1. 基础概念
同时操作多个fd时,如果使用阻塞的方式,可能导致程序效率低下。我们可以使用非阻塞方式的IO,通过不断查询数据操作的结果来进行接下来的操作,这种处理方式就是轮询,缺点就是非常消耗CPU资源。所以在某种意义上其相当于阻塞的调用了IO函数read或者write,可以通过异步IO的方式来解决这个问题,但是因为一个进程只使用一个或者几个信号,当捕获该信号时无法判断是哪个fd数据就绪。最好的方式就是使用IO mutiplexing,虽然该系列函数是阻塞同步的,但是因为能够筛选一个范围中的fd,所以效率也高很多。
2. 主要API
2.1 select/pselect
#include <sys/select.h>
int select(int maxfdp1, fd_set *restrict readfds, fd_set *restrict writefds, fd_set *restrict exceptfds, struct timeval *restrict tvptr);
Returns: count of ready descriptors, 0 on timeout, −1 on error
int pselect(int maxfdp1, fd_set *restrict readfds, fd_set *restrict writefds, fd_set *restrict exceptfds, const struct timespec *restrict tsptr, const sigset_t *restrict sigmask);
Returns: count of ready descriptors, 0 on timeout, −1 on error
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset);
Returns: nonzero if fd is in set, 0 otherwise
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *fdset);
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *fdset);
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *fdset);
tvptr为NULL时,select函数阻塞等待直到有fd就绪或者被信号打断;当其值为0时,select函数非阻塞,其特征为非阻塞同步;当其值大于0时,select函数阻塞等待直到有fd就绪或者该参数指定的时间到期。linux中如果该函数在到期时间内返回,会以剩余时间更新tvptr的值。
readfds,writefds,exceptfds参数指定了需要“捕捉”的fd。使用FD_XXX系列函数对该三个fd_set进行操作。如果这三个参数都为NULL,该函数相当于sleep。maxfdp1应为最大的fd+1,避免内核查询这三个fd_set中其他不相关的位置。具体三个fd_set的布局如下图所示:
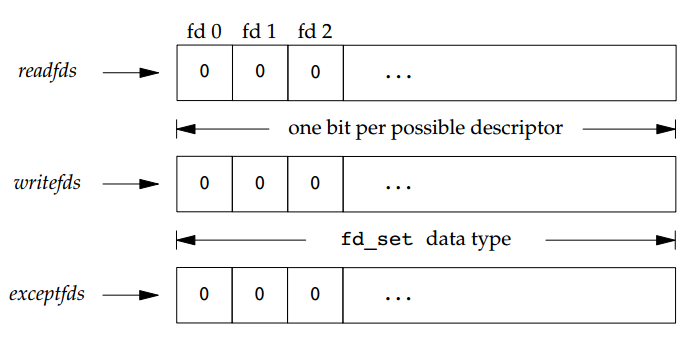
select函数返回值可能有三种情况:
- A return value of −1 means that an error occurred. In this case, none of the descriptor sets will be modified.
- A return value of 0 means that no descriptors are ready. When this happens, all the descriptor sets will be zeroed out.
- A positive return value specifies the number of descriptors that are ready. if the same descriptor is ready to be read and written, it will be counted twice in the return value. The only bits left on in the three descriptor sets are the bits corresponding to the descriptors that are ready.
pselect与select类似,其提供更高精度的时间参数且该参数在该函数返回时不会更改。sigmask参数用来屏蔽信号,等该函数返回时,恢复调用该函数前的sigmask值。
特别的,理解fd就绪的真正含义:
- A descriptor in the read set (readfds) is considered ready if a read from that descriptor won’t block.
- A descriptor in the write set (writefds) is considered ready if a write to that
descriptor won’t block. - A descriptor in the exception set (exceptfds) is considered ready if an exception condition is pending on that descriptor.
NOTE : File descriptors for regular files always return ready for reading, writing, and exception conditions. It is important to realize that whether a descriptor is blocking or not doesn’t affect whether select blocks. If we encounter the end of file on a descriptor, that descriptor is considered readable by select. We then call read and it returns 0.
