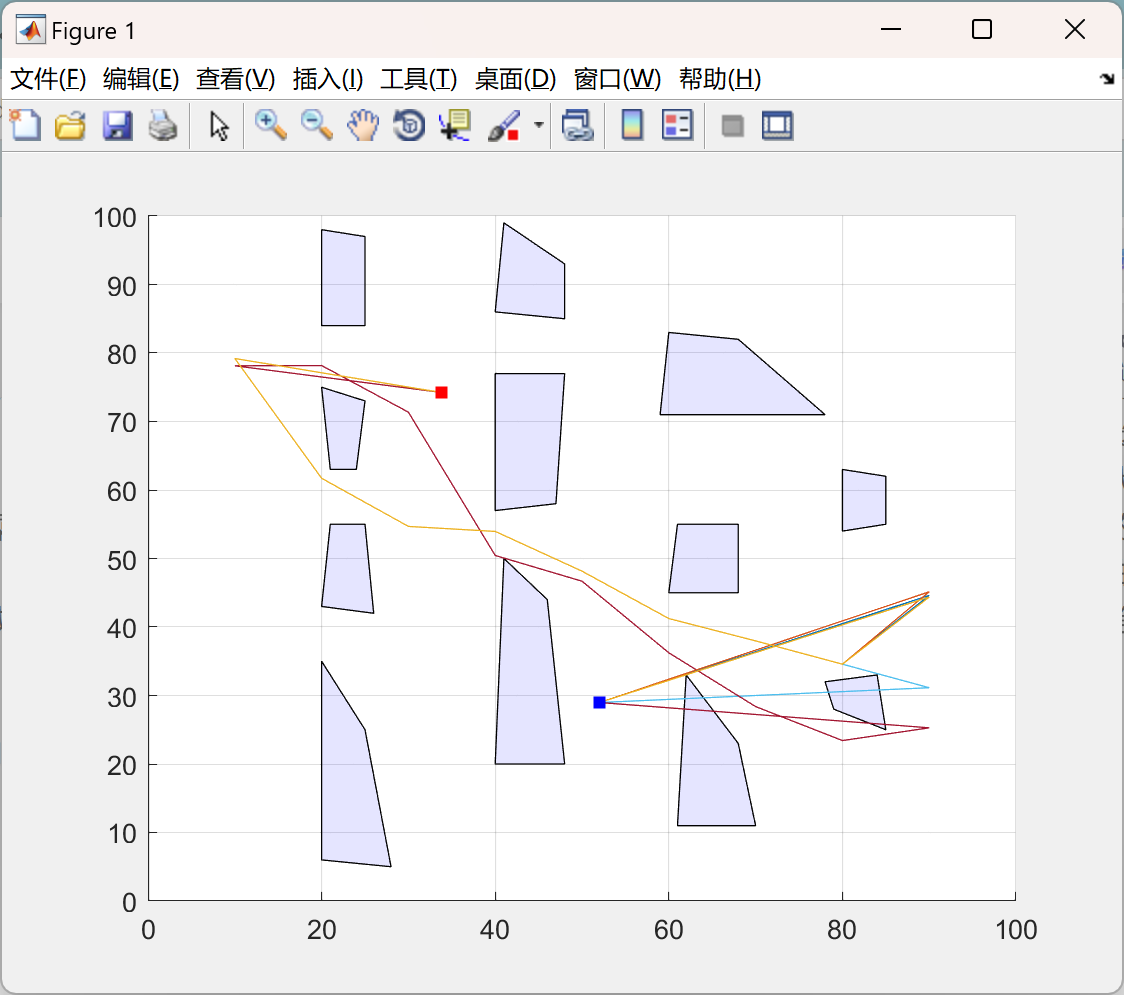
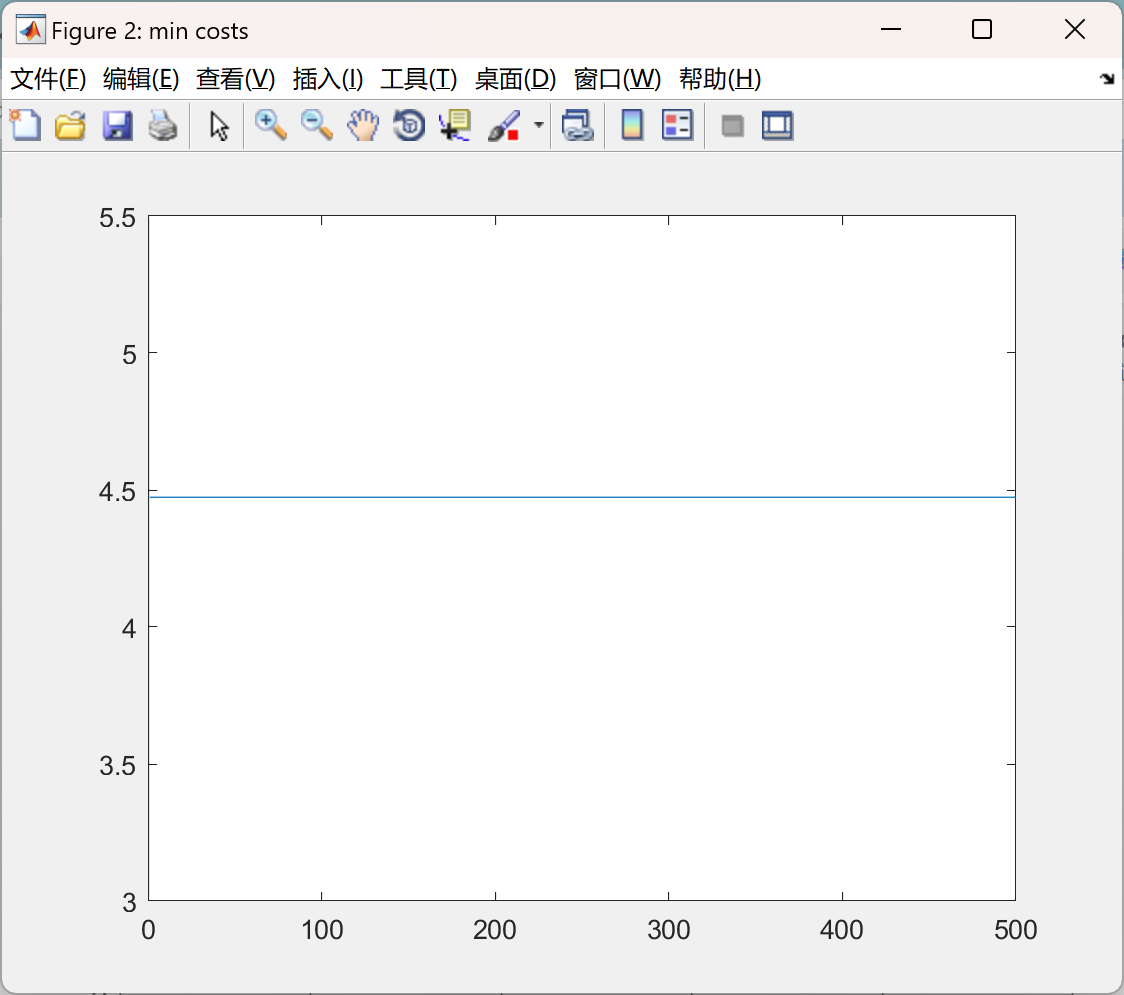
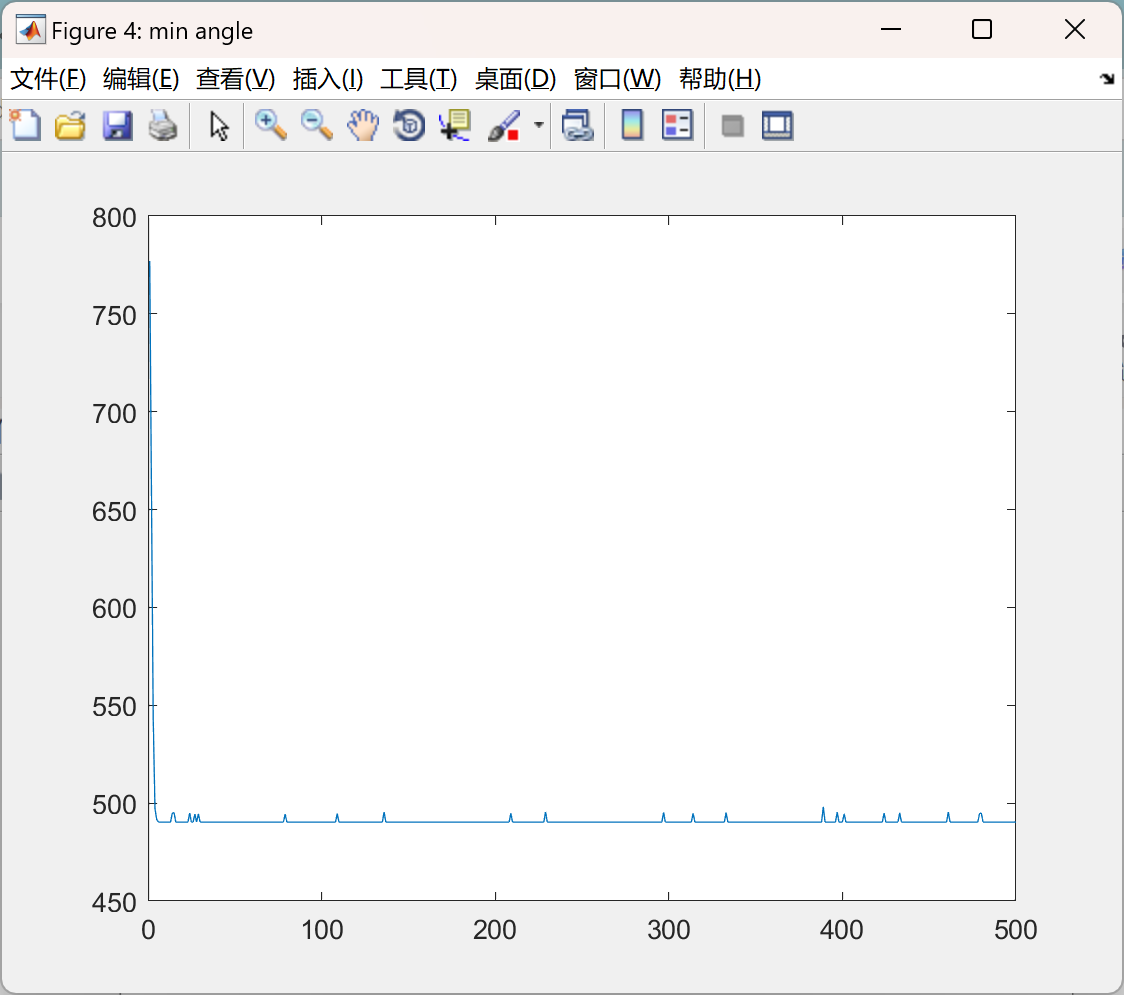
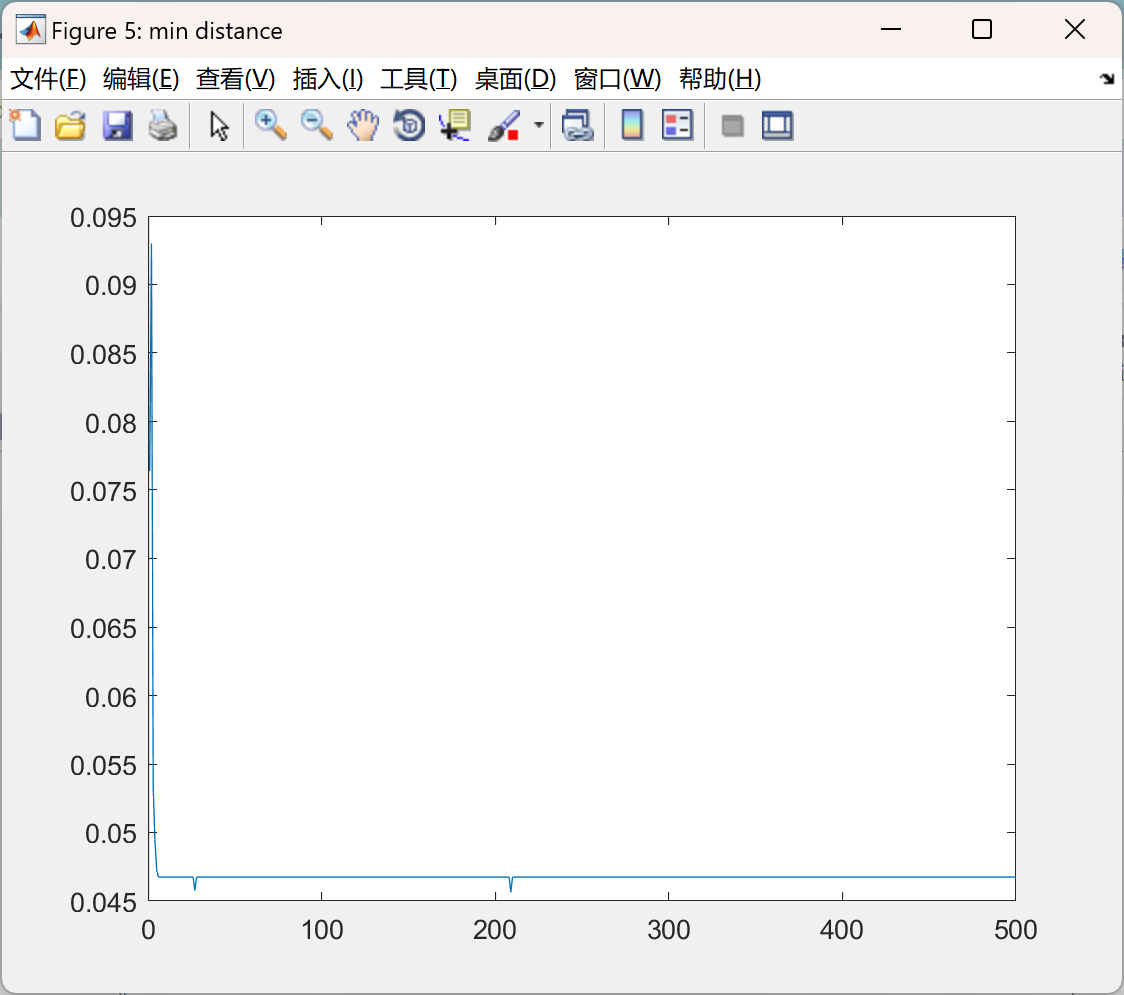
主函数部分代码:
clear all;
close all;
clc;
%% Create and plot Obstacle
areax = 100;
areay = 100;
% Obstacle Locations
O_loc = [[[20 25 25 20]; [98 97 84 84]]; ...
[[20 25 24 21]; [75 73 63 63]]; ...
[[21 25 26 20]; [55 55 42 43]]; ...
[[20 25 28 20]; [35 25 5 6]]; ...
[[41 48 48 40]; [99 93 85 86]]; ...
[[40 48 47 40]; [77 77 58 57]]; ...
[[41 46 48 40]; [50 44 20 20]]; ...
[[60 68 78 59]; [83 82 71 71]]; ...
[[61 68 68 60]; [55 55 45 45]]; ...
