一.查询列(字段)
1.select distinst *|字段|表达式| as 别名 from 表 表别名
SELECT * FROM 表名; →查询某个表中所有的记录的所有字段信息
SELECT 列名 FROM 表名; →查询某个表中所有的记录的指定字段信息
SELECT 列名1,列名2 FROM 表名; → 查询某个表中所有的记录的字段1 字段2
SELECT distinct 列名 FROM 表名; →去除重复记录
SELECT 表达式 FROM 表名; →查询表达式
SELECT xxx as 别名 FROM 表名 表别名 →使用别名
2.部分列
查询部分字段,指定的字段名
--1)、检索单个列
select ename from emp; --查询雇员姓名
--2)、检索多个列
select deptno,dname,loc from dept; --查询部门表的deptno,dname, loc 字段的数据。
--以下查询的数据顺序不同(查询的字段顺序代表数据顺序)
select loc,dname,deptno from dept;
select deptno,dname,loc from dept;
3.所有列
查询所有的字段 通配符 *( 书写方便、可以检索未知列;但是降低检索的性能) ,数据的顺序跟定义表结构的顺序一致:
--1)、检索所有列1
select * from dept; --查询部门的所有信息
--2)、检索所有列2
select deptno,dname,loc from dept; --查询部门的所有信息
3.去除重复
使用distinct去重,确保查询结果的唯一性:
select distinct deptno from emp;--去重
4.别名
使用别名便于操作识别,隐藏底层信息。存在字段别名和表别名:
select ename as "雇员 姓名" from emp;
select ename "雇员姓名" from emp;
select ename 雇员姓名 from emp;
select ename as 雇员姓名 from emp;
select ename as " Ename" from emp;
● as: 字段别名可以使用as,表别名不能使用as
● " ": 原样输出,可以存在空格与区分大小写
5.字符串
使用 ' ' 表示字符串(注意区分“ ”),拼接使用 ||
select 'my' from emp;
select ename||'a'||'-->' info from emp;
6.违例
不存在的列,构建虚拟的列
select empno, 1*2 as count,'cmj' as name,deptno from emp;
7.虚表
用于计算表达式,显示单条记录的值
select 1+1 from dual;
8.null
null遇到数字参与运算的结果为null,遇到字符串为空串
select 1+null from dual;
select '1'||null from dual;
select 1||'2'||to_char(null) from dual;
select ename,sal*12+comm from emp;
--nvl内置函数,判断是否为null,如果为空,取默认值0,否则取字段实际值
select ename,sal*12+nvl(comm,0) from emp;
二.查询行(记录)
where 过滤行记录条件,条件有
a)、= 、 >、 <、 >=、 <=、 !=、 <>、 between and
b)、and 、or、 not、 union、 union all、 intersect 、minus
c)、null :is null、 is not null、 not is null
d)、like :模糊查询 % _ escape('单个字符')
f)、in 、 exists(难点) 及子查询
1.比较条件
= 、>、 <、 >=、 <=、 !=、 <>
select * from emp where deptno !=20;
select * from emp where deptno <>20;
select * from emp where sal between 800 and 950; --between and是成对出现的
--查询 员工的年薪大于20000的 员工名称、岗位 年薪
--1)、nvl select ename,job,12*(nvl(comm,0)+sal) income from emp;
--2)、年薪大于20000 --错误不能使用别名:
select ename,job,12*(nvl(comm,0)+sal) income from emp where income>2000;
--a)、嵌套一个: 查询在前 过滤在后
select ename,job,income from (select ename,job,12*(nvl(comm,0)+sal) income from emp) where income>2000;
--b)、不使用别名 (推荐) :过滤在前,查询在后
select ename,job,12*(nvl(comm,0)+sal) income from emp where 12*(nvl(comm,0)+sal) >2000 ;
--了解 any some all
-- >=any(值列表) 大于最小值 <=any(值列表)小于最大值
select * from emp where sal >=any(900,2000);
select * from emp where sal <=any(900,2000);
-- some与any 一样的效果
2.且或非
and or not
3.null
null不能使用条件判断,只能使用is :
--存在佣金的员工名称