以上注意事项需要重点理解下:一般常规文件都不会阻塞读写函数。select是否阻塞是由tvptr决定,而和fd是否阻塞没有关系。如果遇到文件末尾的时候,select会认为其是可读的,此时调用read函数返回0。
2.2 poll
#include <poll.h>
int poll(struct pollfd fdarray[], nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
Returns: count of ready descriptors, 0 on timeout, −1 on error
//以下是man page的描述:
//On success, a positive number is returned; this is the number of structures which have nonzero revents fields
//个人觉得这个描述会更好,因为不一定一个事件就代表了一个fd。
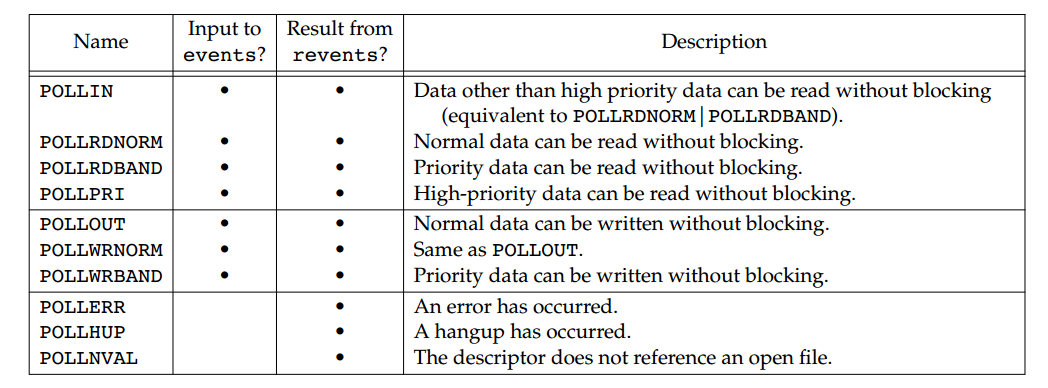
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor to check, or <0 to ignore */
short events; /* events of interest on fd */
short revents; /* events that occurred on fd */
};
poll与select函数类似,但是编程接口不同。fdarray数组每个成员存储我们该兴趣的fd及相应的事件,revents在该函数返回时相应的event参数中的位被置位,来反映哪个事件发生,nfds指定该数组的成员数。timeout可以取三个值:
- timeout == −1
We return when one of the specified descriptors is ready or when a signal is caught. If a signal is caught, poll returns −1 with errno set to EINTR
- timeout == 0
Don’t wait. All the specified descriptors are tested, and we return immediately. This is a way to poll the system to find out the status of multiple descriptors, without blocking in the call to poll.
- timeout > 0
Wait timeout milliseconds. We return when one of the specified descriptors is ready or when the timeout expires. If the timeout expires before any of the descriptors is ready, the return value is 0.
2.3 epoll
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_create(int size);int epoll_create1(int flags);
Returns:On success, a nonnegative file descriptor. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate the error.
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
Returns:When successful, returns zero. When an error occurs, returns -1 and errno is set appropriately.
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
int epoll_pwait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout, const sigset_t *sigmask);
Returns: When successful, returns the number of file descriptors ready for the requested I/O, or zero if no file descriptor became ready during the requested timeout milliseconds. When an error occurs, returns -1 and errno is set appropriately.
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
};
以下引用来自MAN Page:
- Epoll_create() creates an epoll(7) instance. Since Linux 2.6.8, the size argument is ignored, but must be greater than zero; epoll_create() returns a file descriptor referring to the new epoll instance. This file descriptor is used for all the subsequent calls to the epoll interface. When no longer required, the file descriptor returned by epoll_create() should be closed by using close. When all file descriptors referring to an epoll instance have been closed, the kernel destroys the instance and releases the associated resources for reuse.
- Epoll_ctl() performs control operations on the epoll instance referred to by the file descriptor epfd. It requests that the operation op be performed for the target file descriptor, fd. Valid values for the op argument are :
- EPOLL_CTL_ADD
Register the target file descriptor fd on the epoll instance referred to by the file descriptor epfd and associate the event event with the internal file linked to fd. - EPOLL_CTL_MOD
Change the event event associated with the target file descriptor fd. - EPOLL_CTL_DEL
Remove (deregister) the target file descriptor fd from the epoll instance referred to by epfd. The event is ignored and can be NULL.
- Epoll_wait() system call waits for events on the epoll(7) instance referred to by the file descriptor epfd. The memory area pointed to by events will contain the events that will be available for the caller. Up to maxevents are returned by epoll_wait(). The maxevents argument must be greater than zero. The timeout argument specifies the minimum number of milliseconds that epoll_wait() will block. Specifying a timeout of -1 causes epoll_wait() to block indefinitely, while specifying a timeout equal to zero cause epoll_wait() to return immediately, even if no events are available. The data of each returned structure will contain the same data the user set with an epoll_ctl(2) (EPOLL_CTL_ADD,EPOLL_CTL_MOD) while the events member will contain the returned event bit field.
总结一下上面的引用:epoll_create用来创建一个实例,返回的efd指向这个实例。epoll_ctl将自己感兴趣的fd注册到epoll_create所创建的实例上并和自己感兴趣的event绑定。epoll_wait等待参数epfd所指定的实例上事件的发生,**epoll与select或者poll相似,笔者推测都是在内核中进行了短期的轮询,也就是保证返回就绪的fd大于等于1。**其他的知识,比如Edge Triggered以后还会继续深入。
无论使用哪个函数,无论epoll做了什么样的改进,总体来说以上三个函数都是同步的。阻塞是否由参数决定,所以使用上述三个函数返回以后,必须人为轮询其对应返回事件或者fd值域。
3. 实验部分
>NOTE : 本题目和本身上述三个函数用于socket编程的思路无关,单纯对其使用特性的简单尝试。不增加篇幅,单独记录。对以上内容有质疑,请及时指正。笔者出题:分别使用select, poll, epoll实现回显程序























 811
811

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








