一、输入流与输出流
流就是指一连串流动的字符,以先进先出的方式发送信息的通道。
- 输入流 = 读
- 输出流 = 写
根据流处理的最基本单位可划分为字节流(基本处理单位一个字节)和字符流(基本处理单位为两个字节)。
二、字节流
- 字节流通常用来处理二进制数据。
- 基本的字节流类:InputStream(字节输入流)和OutputStream(字节输出流)。
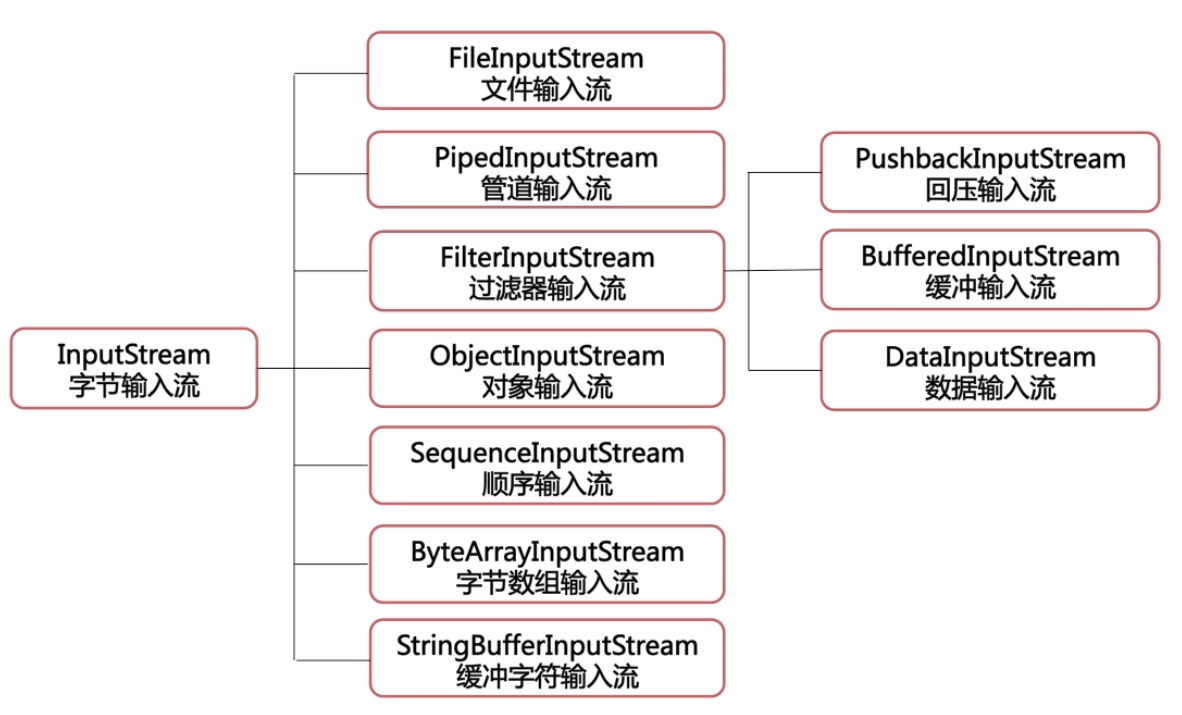
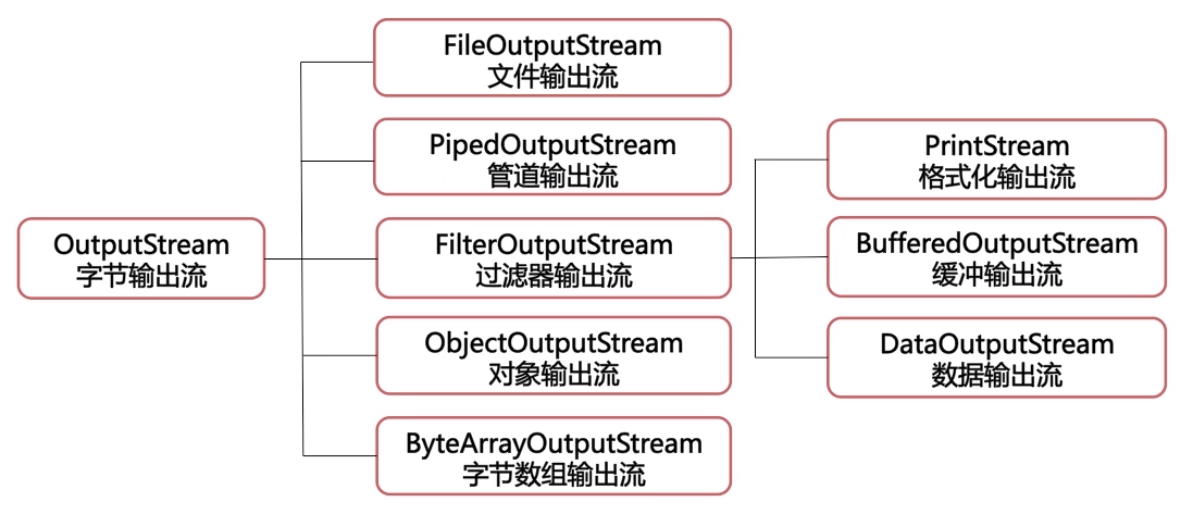
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
- 从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节
- 用于读取诸如图像数据之类的原始字节流
try {
// 输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(".\\test.txt");
String msg = "123456";
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes);
fos.close();
// 输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(".\\test.txt");
int n = 0;
while ((n=fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)n);
}
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* copy文件
* @param oldPath 旧文件路径
* @param newPath 新文件路径
*/
public void fileCopy(String oldPath, String newPath) {
// 输出流
try {
// 输入输出流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(oldPath);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(newPath);
