一、数据库管理中的DB回溯
DB回溯是数据库管理中的一种恢复技术,允许将数据库回退到特定时间点,常用于撤销错误操作或恢复数据。以下是关键信息:
1. 核心概念
- 定义:通过时间点回退实现数据恢复,无需传统备份还原。如数据库恢复、版本回退等。
- 优势:服务中断时间短(通常几分钟),支持反复回溯验证数据变化。
2. 技术实现
- Amazon Aurora:通过控制台选择时间点执行回溯,自动处理连接中断和未提交事务。
- 分布式数据库:结合GTM(全局事务管理)确保跨节点操作的一致性。
3. 应用场景
- 错误恢复:如误删表或数据损坏。
- 数据验证:对比不同时间点数据差异。
3. 注意事项
- 非备份替代:需配合常规备份策略使用。
- 当前限制:仅部分数据库(如MySQL版Aurora)支持
二、在MySQL中,实现数据的回溯或恢复主要有
1. 使用事务(Transactions)
MySQL支持事务,这使得你可以在多个步骤的操作中保持数据的一致性。如果在事务中发生了错误,你可以选择回滚(ROLLBACK)到事务开始前的状态。
示例:
START TRANSACTION; -- 执行一些数据库操作
UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance - 100 WHERE id = 1;
UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance + 100 WHERE id = 2;
-- 如果需要回滚
ROLLBACK;
-- 或者,如果一切正常,提交事务
COMMIT;
2. 使用二进制日志(Binary Log)
MySQL的二进制日志(Binary Log)记录了所有的数据库更改,可以用来恢复数据到过去的某个状态。这通常用于灾难恢复或数据恢复。
启用二进制日志:
在MySQL的配置文件(通常是my.cnf或my.ini)中设置:
[mysqld] log_bin=mysql-bin server_id=1
然后重启MySQL服务。
使用二进制日志恢复:
可以使用mysqlbinlog工具来查看或应用二进制日志中的事件。例如,恢复到特定的时间点:
mysqlbinlog --start-datetime="2023-03-01 00:00:00" --stop-datetime="2023-03-02 00:00:00" /var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.000001 | mysql -u root -p
3. 使用备份和还原
定期备份数据库,并在需要时从备份中恢复数据。MySQL提供了多种备份和还原工具,如mysqldump和mysql命令。
备份数据库:
mysqldump -u root -p database_name > backup.sql
还原数据库:
mysql -u root -p database_name < backup.sql
4. 使用第三方工具和插件
还有一些第三方工具和插件,如Percona Toolkit,可以用来管理和恢复MySQL数据库。例如,使用pt-table-checksum来检查数据的一致性,或使用pt-online-schema-change来在线修改表结构而不锁定表。
5. 使用复制(Replication)中的主从切换(Failover)
在主从复制架构中,可以在主服务器出现故障时,将一个从服务器提升为主服务器,以继续提供服务并恢复数据。这通常涉及到配置和管理复制的细节,例如设置新的主服务器并同步数据。
在多级缓存架构中,DB回溯(或回源)是关键环节,指当各级缓存均未命中时,需要回到数据库查询数据并重建缓存的机制。以下是完整的设计与实现方案。
三、多级缓存DB回溯的核心挑战与设计原则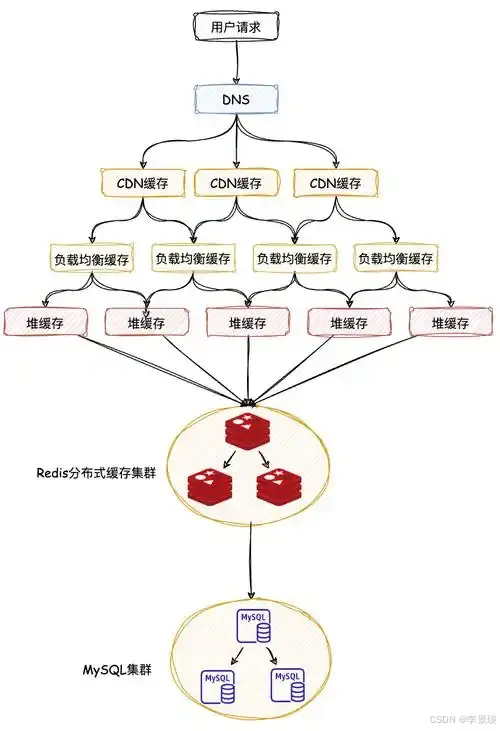
主要挑战
-
缓存击穿(Cache Breakdown):热点数据失效瞬间,大量请求同时回源DB,造成数据库压力
-
缓存穿透(Cache Penetration):频繁查询不存在的数据,每次都穿透到数据库
-
缓存雪崩(Cache Avalanche):大量缓存同时失效,请求直接冲击数据库
-
数据一致性问题:回源期间数据被更新,导致缓存与数据库不一致
设计原则
-
单线程回源:同一时间只有一个请求回源数据库
-
空值缓存:缓存不存在的数据,防止穿透
-
错峰过期:为不同数据设置随机过期时间,防止雪崩
-
热点数据保护:识别并预加载热点数据
四、多级缓存中DB回溯方案对比
方案对比表
| 方案 | 实现方式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 互斥锁(Mutex Lock) | 使用分布式锁控制只有一个线程回源 | 绝对防止击穿,实现简单 | 性能有损耗,可能死锁 | 数据一致性要求高 |
| 逻辑过期 | 缓存实际数据+逻辑过期时间,异步更新 | 零等待时间,用户体验好 | 实现复杂,可能读到旧数据 | 高并发读场景 |
| 布隆过滤器 | 使用位数组判断数据是否存在 | 内存占用小,防止穿透效果好 | 存在误判率,无法删除 | 防止缓存穿透 |
| 热点探测+预热 | 监控热点数据,提前更新缓存 | 平滑回源,无压力峰值 | 需要监控系统,实现复杂 | 电商大促、热点数据 |
| 多级降级 | 快速失败->本地缓存->数据库 | 保护DB,自动降级 | 可能降低用户体验 | 系统容错场景 |
非表格形式对比:
-
互斥锁方案最常用,但存在性能瓶颈
-
逻辑过期方案用户体验最佳,适合读多写少
-
布隆过滤器是防穿透利器,但需容忍误判
-
组合方案(如互斥锁+布隆过滤器)在实践中效果最好
五、多级缓存完整DB回溯方案实现
1. 基于分布式锁的回溯方案(推荐)
java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheBackSourceManager {
@Autowired
private Cache<String, Object> caffeineCache;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private static final String NULL_PLACEHOLDER = "__NULL__";
