1 异常检测Anomaly detection
在本练习中,您将实现异常检测算法来检测服务器计算机中的异常行为。这些功能可测量每个服务器的响应吞吐量 (mb/s) 和延迟 (ms)。当您的服务器正在正常运行,您收集了m = 307个关于他们行为样本,因此有一个未标记的数据集
您怀疑在这些绝大多数都是服务器“正常”(非异常)运行的样本中也可能有一些服务器样本在此数据集中异常运行。
您将使用高斯模型来检测异常样本数据。您将首先从2D数据集开始,该数据集将可以可视化
算法在做什么。在该数据集上,您将拟合高斯分布,然后找到概率非常低的值,因此可以被视为异常。之后,您将应用异常检测算法到多维度的较大数据集。
步骤:①求均值μ和方差 ;
②计算正态分布密度函数;
③求阈值(F1的选择基于查准率和查全率,在验证集上尝试不同的阈值,选择能最大化F1值得阈值)
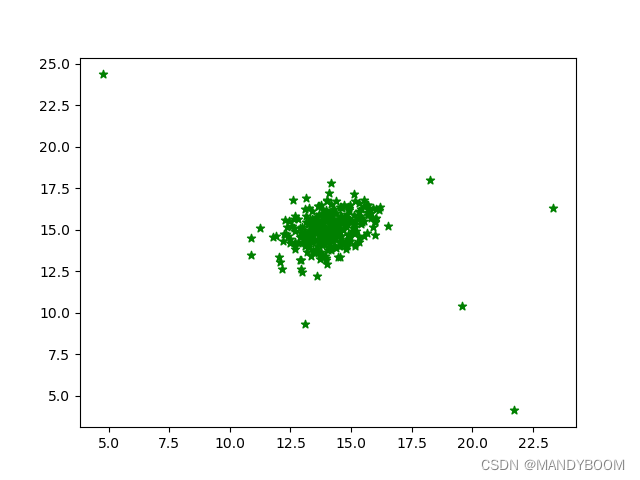
可视化数据:
# 导入数据 可视化数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.io as sio
data = sio.loadmat('ex8data1.mat')
print(data.keys()) # dict_keys(['__header__', '__version__', '__globals__', 'X', 'Xval', 'yval'])
X, Xval, yval = data['X'], data['Xval'], data['yval']
print(X.shape, Xval.shape, yval.shape) # (307, 2) (307, 2) (307, 1)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1],marker='*', color='green')
plt.show()
1.1 高斯分布Gaussian distribution
给定一个训练集(
),需要知道他们的均值和方差。
# 计算均值和方差
def estimateGaussian(X, isCovariance):
means = np.mean(X, axis = 0)
if isCovariance: # 如果特征之间有线性关系
sigma = (X - means).T@(X - means)/len(X)
else:
sigma = np.var(X, axis = 0) # 特征之间没有线性关系
return means, sigma
means, sigma = estimateGaussian(X, isCovariance= True)
print(means, sigma) # [14.11222578 14.99771051] [[ 1.83263141 -0.22712233]
means,sigma = estimateGaussian(X, isCovariance= False)
print(means, sigma) # [14.11222578 14.99771051] [1.83263141 1.70974533]
求密度函数:
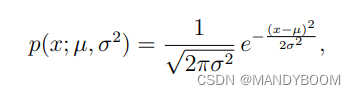
# 求密度函数
def gaussion(X, means, sigma):
p = np.zeros((X.shape[0],1)) # (307,1)
n = len(means)
if np.ndim(sigma) == 1: # 如果sigma的维度是1
sigma = np.diag(sigma) # 将一维数组转化成方阵,非对角线元素为0
for i in range(X.shape[0]): # 遍历每一行,计算每一行的密度函数
p[i] = (2*np.pi)**(-n/2) * np.linalg.det(sigma)**(-1/2)*np.exp(-0.5*(X[i,:]-means).T@np.linalg.inv(sigma)@(X[i,:]-means))
# np.linalg.inv 矩阵求逆
return p
P = gaussion(X, means, sigma)
print(P.shape) # (307, 1)
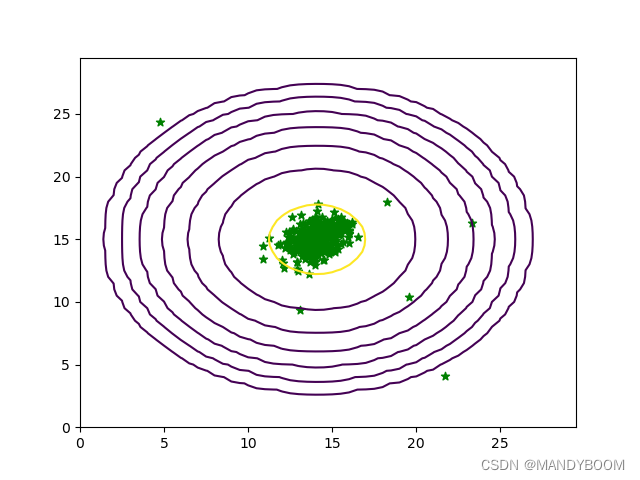
1.2 画出密度函数等高线
# 画出等高线图
def plotGaussian(X, means, sigma):
x = np.arange(0, 30, 0.5)
