在Web的应用开发中,大多数情况是通过同步方式实现数据交互处理的,但处理与第三方系统的交互时,会容易造成响应迟缓的情况,所以处理与第三方软件交互时大多数使用多线程完成,也可以用异步调用方法来解决。规矩处理方式的不同,异步又分为有返回值和无返回值的异步任务调用,现在我们用spring boot框架来把两种异步调用方法来运用一下。
一:无返回值的异步任务调用
1.首先我们在项目中创建一个名为service的包和名为controller的包
2.(编写异步调用方法)然后在service包下创建一个业务实现类,并编写模拟用户短信验证码发送的方法,如下:
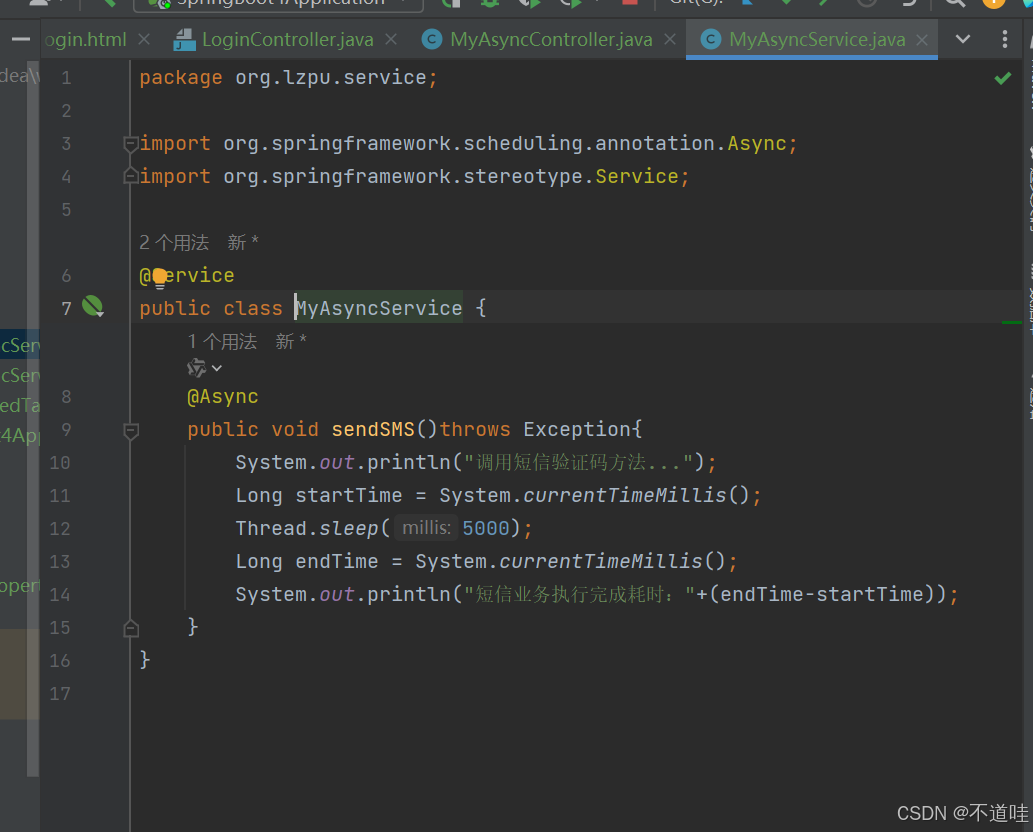
package org.lzpu.service;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyAsyncService {
@Async
public void sendSMS()throws Exception{
System.out.println("调用短信验证码方法...");
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("短信业务执行完成耗时:"+(endTime-startTime));
}
}
上述代码中,@Async注释将sendSMS()标注为异步方法,用于模拟发送短信验证码;
3.(开启基于注释的异步任务支持)创建启动类,使用了@Async注释标注了异步方法后,要想异步方法生效,还需要在项目启动类中添加@EnableAsync注释,如下:
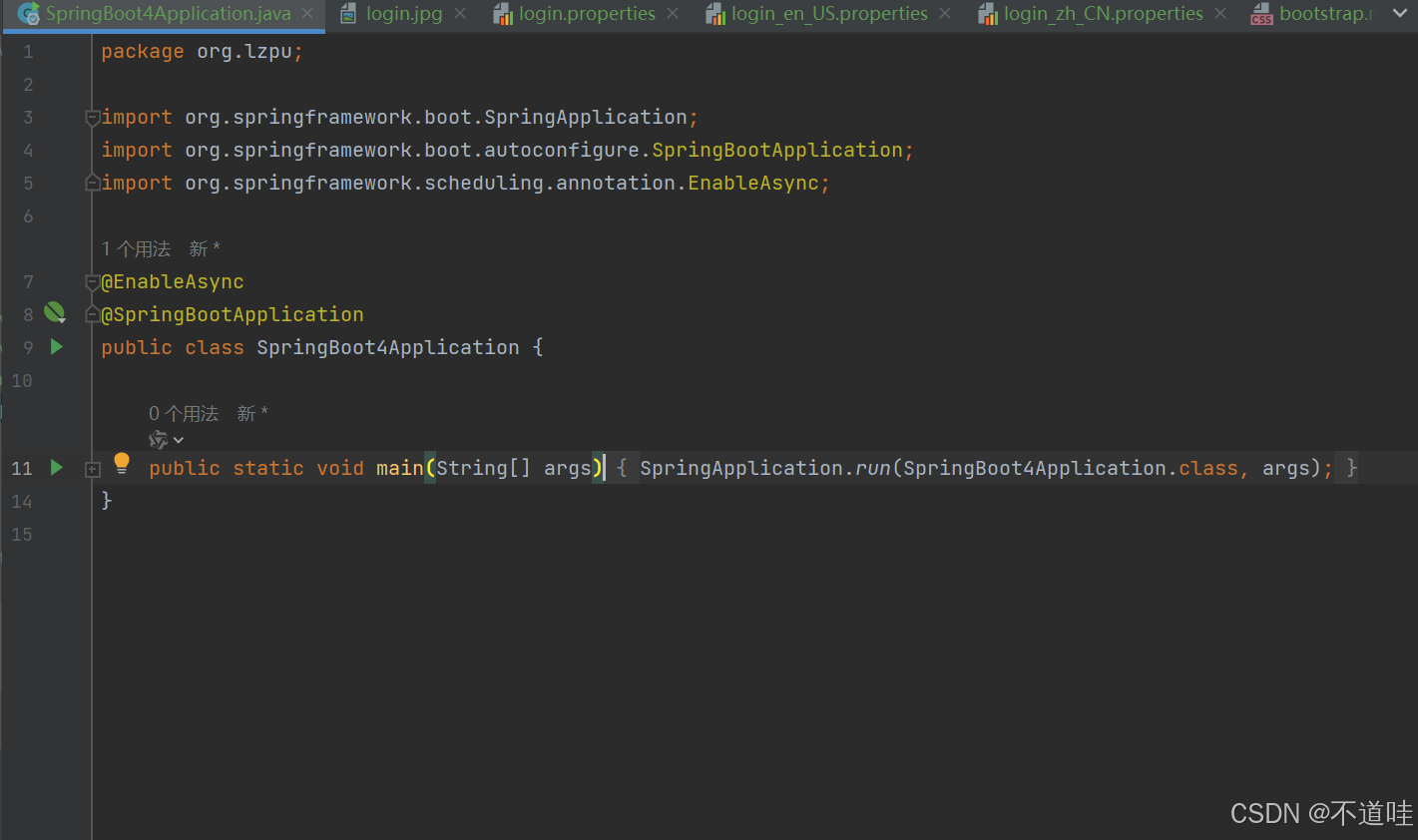
package org.lzpu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBoot4Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot4Application.class, args);
}
}
4.(编写控制业务调用方法)接着在上面创建的controller包中创建一个模拟编写用户短信验证码发送的处理方法类,如:
package org.lzpu.controller;
import org.lzpu.service.MyAsyncService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MyAsyncController {
@Autowired
private MyAsyncService myAsyncService;
@GetMapping("/sendSMS")
public String sendSMS()throws Exception{
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
myAsyncService.sendSMS();
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("主流程耗时:"+(endTime-startTime));