private static final long LOCK_TIMEOUT = 3000; // 锁超时时间3秒
private static final long CACHE_NULL_TTL = 60; // 空值缓存60秒
/**
* 三级缓存读取(含防击穿、防穿透)
*/
public <T> T getWithBackSource(String key, Class<T> clazz,
Supplier<T> dbLoader,
long redisTTL, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
// 1. 检查本地缓存
Object value = caffeineCache.getIfPresent(key);
if (value != null) {
if (NULL_PLACEHOLDER.equals(value)) {
log.debug("L1空值命中: {}", key);
return null;
}
log.debug("L1命中: {}", key);
return clazz.cast(value);
}
// 2. 检查Redis缓存
value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (value != null) {
if (NULL_PLACEHOLDER.equals(value)) {
// 缓存空值,设置较短的本地缓存时间
caffeineCache.put(key, NULL_PLACEHOLDER, Duration.ofSeconds(30));
return null;
}
caffeineCache.put(key, value);
return clazz.cast(value);
}
// 3. 获取分布式锁,防止缓存击穿
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("LOCK:" + key);
try {
// 尝试获取锁,最多等待100ms,锁持有时间3秒
boolean locked = lock.tryLock(100, LOCK_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!locked) {
// 获取锁失败,说明有其他线程在回源,短暂等待后重试
Thread.sleep(50);
return getWithBackSource(key, clazz, dbLoader, redisTTL, timeUnit);
}
// 4. 再次检查缓存(Double Check)
value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (value != null) {
if (NULL_PLACEHOLDER.equals(value)) {
caffeineCache.put(key, NULL_PLACEHOLDER, Duration.ofSeconds(30));
return null;
}
caffeineCache.put(key, value);
return clazz.cast(value);
}
// 5. 回源数据库
log.info("DB回源: {}", key);
T data = dbLoader.get();
if (data == null) {
// 防穿透:缓存空值
cacheNullValue(key);
return null;
}
// 6. 写入各级缓存
writeToCache(key, data, redisTTL, timeUnit);
return data;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
log.error("获取锁被中断: {}", key, e);
throw new RuntimeException("系统繁忙,请重试");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("回源失败: {}", key, e);
throw new RuntimeException("系统异常");
} finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* 异步回源(无阻塞方案)
*/
public <T> CompletableFuture<T> getAsync(String key, Class<T> clazz,
Supplier<T> dbLoader,
long redisTTL, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
CompletableFuture<T> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 1. 先尝试从缓存获取
Object value = caffeineCache.getIfPresent(key);
if (value != null && !NULL_PLACEHOLDER.equals(value)) {
future.complete(clazz.cast(value));
return future;
}
// 2. 异步执行回源
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
return getWithBackSource(key, clazz, dbLoader, redisTTL, timeUnit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CompletionException(e);
}
}).whenComplete((result, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
future.completeExceptionally(throwable);
} else {
future.complete(result);
}
});
return future;
}
/**
* 热点数据预加载
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 60000) // 每分钟执行一次