select * from emp where comm is null;
--不存在佣金的员工名称
select * from emp where comm is not null;
select * from emp where not comm is null;
4.集合操作
Union、Union All、Intersect、Minus
Union,并集(去重) 对两个结果集进行并集操作,不包括重复行同时进行默认规则的排序;
Union All,全集(不去重) 对两个结果集进行并集操作,包括重复行,不进行排序 ;
Intersect,交集(找出重复) 对两个结果集进行交集操作,不包括重复行,同时进行默认规则的排序;
Minus,差集(减去重复) 对两个结果集进行差操作,不包括重复行,同时进行默认规则的排序
--查询工资大于1500 或 含有佣金的人员姓名
--union 去除重复行
select ename from emp where sal>1500 union
select ename from emp where comm is not null;
-- union all 不去除重复行
select ename from emp where sal>1500 union all
select ename from emp where comm is not null;
--查询显示不存在雇员的所有部门号。
select deptno from dept minus select distinct deptno from emp
--查询工资大于1500 且 含有佣金的人员姓名
select ename,sal,comm from emp where sal>1500 intersect
select ename,sal,comm from emp where comm is not null;
5.like 模糊查询
模糊查询,使用通配符:
1)%:零个及以上(任意个数的)的字符
2)_ :一个字符
3)遇到内容中包含% _使用escape(‘单个字符’)指定转义符
--查询员工姓名中包含字符A的员工信息
select * from emp where ename like '%A%';
--查询员工姓名中包含第二个A的员工名称信息
select * from emp where ename like '_A%';
--数据中 员工姓名中 存在 _ % ,如何查找:
--1)、编写测试数据
insert into emp(empno,ename,sal) values(1000,'t_%test',8989);
insert into emp(empno,ename,sal) values(1200,'t_tes%t',8000);
--2)、查找
--查询员工姓名中包含字符%的员工名称 岗位 工资 部门编号
select ename,job,sal,deptno from emp where ename like '%a%%' escape('a');
--查询员工姓名中包含第二个_的员工名称 岗位 工资 部门编号
6.in 与 exists
in相当于使用or的多个等值,定值集合 ,如果存在 子查询,确保 类型相同、字段数为1,如果记录多,效率不高,用 于一些 少量定值判断上:
select * from emp where sal in(900,800)
--子查询(查询中再有查询) in 只能存在一个字段
select * from emp where sal in (select sal from emp e where deptno=10)
--10或30部门的雇员信息
select * from emp where deptno in(10,30);
--部门名称为 SALES 或 ACCOUNTING 的雇员信息
select deptno from dept where dname in('SALES','ACCOUNTING');
select *
from emp
where deptno in
(select deptno from dept where dname in ('SALES', 'ACCOUNTING'));
/* 便于理解 使用java思维
while(外层结果集){
while(内层结果集){
if(emp.deptno==10){
syso("...."); } if(emp.deptno==30){
syso("...."); } } }
==>in :如果记录多,效率不高,用于 一些 少量定值判断上 */
exists条件为true,存在记录则返回结果,后续不再继续 比较查询,与查询的字段无关,与记录有关:
7.获取所有行的记录
select * from emp;
select * from emp where 1=1 ;
select * from emp where ename like '%';
三.排序
1.使用ORDER BY排序,排序不是真实改变存储结构的顺序,而是获取的集合的顺序。
顺序 :asc(默认) desc
多字段: 在前面字段相等时,使用后面的字段排序
空排序: 降序为desc,注意null为最后
--按工资降序
select * from emp order by sal desc;
--null问题
select * from emp order by nvl(comm,0),comm desc;
select * from emp order by comm nulls first;
--查询雇员姓名,年薪 按佣金排序 默认为升序(asc),降序为desc,注意null为最后
select ename,(sal+nvl(comm,0))*12,comm total from emp order by comm desc;