y = np.arange(0, 30, 0.5)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
z = gaussion(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()], means, sigma) # 计算对应的高斯分布函数
print(z) # [[6.14537868e-54],[2.69820093e-52],[1.03360659e-50]...[5.17861206e-53],[9.54538692e-55],[1.53507302e-56]]
zz = z.reshape(xx.shape)
contour_levels = [10**h for h in range (-20,0,3)]
plt.contour(xx, yy, zz, contour_levels)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], marker='*',color='green')
plt.show()
plotGaussian(X, means, sigma)
1.3 选择最佳的参数 Selecting the threshold, '
Selecting the threshold, ' '
'
此部分需要计算F1,使其最大化,需要用到验证集,data中给出了Xval,yval
# 计算最佳的ε
def selecteps(yval, p):
bestepsilon = 0
bestF1 = 0
epsilons = np.linspace(min(p), max(p), 1000)
for e in epsilons:
p_ = p < e
tp = np.sum((yval == 1) & (p_ ==1))
fp = np.sum((yval == 0) & (p_ == 1))
tn = np.sum((yval == 0) & (p_ == 0))
fn = np.sum((yval == 1) & (p_ == 0))
precious = tp/(tp+fp) if (tp+fp) else 0
recious = tp/(tp+fn) if (tp + fn) else 0
F1 = (2*precious*recious)/(precious+recious) if(precious + recious) else 0
if F1 > bestF1:
bestF1 = F1
bestepsilon = e
return bestF1, bestepsilon
pval = gaussion(Xval, means, sigma) # 用验证集计算验证集的密度函数
bestF1, bestepsilon = selecteps(yval, pval)
print(bestF1, bestepsilon) # 0.8750000000000001 [8.99985263e-05]
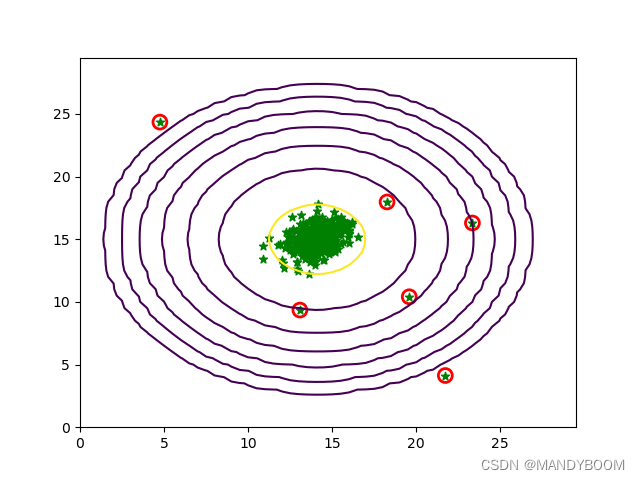
圈出异常的样本点
# 圈出异常的样本点
p = gaussion(X, means, sigma)
anoms = np.array([X[i] for i in range(X.shape[0]) if p[i] < bestepsilon])
print(anoms.shape)
# 画出等高线图
def newplotGaussian(X, means, sigma,anoms):
x = np.arange(0, 30, 0.5)
y = np.arange(0, 30, 0.5)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
z = gaussion(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()], means, sigma) # 计算对应的高斯分布函数
print(z) # [[6.14537868e-54],[2.69820093e-52],[1.03360659e-50]...[5.17861206e-53],[9.54538692e-55],[1.53507302e-56]]
zz = z.reshape(xx.shape)
contour_levels = [10**h for h in range (-20,0,3)]
plt.contour(xx, yy, zz, contour_levels)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], marker='*',color='green')