[[62 68 70 61]; [33 23 11 11]]; ...
[[80 85 85 80]; [63 62 55 54]]; ...
[[78 84 85 79]; [32 33 25 28]]; ...
];
swap = size(O_loc);
O_num = swap(1)/2; %Number of obstacle
% Create obstacles
for i=1:O_num
n = i*2;
pgon(i) = polyshape(O_loc(n-1,:),O_loc(n,:));
end
% Plot obstacle
plot(pgon,'FaceColor','blue','FaceAlpha',0.1)
xlim([0,100]);
ylim([0,100]);
hold on
grid on
%% Insert begining and end point
disp('Please,');
disp('select bigining point and then select end point.')
% Ask user for input begining and end point
swap = getline();
beginP = swap(1,:);
endP = swap(2,:);
% Plot begin and end point
scatter(beginP(1), beginP(2),40, 'red', 'filled','s');
scatter(endP(1), endP(2),40, 'blue', 'filled','s');
min_dis = Path_length([beginP; endP]);
disp("minimum distance is: " + min_dis);
disp(".");
disp("..");
disp("...");
%% Initialize population
pop_num = 50;
init_num = 25;
famous = 100*ones(pop_num/5,12);
y_best = (endP(2)-beginP(2))/9*(1:9) + beginP(2);
pop = zeros(init_num,9);
for i=1:9
pop(:,i) = random('Normal',y_best(i), 8, init_num,1);
end
begin_mat = repmat(beginP(2),init_num,1);
end_mat = repmat(endP(2),init_num,1);
pop = [begin_mat pop end_mat];
x_val = [beginP(1) 10:10:90 endP(1)];
check_flag = 0;
tic;
for j=1:init_num
k=2;
while k <= 9
i=0;
while i < O_num
i = i+1;
while Collision_detect(pgon(i),[x_val(1:k+1); pop(j,1:k+1)])
pop(j,k:k+1) = random('Normal',(y_best(k)+y_best(k))/2 , 8, 1, 2);
check_flag = 1;
end
if check_flag == 1
i = 0;
check_flag = 0;
end
end
k = k+1;
end
% plot(x_val, pop(j,:));
end
disp(toc + " Second primary papulation generating taked!!")
% pop = [pop; zeros(pop_num-init_num,9)];
swap = CrossOver(pop, pop_num-init_num);
swap = Rm_wr_child(pgon, x_val, swap);
disp("primary population cost values");
costs = Cost_func(O_loc, pop, x_val);
pop = [pop; swap];
Draw_path(pgon, x_val, pop);
%% Main Loop (Cost Assignment, Selection, Cross Over and Mutation)
cnt = 0;
it_num = 500;
results = zeros(it_num, 4);
for i=1:it_num
disp("Iteration " + i + " ====================>");
[costs,results(i,2), results(i,3), results(i,4)] = Cost_func(O_loc, pop, x_val);
rank = Sort_Costs(costs);
results(i,1) = costs(rank(1));
disp("Minimum error " + costs(rank(1)));
famous = Hall_of_fame(pop, costs, rank, famous);
pop = Path_Selection(rank, pop, init_num);
swap = CrossOver(pop, pop_num-init_num);
swap = Mutation(swap,cnt);
swap = Rm_wr_child(pgon, x_val, swap);
pop = [pop; swap];
% size(pop,1)
cnt = cnt+1;
end
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]郭聚刚,于军琪,冯春勇,等.基于改进A*算法的机器人不平坦地形全局路径规划[J/OL].计算机工程与应用,1-16[2024-10-23].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2127.TP.20241015.1802.016.html.
[2]王影,王晓茹,孙万龙,等.改进自适应精英蚁群算法的机器人路径规划[J].吉林化工学院学报,2024,41(03):1-8.DOI:10.16039/j.cnki.cn22-1249.2024.03.001.
🌈4 Matlab代码实现






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