public void preloadHotData() {
// 从Redis获取热点Key列表(可通过监控统计获得)
Set<String> hotKeys = getHotKeysFromMonitor();
for (String key : hotKeys) {
// 检查缓存剩余时间
Long ttl = redisTemplate.getExpire(key);
if (ttl != null && ttl < 300) { // 剩余时间小于5分钟
// 异步预加载
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
refreshCache(key);
});
}
}
}
/**
* 缓存空值(防穿透)
*/
private void cacheNullValue(String key) {
// Redis缓存空值,设置较短TTL
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, NULL_PLACEHOLDER,
Duration.ofSeconds(CACHE_NULL_TTL));
// 本地缓存空值,TTL更短
caffeineCache.put(key, NULL_PLACEHOLDER, Duration.ofSeconds(30));
}
/**
* 写入缓存(错峰过期)
*/
private void writeToCache(String key, Object data, long baseTTL, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
// 随机抖动,防止雪崩(±10%)
long randomOffset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong((long)(baseTTL * 0.1));
long finalTTL = baseTTL + randomOffset;
// 写入Redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, data, finalTTL, timeUnit);
// 写入本地缓存(设置比Redis稍短的TTL)
long localTTL = TimeUnit.SECONDS.convert(finalTTL, timeUnit) - 60;
if (localTTL > 0) {
caffeineCache.put(key, data, Duration.ofSeconds(localTTL));
} else {
caffeineCache.put(key, data);
}
}
/**
* 刷新缓存(后台异步)
*/
private void refreshCache(String key) {
// 根据Key解析业务逻辑,重新加载数据
// 这里需要根据实际业务实现
log.info("刷新热点数据缓存: {}", key);
}
private Set<String> getHotKeysFromMonitor() {
// 实际实现中,可以从Redis的监控数据或业务统计中获取热点Key
// 这里返回空集作为示例
return Collections.emptySet();
}
}
2. 逻辑过期方案实现(无锁方案)
java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LogicalExpireCacheManager {
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class CacheWrapper<T> {
private T data;
private long expireTime; // 逻辑过期时间戳
}
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
/**
* 逻辑过期方案读取
*/
public <T> T getWithLogicalExpire(String key, Class<T> clazz,
Supplier<T> dbLoader,
long expireSeconds) {
String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (json == null) {
// 缓存不存在,需要回源
return loadFromDbAndSetCache(key, clazz, dbLoader, expireSeconds);
}
try {
// 解析缓存包装对象
JavaType type = objectMapper.getTypeFactory()
.constructParametricType(CacheWrapper.class, clazz);
CacheWrapper<T> wrapper = objectMapper.readValue(json, type);
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (currentTime < wrapper.getExpireTime()) {
// 未过期,直接返回
return wrapper.getData();
} else {
// 已过期,异步重建缓存
rebuildCacheAsync(key, clazz, dbLoader, expireSeconds);
// 仍然返回旧数据(保证可用性)
return wrapper.getData();
}
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.error("解析缓存失败: {}", key, e);
return loadFromDbAndSetCache(key, clazz, dbLoader, expireSeconds);
}
}
/**
* 异步重建缓存
*/
private <T> void rebuildCacheAsync(String key, Class<T> clazz,
Supplier<T> dbLoader, long expireSeconds) {