// 读取文件内容生成copy文件
int n = 0;
while ((n=fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(n);
}
// 关闭流
fis.close();
fos.close();
System.out.println("文件Copy完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
缓冲输入流和缓冲输出流
String filePath = ".\\test.txt";
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos.write(50);
bos.write('a');
bos.flush();
System.out.println(bis.read());
System.out.println((char)bis.read());
fos.close();
fis.close();
bos.close();
bis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
三、字符流
- 字符流通常用来处理文本数据;
- 基本的字符流类:Reader(字符输入流)和Writer(字符输出流)。
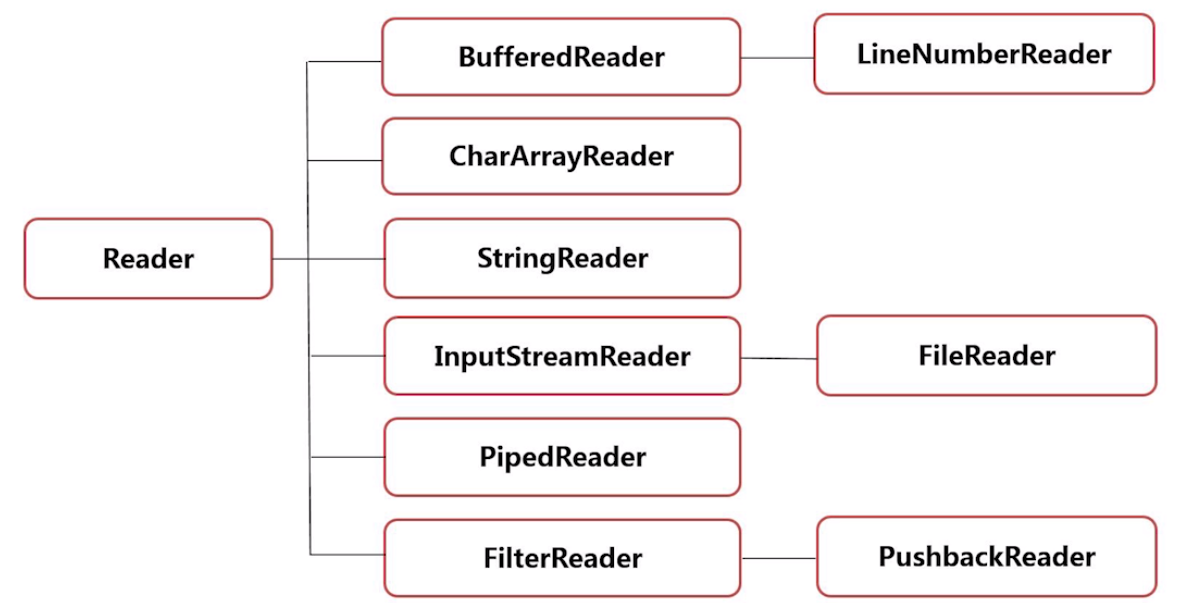
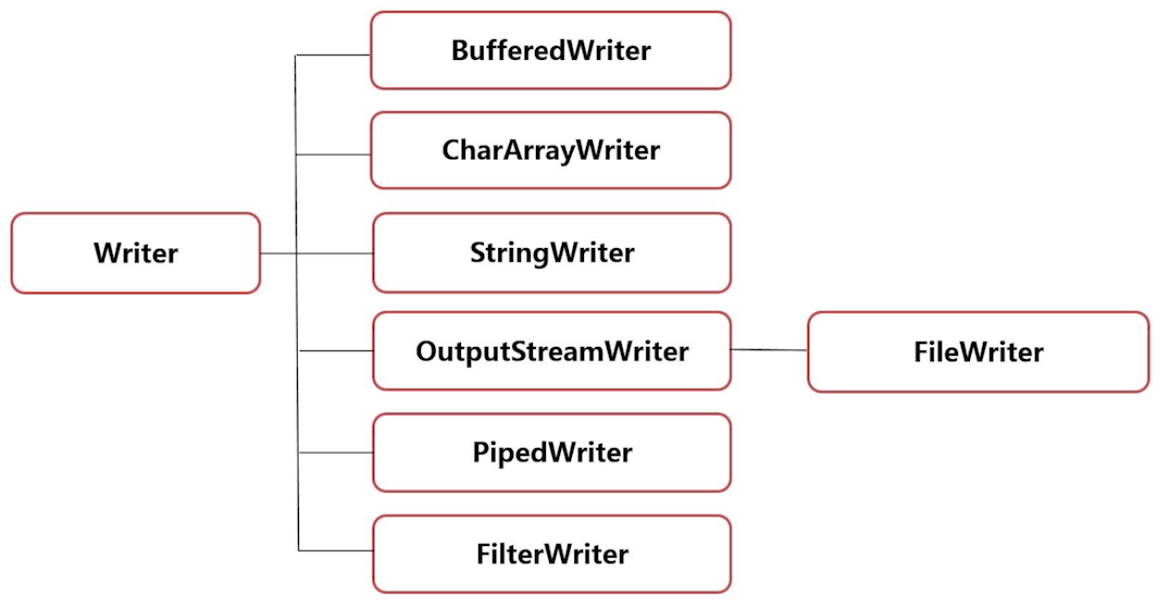
FileReader和FileWriter
String filePath = ".\\test.txt";
try {
// 输出流
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(filePath);
fw.write("翻滚吧!牛牛");
fw.flush();
// 输入流
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filePath);
// 读取方法1
int n;
while ((n=fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)n);
}
// 读取方法2
char[] ch = new char[50];
fr.read(ch);
for (char c : ch)
System.out.print(c);
fw.close();
fr.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
缓冲输入流和缓冲输出流
String filePath = ".\\test.txt";
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(filePath);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filePath);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
bw.write("翻滚吧!牛牛");
bw.flush();
// 读取方法1
int n;
while ((n=br.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)n);
}
// 读取方法2
char[] ch = new char[50];
br.read(ch);
for (char c : ch)
System.out.print(c);
fw.close();
fr.close();
bw.close();
br.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
四、字节字符转换流
InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter 将字节流转换为字符流。是字节流通向字符流的桥梁。如果不指定字符集编码,该解码过程将使用平台默认的字符编码,如:GBK。
String filePath = ".\\test.txt";
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
osw.write("扬帆,起航!");
osw.flush();
int n;
while ((n=isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)n);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
五、File类
什么是文件?