plt.scatter(anoms[:, 0], anoms[:, 1], s=100, marker='o', facecolors='none', edgecolors='r', linewidths=2)
plt.show()
newplotGaussian(X,means, sigma, anoms)
2 推荐系统Recommender Systems
在本部分练习中,您将实现协作过滤学习算法并将其应用于电影推荐。数据集由1至5级的评级组成。数据集的
= 943 个用户,并且
= 1682 部电影。
2.1 导入和提取数据
# 导入数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.io as sio
from sympy.physics.vector.printing import params
mat = sio.loadmat('ex8_movies.mat')
print(mat.keys()) # dict_keys(['__header__', '__version__', '__globals__', 'Y', 'R'])
Y, R = mat['Y'], mat['R']
print(Y.shape, R.shape) # (1682, 943) (1682, 943)
data = sio.loadmat('ex8_movieParams.mat')
print(data.keys()) # dict_keys(['__header__', '__version__', '__globals__', 'X', 'Theta', 'num_users', 'num_movies', 'num_features'])
X, Theta, nu, nm, nf = data['X'], data['Theta'], data['num_users'], data['num_movies'], data['num_features']
print(X.shape, Theta.shape, nu, nm, nf) # (1682, 10) (943, 10) [[943]] [[1682]] [[10]]
# 将用户数量、电影数量、特征数量从数组形式转换成整数形式
nu = int(nu)
nm = int(nm)
nf = int(nf)
# 序列化、解序列化
# 1 序列化
def serialize(X, Theta):
return np.append(X.flatten(), Theta.flatten()) # 降维
# 2 解序列化
def deserialize(X, Theta):
X = params[:nm*nf].reshape(nm, nf)
Theta = params[nm*nf:].reshape(nu,nf)
return X, Theta
2.2 代价函数
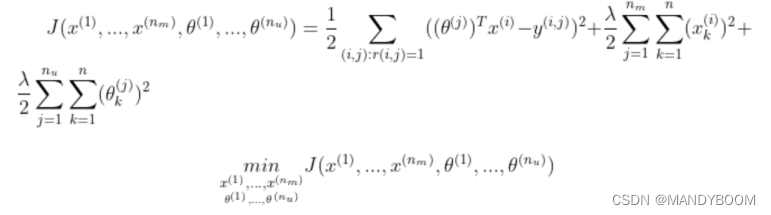
# 代价函数
def costFunc(params, Y, R, nm, nu, nf, lam):
X, Theta = deserialize(params, nm, nu, nf)
cost = 0.5 * np.square((X@Theta.T- Y)*R).sum() # 点乘R,也就是对应位置相乘,R为0没打分,需要预测
reg1 = 0.5 * lam * np.square(X).sum()
reg2 = 0.5 * lam * np.square(Theta).sum()
return cost + reg1 +reg2
2.3 梯度下降
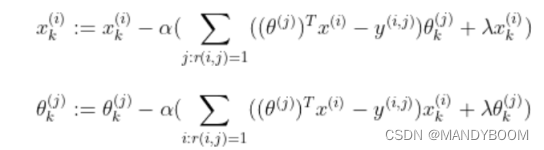
# 梯度下降
def costGradient(params, Y, R, nm, nu, nf, lam):
X, Theta = deserialize(params, nm, nu, nf) # 解序列化
X_grad = ((Theta @ X.T-Y)*R).T@Theta + lam*X
Theta_grad = ((Theta@X.T-Y)*R)@X + lam*Theta
return serialize(X_grad, Theta_grad)
# 添加一个用户对部分电影的评分
my_ratings = np.zeros((nm,1))
my_ratings[8] = 5
my_ratings[18] = 3
my_ratings[28] = 2
my_ratings[29] = 5
my_ratings[38] = 5
my_ratings[48] = 4