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
// 获取分布式锁,防止多个线程同时重建
Boolean locked = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent("REBUILD_LOCK:" + key, "1", Duration.ofSeconds(5));
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(locked)) {
try {
// 双重检查
String oldJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (oldJson != null) {
CacheWrapper<T> oldWrapper = parseWrapper(oldJson, clazz);
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < oldWrapper.getExpireTime()) {
return; // 已被其他线程更新
}
}
// 从数据库加载
T data = dbLoader.get();
if (data != null) {
setCacheWithLogicalExpire(key, data, expireSeconds);
}
} finally {
redisTemplate.delete("REBUILD_LOCK:" + key);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("异步重建缓存失败: {}", key, e);
}
});
}
private <T> T loadFromDbAndSetCache(String key, Class<T> clazz,
Supplier<T> dbLoader, long expireSeconds) {
T data = dbLoader.get();
if (data != null) {
setCacheWithLogicalExpire(key, data, expireSeconds);
}
return data;
}
private <T> void setCacheWithLogicalExpire(String key, T data, long expireSeconds) {
try {
long expireTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + (expireSeconds * 1000);
CacheWrapper<T> wrapper = new CacheWrapper<>(data, expireTime);
String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(wrapper);
// 设置较长的物理过期时间,确保有足够时间触发逻辑过期
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, json, Duration.ofHours(24));
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.error("序列化缓存失败: {}", key, e);
}
}
private <T> CacheWrapper<T> parseWrapper(String json, Class<T> clazz)
throws JsonProcessingException {
JavaType type = objectMapper.getTypeFactory()
.constructParametricType(CacheWrapper.class, clazz);
return objectMapper.readValue(json, type);
}
}
3. 布隆过滤器防穿透实现
java
@Component
public class BloomFilterManager {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
private static final String BLOOM_FILTER_KEY = "bloom:filter";
private static final long EXPECTED_INSERTIONS = 1000000L; // 预期插入量
private static final double FALSE_POSITIVE_RATE = 0.01; // 误判率1%
/**
* 初始化布隆过滤器
*/
public void initBloomFilter() {
// 使用Redisson的布隆过滤器(需添加Redisson依赖)
// 或者使用Redis的Bitmap自行实现
}
/**
* 判断数据是否存在
*/
public boolean mightContain(String key) {
// 实际业务中,需要根据key提取业务ID
String businessId = extractBusinessId(key);
if (businessId == null) {
return true; // 无法判断,放行
}
// 检查布隆过滤器
return checkBloomFilter(businessId);
}
/**
* 添加数据到布隆过滤器
*/
public void addToBloomFilter(String key) {
String businessId = extractBusinessId(key);
if (businessId != null) {
addToBloomFilterInternal(businessId);
}
}
/**
* 结合布隆过滤器的缓存查询
*/
public <T> T getWithBloomFilter(String key, Class<T> clazz,
Supplier<T> dbLoader) {
// 1. 检查布隆过滤器
if (!mightContain(key)) {
log.debug("布隆过滤器拦截: {}", key);
return null;
}
// 2. 正常缓存查询流程...
