线程安全主要目的是在受控的并发访问中防止数据发生变化。除了使用synchronized关键字同步对资源的写操作之外,还可以在线程之间不共享资源状态,甚至将资源的状态设置为不可变。
java.lang.String的每一个方法都没有同步修饰,但是在多线程访问的情况下是线程安全的,Java8中通过Stream修饰的ArrayList在函数式方法并行访问的情况下也是线程安全的。
所谓“不可变对象”是没有机会去修改它,每一次的修改都将产生一个新的对象,String str ="hello";str = str+"world"这会产生新的字符串。
非线程安全的累加器:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* 非线程安全的累计器
*/
public class IntegerAccumulator {
private int init;
//构造时传入初始值
public IntegerAccumulator(int init){
this.init = init;
}
public int add(int i){
this.init += i;
return this.init;
}
public int getValue(){
return this.init;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
IntegerAccumulator integerAccumulator = new IntegerAccumulator(0);
IntStream.range(0,3).forEach(i -> new Thread(()->{
int inc = 0;
while(true){
int oldValue = integerAccumulator.getValue();
int result = integerAccumulator.add(inc);
System.out.println(oldValue + "+" + inc + "=" + result);
if(inc + oldValue != result){
System.out.println("ERROR " + oldValue + "+" + inc + "=" +result);
}
inc++;
slowly();
}
}).start());
}
private static void slowly(){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
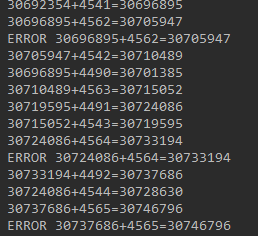
方法同步增加线程安全性:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* 方法同步增加线程安全
*
*/
public class IntegerAccumulator {
private int init;
//构造时传入初始值
public IntegerAccumulator(int init){
this.init = init;
}
public int add(int i){
this.init += i;
return this.init;
}
public int getValue(){
return this.init;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
IntegerAccumulator integerAccumulator = new IntegerAccumulator(0);
IntStream.range(0,3).forEach(i -> new Thread(()->{
int inc = 0;
while(true){
int oldValue;
int result;
synchronized (IntegerAccumulator.class){
oldValue = integerAccumulator.getValue();
result = integerAccumulator.add(inc);
}
System.out.println(oldValue + "+" + inc + "=" + result);
if(inc + oldValue != result){
System.out.println("ERROR" + oldValue + "+" + inc + "=" +result);
}
inc++;
slowly();
}
}).start());
}
private static void slowly(){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
...
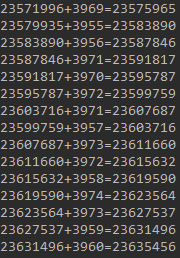
设计一个类似java.lang.String的不可变的int类型累加器
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* 不可变的累计器设计
* 不可变对象不允许被继承
* final修饰防止由于继承引起的线程安全问题
*/
public final class IntegerAccumulator {
//final修饰不允许线程对其改变,在构造函数中赋值后不会再改变
private final int init;
//构造时传入初始值
public IntegerAccumulator(int init){
this.init = init;
}
// public int add(int i){
// this.init += i;
// return this.init;
// }
//构造新的累加器,需要用到另外一个accumulator和初始值
public IntegerAccumulator(IntegerAccumulator integerAccumulator,int init){
this.init = integerAccumulator.getValue() + init;
}
//每次相加都会产生一个新的IntegerAccumulator,不会在原有的init基础上增加,不修改原有的IntegerAccumulator
public IntegerAccumulator add(int i){
return new IntegerAccumulator(this,i);
}
public int getValue(){
return this.init;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
IntegerAccumulator integerAccumulator = new IntegerAccumulator(0);
IntStream.range(0,3).forEach(i -> new Thread(()->{
int inc = 0;
while(true){
int oldValue = integerAccumulator.getValue();
int result = integerAccumulator.add(inc).getValue();
System.out.println(oldValue + "+" + inc + "=" + result);
if(inc + oldValue != result){
System.out.println("ERROR " + oldValue + "+" + inc + "=" +result);
}
inc++;
slowly();
}
}).start());
}
private static void slowly(){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:不会出现ERROR情况。
 线程安全与不可变对象
线程安全与不可变对象







 本文探讨了线程安全的概念及其实现方式,包括使用synchronized关键字和设计不可变对象。通过实例展示了如何设计一个不可变的int类型累加器,并对比了线程安全与非线程安全的累加器在多线程环境下的表现。
本文探讨了线程安全的概念及其实现方式,包括使用synchronized关键字和设计不可变对象。通过实例展示了如何设计一个不可变的int类型累加器,并对比了线程安全与非线程安全的累加器在多线程环境下的表现。
















 2872
2872

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