--查询雇员姓名,年薪 按佣金排序 默认为升序(asc),降序为desc,注意null为最后
select ename,(sal+nvl(comm,0))*12,comm total from emp order by comm desc;
--对部门编号为 20 或30的雇员,工资+佣金 进行升序排序,如果相同,则按姓名降序。
--1、查询20、30 雇员 select * from emp where deptno in(20,30);
--2、工资+佣金排序
select ename,sal,comm,sal+nvl(comm,0) c from emp where deptno in(20,30) order by c;
--3、多个字段排序使用, 排序的字段可以使构建出来的虚拟的字段
select ename,sal,comm from emp where deptno in(20,30) order by sal+nvl(comm,0),ename desc;
四.函数——单行函数
函数分为系统内置函数 自定义函数(后期学习的plsql中定义);了解系统内置函数(方法),重点掌握to_date 、 to_char (字符和日期的转换)
根据函数的返回结果,我们将函数分为单行函数和多行函数
单行函数:一条记录返回一个结果
多行函数 组函数 聚合函数 (重点) :多条记录 返回一个结果 (重点)
1.日期函数
日期函数: 注意区分 db数据库时间 ,java应用服务器的时间。以一方为准
oracle以内部数字格式存储日期:年,月,日,小时,分钟,秒
sysdate/current_date 以date类型返回当前的日期
add_months(d,x) 返回加上x月后的日期d的值
LAST_DAY(d) 返回的所在月份的最后一天
months_between(date1,date2) 返回date1和date2之间月的数目
next_day(sysdate,'星期一') 下周星期一
1)当前时间
select current_date from dual where 1=1;
select sysdate from dual where 1=1;
2)修改日期(天数+-) --两天后的时刻
select sysdate+2 from dual;
3)修改月份 --当前5个月后的时间
select add_months(sysdate,5) from dual;
--雇佣日期 2个月的时间
select ename,hiredate, add_months(hiredate,2) after from emp;
4)月份之差
--雇佣日期 距离现在的 月份数
select ename, months_between(sysdate , hiredate) from emp;
5)最后一天 --返回雇佣日期 当月最后一天的时间
select ename, last_day(hiredate) d from emp;
6)下一个星期的时间
--下一个星期二
select next_day(sysdate, '星期二') from dual;
2.转换函数(重点*****)
to_data(c,m) 字符串以指定格式转换为日期
to_char(d,m) 日期以指定格式转换为字符串
select to_date('2017-3-21 18:12:12','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') time from dual;
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual;
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy/mm/dd') from dual;
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy\mm\dd') from dual;
注意中文的问题
--select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy年mm月dd日') from dual;
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy"年"mm"月"dd"日"') from dual;
3.其它函数(保证类型兼容)
4.分析函数(了解)
五.组函数
组函数|多行函数|聚合函数 即多条记录 返回一个结果。我们需要掌握如下几个组函数:avg 、sum、 min、 max、 count
1)count :统计记录数 count() -->* 或一个列名
2)max min: 最大值 最小值
3)sum:求和
4)avg:平均值
注意:
1)组函数仅在选择列表和Having子句中有效
2)出现组函数,select 只能有组函数或分组字段
说明:
组信息 与单条记录不能同时查询
组函数 不能用在 where中,能使用的地方 select having
null 不参与运算
1.count
--2、null不参与运算
--存在佣金的员工数
--不推荐/不需要
select count(comm) from emp where comm is not null;
--推荐 select count(comm) from emp;
--统计 部门编号30的员工数
select count(1) from emp where deptno=30;
--统计数量过程中 ,可能处理重复 --统计 存在员工的 部门数量
select count(distinct(deptno)) 有人的部门 from emp;
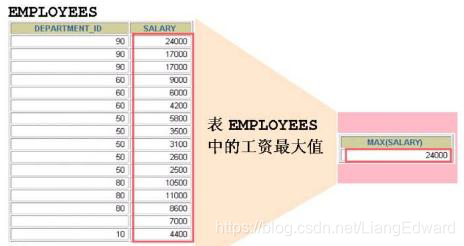
2、max min: 最大值 最小值
--查询所有员工的 最高薪水 ,最低薪水,员工总数
