引言
这篇博客将MobileNet中使用的各种Block提取出来,以便之后用于其他地方。
MobileNet V1
理论
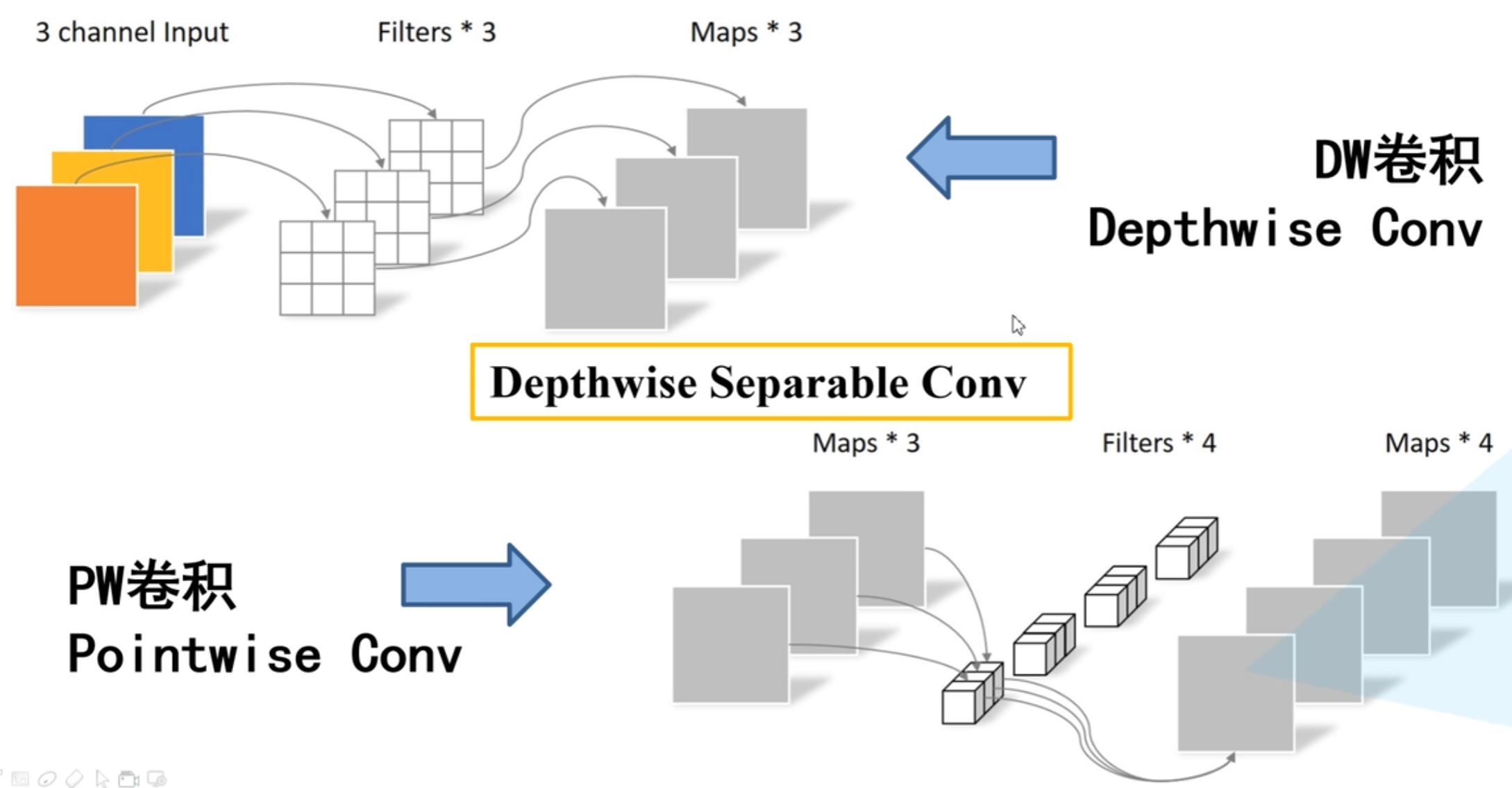
在V1版本中关键是提出了DWConv与PWConv来减低参数量。
DW卷积:只有一个卷积核,其中的每个卷积矩阵都对应着输入数据中的一个通道,输入通道数=输出通道数。在pytorch中,是通过设置nn.Conv2d中的groups参数实现的,让groups=in_channel。同时要设置padding参数来保证stride=1时尺寸不改变。
PW卷积:一个普通的1x1卷积,用于调整通道数。通常与DW卷积配合,来实现普通卷积的功能。
pytorch代码
from torch import nn
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 # 不会修改分辨率
DWConv = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,in_channel,kernel_size,stride,padding=padding,groups=in_channel)
PWConv = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,out_channel,kernel_size=1)
MobileNet V2
理论
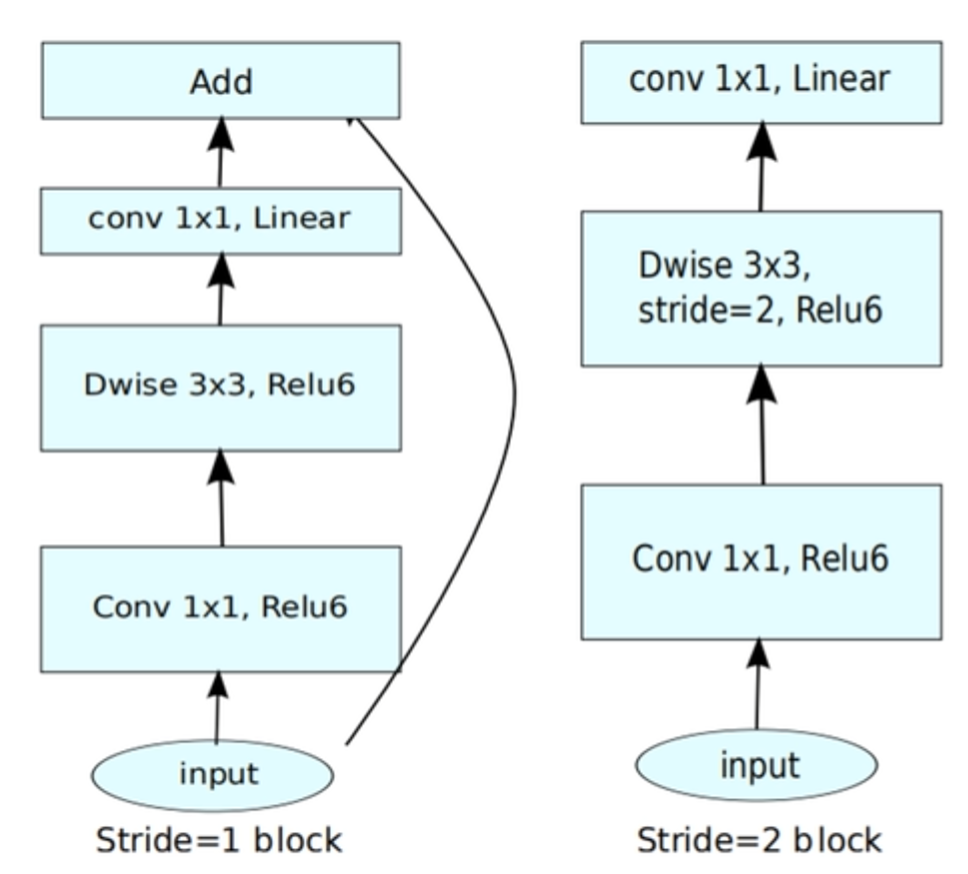
在MobileNetV2中,关键的是提出了倒残差结构。
先通过一个1x1的卷积来升维,然后通过一个3x3的DW卷积,最后通过一个1x1的卷积来降维。
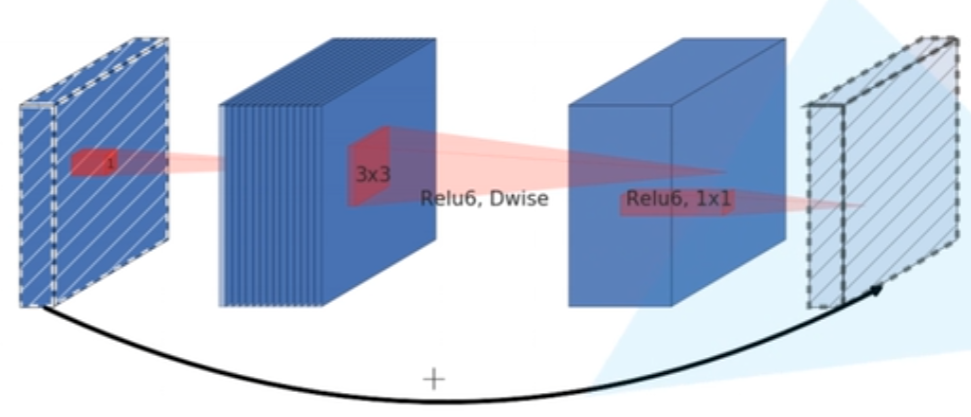
其中若in_channel==out_channel且DW卷积的stride=1,则会使用shortcut分支。
并且第一个1x1卷积与DW卷积会使用Relu6=
m
i
n
(
m
a
x
(
x
,
0
)
,
6
)
min(max(x,0),6)
min(max(x,0),6)激活函数。
pytorch代码
import torch.nn as nn
'''
包含了卷积、归一化与ReLU6的卷积模块
可以用于构造第一个1x1卷积与Dw卷积
'''
class ConvBNRELU6(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1):
super(ConvBNRELU6, self).__init__()
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 # stride=1时,不会修改分辨率