文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合。
在Java中,使用 java.io.File 类对文件进行操作。
常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| String getName() | 返回文件名称 |
| String getParent() | 返回文件父目录路径 |
| File getParentFile() | 返回文件所在文件夹的路径 |
| String getPath() | 返回文件潜在相对路径 |
| String getAbsolutePath() | 返回文件的绝对路径 |
| boolean mkdir() | 创建文件夹 |
| boolean mkdirs() | 创建多级文件夹 |
| boolean creatNewFile() | 创建文件 |
// 创建File对象
File file = new File("D:\\f");
File file1 = new File(file, "folder\\test");
File file2 = new File(file1, "msg.txt");
// 创建目录
if (!file.exists()) {
file1.mkdir();
}
// 创建目录树
if (!file1.exists()) {
file1.mkdirs();
}
// 创建文件
if (!file2.exists()) {
try {
file2.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("file是否是目录:" + file.isDirectory()); // true
System.out.println("file是否是文件:" + file.isFile()); // false
System.out.println("file1是否是目录:" + file1.isDirectory()); // true
System.out.println("file1是否是文件:" + file1.isFile()); // false
System.out.println("file2是否是目录:" + file2.isDirectory()); // false
System.out.println("file2是否是文件:" + file2.isFile()); // true
System.out.println(file2.getName()); // msg.txt
System.out.println(file2.getPath()); // D:\f\folder\test\msg.txt
System.out.println(file2.getParent()); // D:\f\folder\test
System.out.println(file2.getParentFile()); // D:\f\folder\test
System.out.println(file2.getAbsolutePath()); // D:\f\folder\test\msg.txt
六、序列化与反序列化
- 序列化:把Java对象转换成字节序列的过程。
- 反序列化:把字节序列恢复为Java对象的过程。
- ObjectInputStream:对象输入流
- ObjectOutputStream:对象输出流
对象序列化过程:
- 创建一个类,继承Serializable接口
- 创建对象
- 将对象写入文件
- 从文件读取对象信息
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestObject testObject = new TestObject("小明");
String filePath = ".\\test.txt";
TestMain6 testMain6 = new TestMain6();
testMain6.write(filePath, testObject);
testMain6.read(filePath);
}
/**
* 序列化
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @param testObject 序列化对象
*/
public void write(String filePath, TestObject testObject) {
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
oos.writeObject(testObject);
oos.writeObject(null);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (EOFException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 反序列化
* @param filePath 文件路径
*/
public void read(String filePath) {
try {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath)); // 文件中无数据时不要放至写入数据的代码前,会抛出异常
TestObject testObject2 = null;
while ((testObject2 = (TestObject)ois.readObject()) != null) {
System.out.println(testObject2);
}
ois.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (EOFException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.praintStackTrace();
}
}





 本文详细介绍了Java中的IO流概念及应用,包括字节流与字符流的区别和使用方法,如FileInputStream/FileOutputStream和FileReader/FileWriter等。同时,还探讨了缓冲流、字符编码转换流的使用,并对File类的基本操作进行了说明。
本文详细介绍了Java中的IO流概念及应用,包括字节流与字符流的区别和使用方法,如FileInputStream/FileOutputStream和FileReader/FileWriter等。同时,还探讨了缓冲流、字符编码转换流的使用,并对File类的基本操作进行了说明。
















 398
398

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