// 这里可以结合前面的CacheBackSourceManager使用
return null;
}
private String extractBusinessId(String key) {
// 根据key模式提取业务ID
// 例如 key="user:1001",提取"1001"
if (key.startsWith("user:")) {
return key.substring(5);
} else if (key.startsWith("product:")) {
return key.substring(8);
}
return null;
}
private boolean checkBloomFilter(String id) {
// 实现布隆过滤器检查逻辑
// 可以使用Redisson RBloomFilter或基于Redis Bitmap实现
return true; // 示例实现
}
private void addToBloomFilterInternal(String id) {
// 实现布隆过滤器添加逻辑
}
}
4. 完整的业务层整合
java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private CacheBackSourceManager cacheManager;
@Autowired
private BloomFilterManager bloomFilterManager;
@Autowired
private ProductMapper productMapper;
/**
* 综合方案:布隆过滤器 + 互斥锁回源
*/
public Product getProductWithFullProtection(Long productId) {
String key = "product:" + productId;
// 1. 布隆过滤器检查(防止穿透)
if (!bloomFilterManager.mightContain(key)) {
log.info("商品{}不存在,被布隆过滤器拦截", productId);
return null;
}
// 2. 带保护的回源查询
return cacheManager.getWithBackSource(
key,
Product.class,
() -> {
log.info("查询数据库获取商品: {}", productId);
Product product = productMapper.selectById(productId);
if (product != null) {
// 添加到布隆过滤器
bloomFilterManager.addToBloomFilter(key);
}
return product;
},
30, // Redis缓存30分钟
TimeUnit.MINUTES
);
}
/**
* 批量查询优化
*/
public Map<Long, Product> batchGetProducts(List<Long> productIds) {
Map<Long, Product> result = new HashMap<>();
List<Long> missingIds = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. 批量查询本地缓存
for (Long id : productIds) {
String key = "product:" + id;
Object value = cacheManager.getCaffeineCache().getIfPresent(key);
if (value != null && !cacheManager.isNullPlaceholder(value)) {
result.put(id, (Product) value);
} else {
missingIds.add(id);
}
}
// 2. 批量查询Redis
if (!missingIds.isEmpty()) {
List<String> keys = missingIds.stream()
.map(id -> "product:" + id)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Object> redisValues = cacheManager.getRedisTemplate()
.opsForValue().multiGet(keys);
for (int i = 0; i < missingIds.size(); i++) {
Long id = missingIds.get(i);
Object value = redisValues.get(i);
if (value != null) {
if (!cacheManager.isNullPlaceholder(value)) {
Product product = (Product) value;
result.put(id, product);
// 回填本地缓存
cacheManager.getCaffeineCache().put("product:" + id, product);
}
} else {
// 需要回源
result.put(id, getProductWithFullProtection(id));
}
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 更新商品信息(包含缓存处理)
*/
@Transactional
public void updateProduct(Product product) {
String key = "product:" + product.getId();
// 1. 更新数据库
productMapper.updateById(product);
// 2. 删除缓存(使用延迟双删)
cacheManager.getRedisTemplate().delete(key);
// 3. 广播缓存失效
cacheManager.evictLocalAndBroadcast(key);
// 4. 延迟双删
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
cacheManager.getRedisTemplate().delete(key);
log.info("商品延迟双删完成: {}", key);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
}
}
六、监控与运维配置
1. 缓存监控配置
yaml
# application.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health,metrics,cache
metrics:
export:
prometheus:
enabled: true
cache:
caffeine:
stats: true
2. 监控指标实现
java
@Component
public class CacheMonitor {
@Autowired
private Cache<String, Object> caffeineCache;
@Autowired
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分钟采集一次
public void collectCacheMetrics() {
CacheStats stats = caffeineCache.stats();
// 记录命中率
meterRegistry.gauge("cache.caffeine.hit.rate",
stats.hitRate() * 100);
// 记录加载次数