-->组信息
select max(sal) maxSal , min(sal) minSal , count(1) from emp;
--查询 最高薪水的员工名称 及薪水
--组信息 与单条记录不能同时查询
select max(sal), ename, sal from emp;
错误 select ename, sal from emp where sal=(select max(sal) from emp );
3.sum:求和
-- 查询10部门的所有员工的工资总和
select sum(sal) from emp where deptno=10;
4.avg平均
-- 查询工资低于平均工资的员工编号,姓名及工资
select empno, ename,sal from emp where sal<(select avg(sal)from emp);
--查看 高于本部门平均薪水员工姓名
select * from emp e1 where sal>(select avg(sal) from emp e2 where e1.deptno=e2.deptno );
六.分组
分组: group by , 将符合条件的记录 进一步的分组
过滤组:having , 过滤组信息 ,表达式 同 where 一致

现在的结构如下:
select distinct * | 字段 | 表达式 | 函数 as 别名
from 表 表别名
where 过滤行记录条件
group by 分组字段列表
having 过滤组
order by 字段列表 asc | desc
解析步骤
1)、from 2)、where 3)、group 4)、having 5)、select 6)、order by
group by :分组
1)、select 出现分组函数,就不能使用 非分组信息,可以使用 group by 字段
2)、group by字段 可以不出现 select 中 ,反之select 除组函数外的,其他字段必须出现在group by 中
过滤组 having :
where :过滤行记录,不能使用组函数, having:过滤组 可以使用组函数
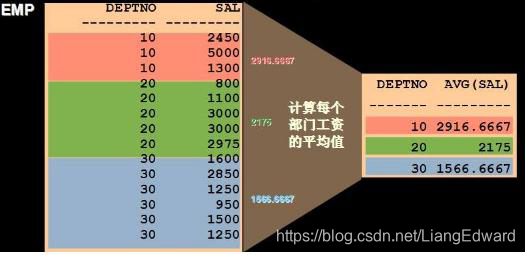
--按 部门 查询 平均工资
select avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;
--按 部门岗位 查询 平均工资
select avg(sal) from emp group by deptno,job;
--按 部门 查询 平均工资,且平均工资大于2000的部门编号
--1、先分组 后过滤 (不推荐)
select * from (select deptno, avg(sal) avsal from emp where 1 = 1 group by deptno) where avsal > 2000;
--2、过滤组 ,分组同时 过滤
select avg(sal), deptno from emp group by deptno having avg(sal)>2000;
--查询 最低平均工资的部门编号
--1)、按部门求出平均薪水
select avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;
--2)、找出最低的平均薪水
select min(avg(sal)) from emp group by deptno;
--3)、过滤组
select deptno
from emp where 1 = 1
group by deptno
having avg(sal) = (select min(avg(sal)) from emp where 1 = 1 group
by deptno);
--查看 高于本部门平均薪水员工姓名
--1、按部门求出平均薪水
--2、关联子查询
select *
from emp e
where exists
(select deptno
from (select deptno, avg(sal) avgsal from emp group by
deptno) e2
where e.deptno = e2.deptno and e.sal > avgsal);
--另外一种 (推荐)
select *
from emp e1
where sal > (select avg(sal) from emp e2 where e2.deptno =
e1.deptno);
 JavaSE数据库查询与排序函数详解
JavaSE数据库查询与排序函数详解








 这篇博客详细介绍了JavaSE中关于数据库的查询操作,包括查询列、查询行、排序以及各种函数的使用,如单行函数、组函数。讨论了如何使用SELECT语句查询特定字段,使用DISTINCT去除重复记录,以及WHERE、ORDER BY子句进行行记录过滤和排序。还深入探讨了日期函数、转换函数以及统计函数如COUNT、MAX、MIN、SUM和AVG的运用,并提到了GROUP BY和HAVING子句在分组过滤中的作用。
这篇博客详细介绍了JavaSE中关于数据库的查询操作,包括查询列、查询行、排序以及各种函数的使用,如单行函数、组函数。讨论了如何使用SELECT语句查询特定字段,使用DISTINCT去除重复记录,以及WHERE、ORDER BY子句进行行记录过滤和排序。还深入探讨了日期函数、转换函数以及统计函数如COUNT、MAX、MIN、SUM和AVG的运用,并提到了GROUP BY和HAVING子句在分组过滤中的作用。
















 529
529

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