return "success";
}
}
如上述代码所示,sendSMS()方法模拟发送短信,专门用于处理请求路径为“/sendSMS”的请求。
5.(效果测试)项目启动且成功后,在浏览器中访问“http://localhost:8080/sendSMS”测试异步任务请求,此时浏览器上会显示“success”信息,同时控制台也会输出,如下图所示:
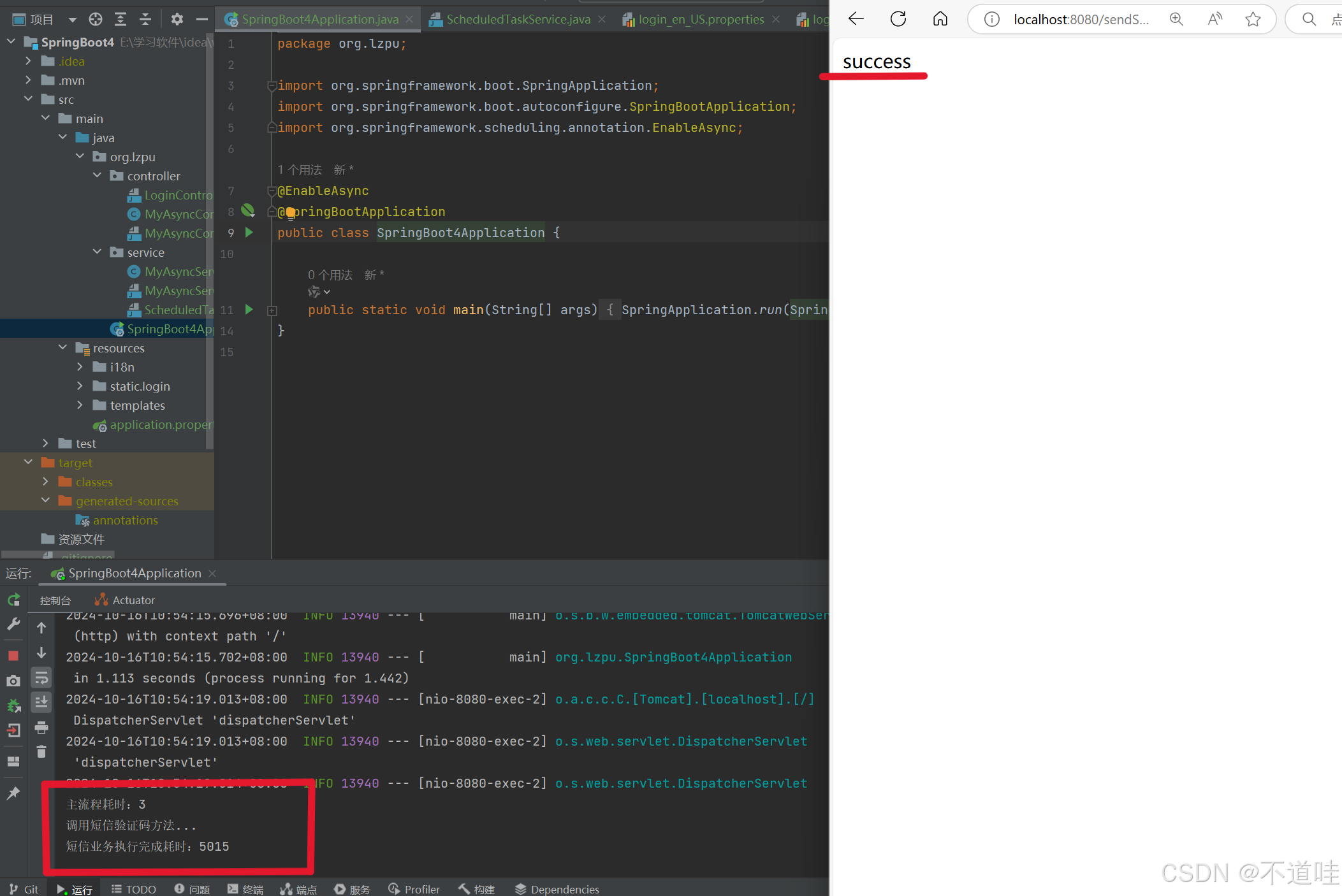
如上,无返回值异步任务调用就完成了。
二、有返回值异步任务调用
1.(编写异步调用方法)在以上创建service包中的异步任务处理类中添加两个模拟有返回值的异步任务业务处理方法,如:
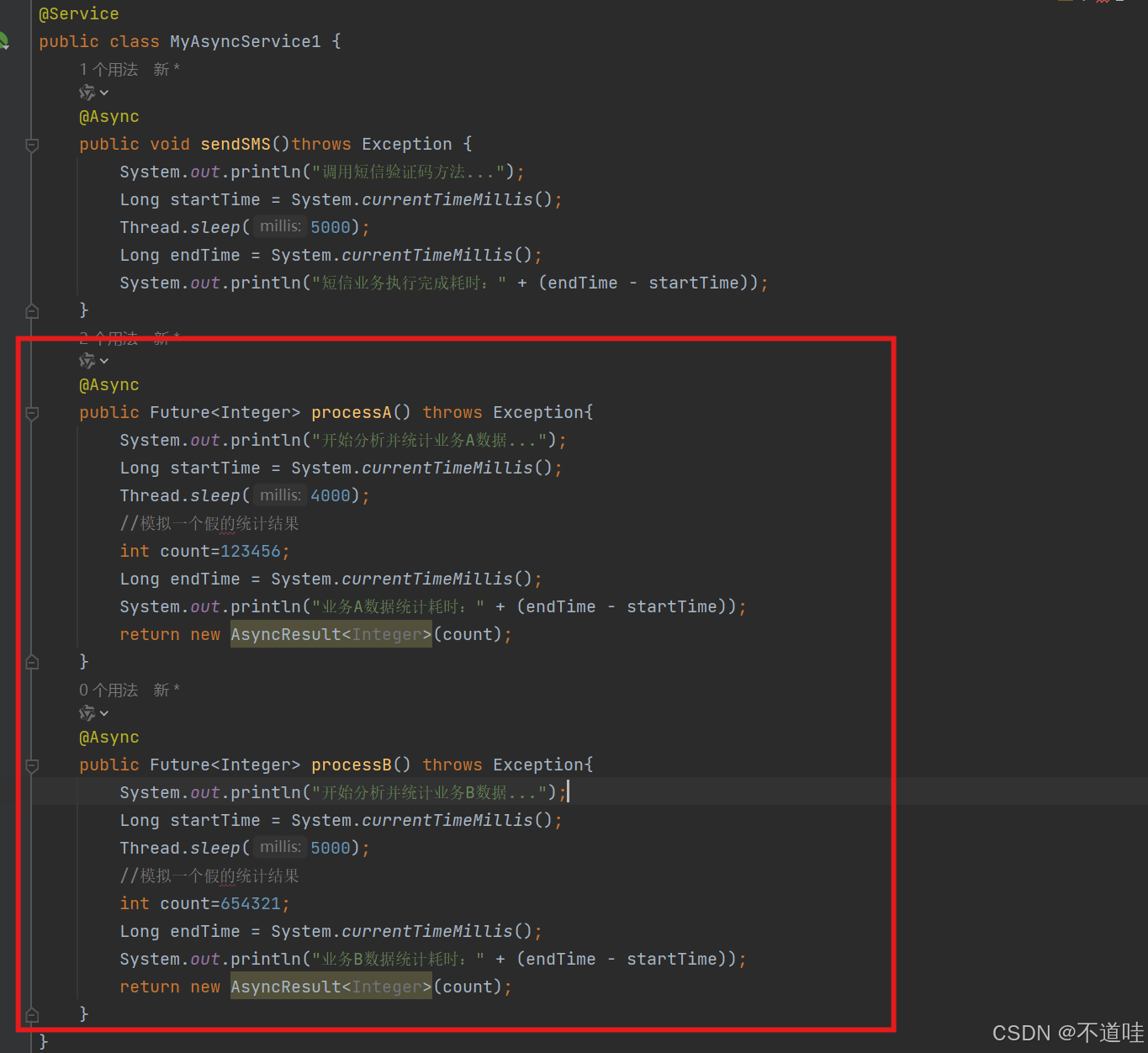
@Async
public Future<Integer> processA() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始分析并统计业务A数据...");
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(4000);
//模拟一个假的统计结果
int count=123456;
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("业务A数据统计耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