meterRegistry.counter("cache.caffeine.load.count",
"result", "success").increment(stats.loadSuccessCount());
meterRegistry.counter("cache.caffeine.load.count",
"result", "failure").increment(stats.loadFailureCount());
// 记录平均加载时间
meterRegistry.gauge("cache.caffeine.load.duration.avg",
stats.averageLoadPenalty() / 1_000_000); // 转换为毫秒
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public Map<String, Object> getCacheStats() {
CacheStats stats = caffeineCache.stats();
Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
result.put("命中率", String.format("%.2f%%", stats.hitRate() * 100));
result.put("加载成功次数", stats.loadSuccessCount());
result.put("加载失败次数", stats.loadFailureCount());
result.put("缓存驱逐次数", stats.evictionCount());
result.put("平均加载时间(ms)", stats.averageLoadPenalty() / 1_000_000);
result.put("缓存大小(估算)", caffeineCache.estimatedSize());
return result;
}
}
3. 告警规则示例(Prometheus)
yaml
# prometheus-alerts.yml
groups:
- name: cache_alerts
rules:
- alert: CacheHitRateLow
expr: cache_caffeine_hit_rate < 80
for: 5m
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "缓存命中率过低"
description: "Caffeine缓存命中率低于80%,当前值: {{ $value }}%"
- alert: CacheLoadFailureHigh
expr: rate(cache_caffeine_load_count{result="failure"}[5m]) > 0.1
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "缓存加载失败率过高"
description: "缓存回源失败率超过10%,可能导致数据库压力增大"
七、生产环境最佳实践
1. 回源策略选择指南
-
高并发读场景:逻辑过期 + 异步刷新
-
数据一致性要求高:互斥锁 + 延迟双删
-
存在大量无效查询:布隆过滤器 + 空值缓存
-
热点数据集中:热点探测 + 预加载
2. 配置调优参数
java
@Configuration
public class CacheOptimizationConfig {
@Bean
public Cache<String, Object> optimizedCaffeineCache() {
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(1000)
.maximumSize(10000)
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
.expireAfterAccess(Duration.ofMinutes(10))
.refreshAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(5)) // 主动刷新
.recordStats()
.build();
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379")
.setConnectionPoolSize(64)
.setConnectionMinimumIdleSize(10)
.setTimeout(3000);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
3. 熔断降级策略
java
@Component
public class CacheFallbackManager {
private final CircuitBreakerRegistry circuitBreakerRegistry;
public CacheFallbackManager() {
circuitBreakerRegistry = CircuitBreakerRegistry.of(
CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50) // 失败率阈值50%
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(60))
.permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState(10)
.slidingWindowSize(100)
.build()
);
}
public <T> T getWithFallback(String key, Supplier<T> cacheSupplier,
Supplier<T> dbSupplier,
Supplier<T> fallbackSupplier) {
CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker = circuitBreakerRegistry
.circuitBreaker("cache-backsource");
return circuitBreaker.executeSupplier(() -> {
try {
// 尝试从缓存获取
T result = cacheSupplier.get();
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
// 缓存未命中,回源数据库
return dbSupplier.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 缓存和数据库都失败,使用降级策略
log.warn("缓存回源失败,使用降级策略: {}", key, e);
return fallbackSupplier.get();
}
});
}
}
八、总结
DB回溯是构建稳健多级缓存系统的核心环节。推荐采用以下组合方案:
-
基础方案:分布式锁 + 空值缓存 + 错峰过期
-
进阶优化:增加布隆过滤器防穿透
-
性能优化:热点数据预加载 + 异步刷新
-
容错保障:熔断降级 + 监控告警
关键建议:
-
根据业务特点选择合适的回源策略组合
-
监控缓存命中率和回源失败率
-
设置合理的超时时间和重试机制
-
定期review和调整缓存配置参数
通过上述方案,可以在保证数据一致性的同时,有效防止缓存击穿、穿透和雪崩问题,构建高性能、高可用的缓存系统。

























 877
877

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










