💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
💥1 概述
随着机器人技术的不断发展,移动机器人在工业、医疗、服务等领域的应用越来越广泛。为了使移动机器人能够高效、安全地到达目标位置,路径规划成为关键问题之一。Dijkstra 法作为一种经典的图论算法,在移动机器人路径规划中有着重要的应用。基于栅格地图进行路径规划,可以将机器人的工作环境进行离散化表示,便于算法的实现和计算。Dijkstra 算法是一种用于求解图中最短路径的算法。它的基本思想是从起始节点开始,逐步向外扩展,每次选择距离起始节点最近且未确定最短路径的节点进行处理,直到到达目标节点。在处理每个节点时,更新其到起始节点的最短距离,并记录下最短路径上的前驱节点。最终,通过回溯前驱节点可以得到从起始节点到目标节点的最短路径。栅格地图将机器人的工作环境划分为一个个大小相等的栅格单元。每个栅格可以表示为空闲区域、障碍物区域或未知区域等不同状态。通过这种离散化的表示方式,可以将机器人的路径规划问题转化为在栅格地图上寻找从起始栅格到目标栅格的最短路径问题。
📚2 运行结果
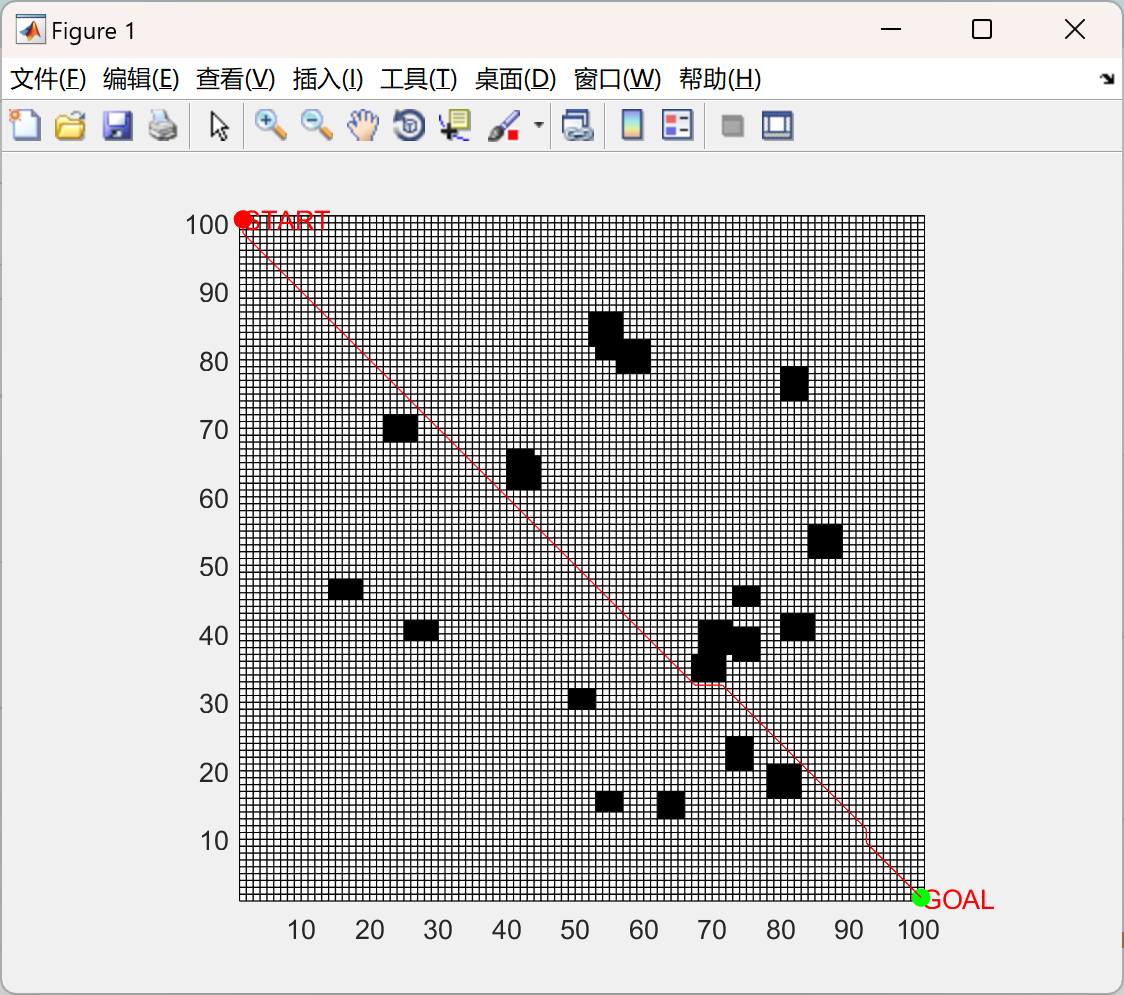
部分代码:
function [Cost, Route] = Dijkstras( Graph, SourceNode, TerminalNode )
%Dijkstras.m Given a graph with distances from node to node calculates the
%optimal route from the Source Node to the Terminal Node as defined by the
%inputs.