my_ratings[58] = 4
my_ratings[588] = 3
my_ratings[688] = 5
my_ratings[788] = 4
my_ratings[888] = 5
my_ratings[988] = 3
2.4 均值归一化
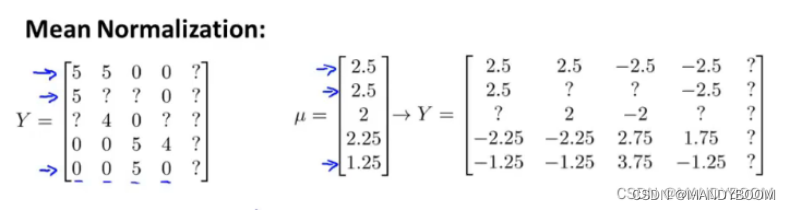
# 均值归一化
def normalizeRatings(Y,R):
Y_mean = (Y.sum(axis = 1)/R.sum(axis = 1)).reshape(-1,1)
Y_norm = (Y-Y_mean)*R
return Y_norm, Y_mean
Y_norm, Y_mean = normalizeRatings(Y,R)
print(Y_norm)
# 参数初始化
X = np.random.random((nm, nf)) # 电影特征随机初始化
Theta = np.random.random((nu,nf)) # 用户参数随机初始化
params = serialize(X, Theta)
lam = 5
2.5 训练模型和预测
# 训练模型
from scipy.optimize import minimize
res = minimize(x0=params, fun = costFunc, args=(Y_norm, R, nm, nu, nf, lam), method = 'TNC', jac=costGradient,options={'maxiter':100})
params_fit = res.x
fit_X, fit_Theta = deserialize(params_fit,num,nu,nf)
# 预测
Y_pre = fit_X@fit_Theta.T
print(Y_pre)
y_pre = Y_pre[:,-1] + Y_mean.flatten() # 因为是均值归一化后的Y计算的预测值,所以最后还要加上均值
index = np.argsort(-y_pre) # argsort输出的是排序后当前位置所应该放的值的索引
index[:10] # 查看排名前10的电影数组
2.6 推荐电影
# 推荐电影
movies = []
with open('movie_ids.txt','r',encoding='latin 1')as f:
for line in f:
tokens = line.strip().split(' ') # 按空格分割
# strip()用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列
movies.append(' '.join(tokens[1:])) # 忽略电影名前边的数字序号
# 推荐十部
for i in range(10):
print(index[i],movies[index[i]],y_pre[index[i]])
'''287 Scream (1996) 5.534543455174823
10 Seven (Se7en) (1995) 5.281607627331978
41 Clerks (1994) 5.101899186293281
55 Pulp Fiction (1994) 5.0784449505979445
297 Face/Off (1997) 5.017943757291861
1292 Star Kid (1997) 5.01436944475707
1188 Prefontaine (1997) 5.006260395014717
1535 Aiqing wansui (1994) 5.005625305669942
1598 Someone Else's America (1995) 5.004511384011729
1121 They Made Me a Criminal (1939) 5.000242703283907'''
绿色部分即推荐系统推荐的10部电影,包括他的序号,名称,感兴趣程度。







 本文介绍了一种基于高斯模型的异常检测算法,并通过可视化展示了如何确定异常样本。此外,还详细介绍了推荐系统的实现过程,包括数据预处理、代价函数计算、模型训练及电影推荐。
本文介绍了一种基于高斯模型的异常检测算法,并通过可视化展示了如何确定异常样本。此外,还详细介绍了推荐系统的实现过程,包括数据预处理、代价函数计算、模型训练及电影推荐。
















 1030
1030

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