return new AsyncResult<Integer>(count);
}
@Async
public Future<Integer> processB() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始分析并统计业务B数据...");
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(5000);
//模拟一个假的统计结果
int count=654321;
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("业务B数据统计耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
return new AsyncResult<Integer>(count);
}上述在异步任务业务处理类中 添加了两个分别处理业务A数据统计的方法processA()和处理业务B数据统计的方法processB(),在方法上都使用了@Async注释标记为异步方法。
2.(编写控制层业务调用方法)在上面创建的controller包中的异步任务处理类中编写业务数据分析统计的请求处理方法,如:
@GetMapping("/statistics")
public String statistics() throws Exception{
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<Integer> futureA = myService.processA();
Future<Integer> futureB = myService.processB();
int total = futureA.get() +futureB.get();
System.out.println("异步任务数据统计汇总结果:"+total);
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("主流程耗时:"+(endTime-startTime));
return "success";
}上述代码中,statistics()方法处理映射路径为“/statistics”的业务数据统计的请求,通过 processA()和 processB()异步方法输出主流程的耗时时长。
3.(异步任务效果测试) 项目启动且成功后,在浏览器中访问“http://localhost:8080/statistics”测试异步任务请求,此时浏览器上响应“success”信息需要一段时间,此时看控制台效果如下:
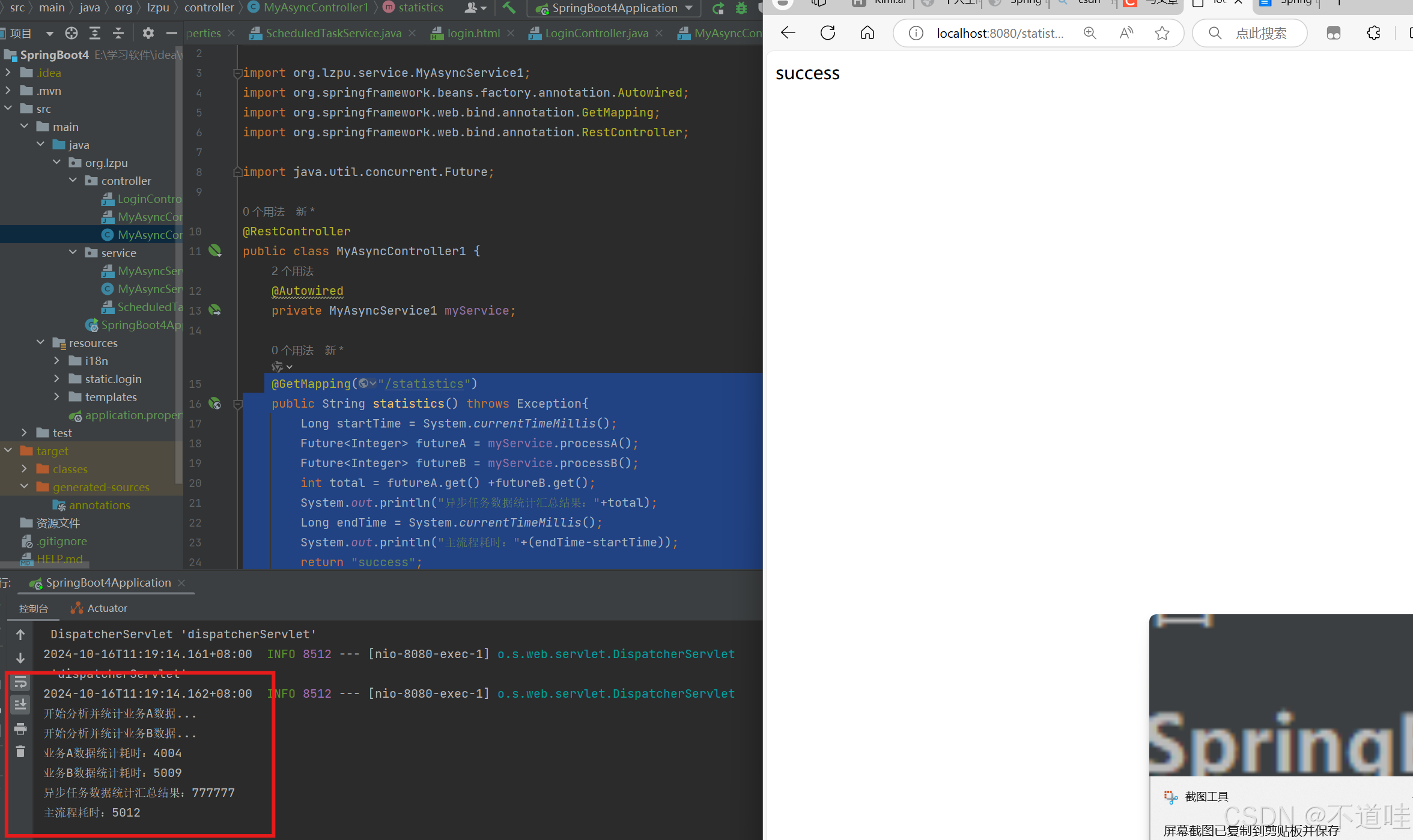
上述的异步方法是有返回值的,当返回值较多时主流程在执行异步方法是会有短暂阻塞的,需要等待并获取异步方法的返回结果。
以上就是有无返回值的异步方法的使用,感谢浏览。
(实力有限,不喜勿喷)




















 1251
1251

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