%
% Inputs:
%
% Graph - A graph of the costs from each node to each other also known as
% an adjacency matrix. In the context of this project it is a matrix of the
% distances from cities within North Carolina to each other. You can mark
% unconnected nodes as such by assigning them values of Inf. For instance,
% if nodes 3 & 5 are unconnected then Graph(3,5)=Graph(5,3)=Inf;
%
% SourceNode - The index of the node (city) which you wish to travel from
%
% TerminalNode - The index of the node (city) which you wish to travel to
%
% Outputs:
%
% Cost - The cost to travel from the source node to the terminal node.
% There are several metrics this could be but in the case of route planning
% which I am working on this is distance in miles.
%
% Route - A vector containing the indices of the nodes traversed when going
% from the source node to the terminal node. Always begins with the source
% node and will always end at the terminal node unless the algorithm fails
% to converge due to there not existing a valid path between the source
% node and the terminal node.
% Check for valid parameters
if size(Graph,1) ~= size(Graph,2)
fprintf('The Graph must be a square Matrix\n');
return;
elseif min(min(Graph)) < 0
fprintf('Dijkstras algorithm cannot handle negative costs.\n')
fprintf('Please use Bellman-Ford or another alternative instead\n');
return;
elseif SourceNode < 1 && (rem(SourceNode,1)==0) && (isreal(SourceNode)) && (SourceNode <= size(Graph,1))
fprintf('The source node must be an integer within [1, sizeofGraph]\n');
return;
elseif TerminalNode < 1 && (rem(TerminalNode,1)==0) && isreal(TerminalNode) && (TerminalNode <= size(Graph,1))
fprintf('The terminal node must be an integer within [1, sizeofGraph]\n');
return;
end
% Special Case so no need to waste time doing initializations
if SourceNode == TerminalNode
Cost = Graph(SourceNode, TerminalNode);
Route = SourceNode;
return;
end
% Set up a cell structure so that I can store the optimal path from source
% node to each node in this structure. This structure stores the
% antecedents so for instance if there is a path to B through A-->C-->D-->B
% you will see [A,C,D] in cell{B} (as well as a bunch of filler 0's after
% that)
PathToNode = cell(size(Graph,1),1);
% Initialize all Node costs to infinity except for the source node
NodeCost = Inf.*ones(1,size(Graph,1));
NodeCost(SourceNode) = 0;
% Initialize the Current Node to be the Source Node🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]张弛,魏巍.基于改进人工势场法的移动机器人路径规划[J/OL].系统仿真学报:1-10[2024-09-23].https://doi.org/10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.24-0665.
[2]王海群,宋国章,晁帅,等.基于蜣螂算法和DWA算法的机器人动态路径规划[J/OL].制造技术与机床:1-13[2024-09-23].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3398.TH.20240918.1739.031.html.
🌈4 Matlab代码实现





















 1935
1935

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