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# 通过groups来实现DW卷积
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class BlockV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride, expand_ratio):
super(BlockV2, self).__init__()
hidde_channel = in_channel * expand_ratio # 升维后的维度
self.Conv1 = ConvBNRELU6(in_channel, hidde_channel, 1, 1) # 第一个1x1卷积
self.DWConv = ConvBNRELU6(hidde_channel, hidde_channel, kernel_size, stride, hidde_channel) # DW卷积
self.Conv2 = nn.Sequential( # 第二个1x1卷积
nn.Conv2d(hidde_channel, out_channel, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
)
self.shortcut = stride == 1 and in_channel == out_channel # 判断是否使用shortcut分支
def forward(self, x):
y = self.Conv1(x)
y = self.DWConv(x)
y = self.Conv2(x)
if self.shortcut:
y = y + x # 残差连接
return y
MobileNetV3
理论
MobileNetV3相比于V2,在DW卷积与1x1卷积之间增加了SE(Squeeze-and-Excitation)注意力机制
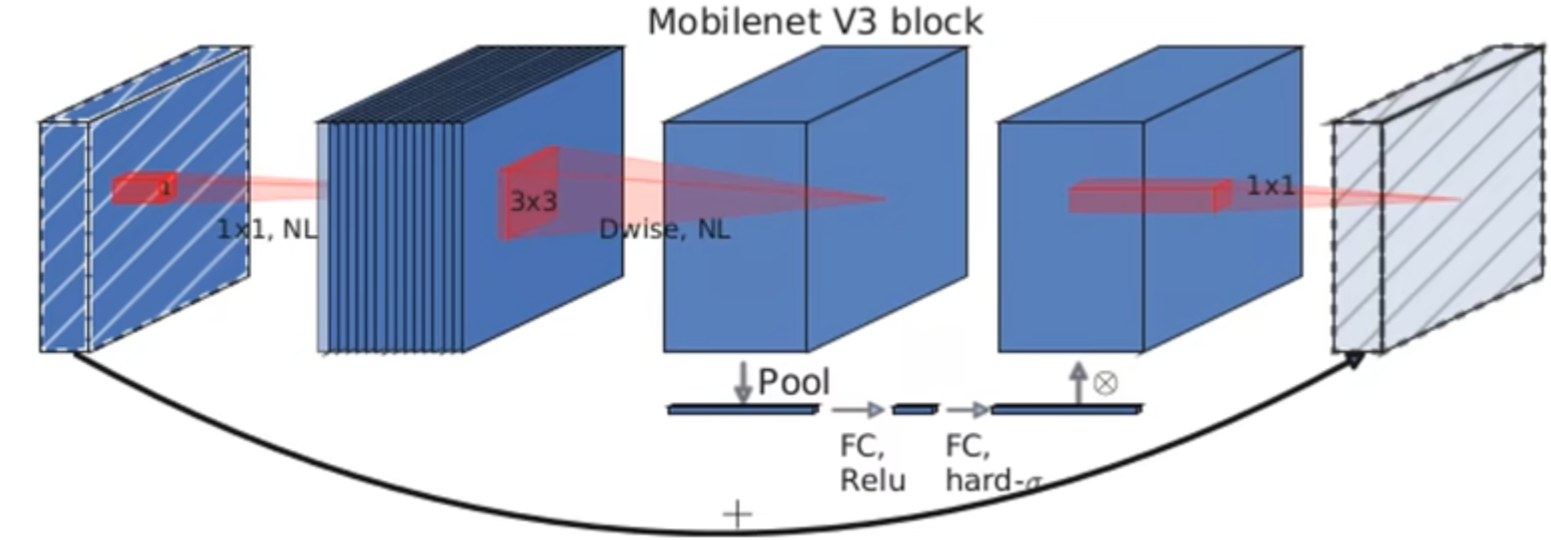
SE注意力机制
SE注意力机制
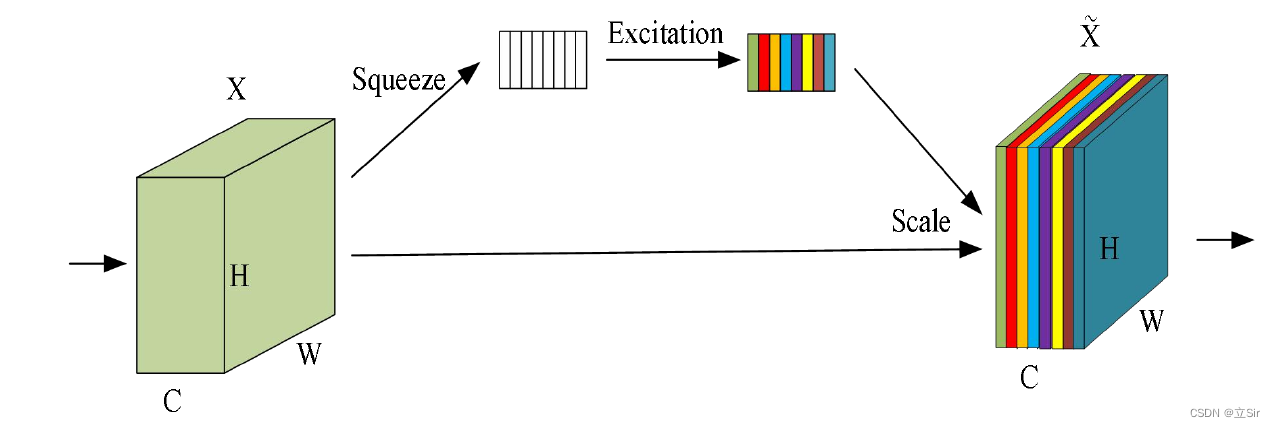
SE注意力机制(Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks)在通道维度增加注意力机制,关键操作是squeeze和excitation。
通过SE,获取到特征图的每个通道的重要程度,然后用这个重要程度去给每个特征赋予一个权重值,从而让神经网络重点关注某些特征通道。
实现步骤:
(1)Squeeze:通过全局平均池化,将每个通道的二维数据压缩为1个数。[C,H,W]->[C,1,1]
(2)Excitation:此步骤是为了得到各个通道之间的相关性,为每个通道生成一个权重值。论文中是通过两个全连接层与激活函数来实现,其中第一个全连接层会将通道数变为原本的1/4,第二个全连接层再恢复为原样。
输出的权重个数与输入特征图的通道数相同。[C,1,1]->[C,1,1]
(3)Scale:将前面得到的归一化权重通过乘法加权到每个通道的特征上。[C,H,W]*[C,1,1]==>[C,1,1]
pytorch代码实现
SE注意力机制
这里通过一个1x1的卷积层来代替全连接层
"""保证除法后的结果为divisor的整数倍"""
def make_divisible(channel, divisor=8, min_ch=None):
if min_ch is None:
min_ch = divisor
new_ch = max(min_ch, int(channel + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
if new_ch < 0.9 * channel:
new_ch += divisor
return new_ch
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, squeeze_factor=4):
super(SE, self).__init__()
hidde_channel = make_divisible(in_channel // squeeze_factor) # 计算降维后的维度
self.se = nn.Sequential( # 注意力模块
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)), # 动态平均池化,每个通道都变为1x1
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, hidde_channel, 1), # 1x1卷积
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(hidde_channel, in_channel, 1),
nn.Hardsigmoid(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.se(x)
return y * x
Block
"""
可以指定归一化与激活函数的卷积模块
默认为BatchNorm2d与ReLU6
"""
class ConvNormActive(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, active_layer=nn.ReLU6):
super(ConvNormActive, self).__init__()
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 # stride=1时,不会修改分辨率
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# 通过groups来实现DW卷积
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups, bias=False),
norm_layer(out_channel),
active_layer(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class BlockV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride, expand_ratio):
super(BlockV3, self).__init__()
self.SE = SE(in_channel) # 注意力机制
hidde_channel = in_channel * expand_ratio
self.Conv1 = ConvNormActive(in_channel, hidde_channel, 1, 1) # 第一个1x1卷积
self.DWConv = ConvNormActive(hidde_channel, hidde_channel, kernel_size, stride, hidde_channel) # DW卷积
self.Conv2 = nn.Sequential( # 第二个1x1卷积
nn.Conv2d(hidde_channel, out_channel, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
)
self.shortcut = stride == 1 and in_channel == out_channel
def forward(self, x):
y = self.Conv1(x)
y = self.DWConv(y)
y = self.SE(y)
y = self.Conv2(y)
if self.shortcut:
y = y + x # 残差连接
return y























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








