1.Mybatis的Dao层实现
1.1 传统开发方式
1.1.1编写UserDao接口
public interface UserDao {
List<User> findAll() throws IOException;
}
1.1.2.编写UserDaoImpl实现
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
public List<User> findAll() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream =
Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("userMapper.findAll");
sqlSession.close();
return userList;
}
}
1.1.3 测试传统方式
@Test
public void testTraditionDao() throws IOException {
UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
List<User> all = userDao.findAll();
System.out.println(all);
}
1.2 代理开发方式
1.2.1 代理开发方式介绍
采用 Mybatis 的代理开发方式实现 DAO 层的开发,这种方式是我们后面进入企业的主流。
Mapper 接口开发方法只需要程序员编写Mapper 接口(相当于Dao 接口),由Mybatis 框架根据接口定义创建接口的动态代理对象,代理对象的方法体同上边Dao接口实现类方法。
Mapper 接口开发需要遵循以下规范:
1) Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的全限定名相同
2) Mapper接口方法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个statement的id相同
3) Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的parameterType的类型相同
4) Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
1.2.2 编写UserMapper接口

1.2.3测试代理方式
@Test
public void testProxyDao() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获得MyBatis框架生成的UserMapper接口的实现类
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.findById(1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
1.3 知识小结
MyBatis的Dao层实现的两种方式:
手动对Dao进行实现:
传统开发方式
代理方式对Dao进行实现:
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
2. 动态sql
动态sql语句概述
Mybatis 的映射文件中,前面我们的 SQL 都是比较简单的,有些时候业务逻辑复杂时,我们的 SQL是动态变化的,此时在前面的学习中我们的 SQL 就不能满足要求了。
动态sql:sql语句是在程序运行期间动态生成的
静态sql:sql语句是预先编写好的
<if>标签:
我们根据实体类的不同取值,使用不同的 SQL语句来进行查询。比如在 id如果不为空时可以根据id查询,如果username 不同空时还要加入用户名作为条件。这种情况在我们的多条件组合查询中经常会碰到。
语法:
<if test="条件表达式">
sql语句信息
</if>
<select id="findByCondition" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from User
<where>
<if test="id!=0">
and id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<where>标签
1. 如果第一个成立的条件前的关键字不是where,会自动修改成where
2. 如果第一个成立的条件前没有where关键字,会自动添加where
3. 如果没有任何条件成立,则sql后不会出现where关键字
<foreach>标签:
循环执行sql的拼接操作,例如:SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id IN (1,2,5)。
语法:
<foreach collection="list" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="user">
select * from User
<where>
<foreach collection="array" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
foreach标签的属性含义如下:
<foreach>标签用于遍历集合
属性:
collection:代表要遍历的集合元素,注意编写时不要写#{}
open:代表语句的开始部分
close:代表结束部分
item:代表遍历集合的每个元素,生成的变量名
sperator:代表分隔符
注意事项:
1. #{}中的值必须和item属性的属性值保持一致
2. 如果参数是List集合,collection属性有如下两个固定的可选属性值:
list
connection
3. 如果参数是数组,collection属性值必须为array
SQL片段抽取
Sql 中可将重复的 sql 提取出来,使用时用 include 引用即可,最终达到 sql 重用的目的
<!--抽取sql片段简化编写-->
<sql id="selectUser" select * from User</sql>
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="user">
<include refid="selectUser"></include> where id=#{id}
</select>
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="user">
<include refid="selectUser"></include>
<where>
<foreach collection="array" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
知识小结:
MyBatis映射文件配置:
<select>:查询
<insert>:插入
<update>:修改
<delete>:删除
<where>:where条件
<if>:if判断
<foreach>:循环
<sql>:sql片段抽取
3.PageHelper分页助手插件
插件的概念:所谓的插件是第三方的开发者可以自己扩展mybaits的功能
PageHelper插件的作用:用于简化分页操作
使用步骤:
1. 导入相关jar包
2. 在核心配置文件中配置插件
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<!--配置分页的方言,这样pagehelper才知道我们用的是什么类型的数据,该采用什么关键字实现分页-->
<property name="dialect" value="mysql"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
3. 在需要分页的查询操作之前指定分页的必有参数
PageHelper.startPage(2,3);
参数1:当前页码
参数2:每页查询的记录数
4. 调用查询方法
5. 在得到查询的List集合之后,通过PageInfo对象包装结果,获取分页相关信息
整体代码如下:
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
// 设置分页的必有参数
PageHelper.startPage(2,3);
// 调用实现类的方法
List<User> userList = userMapper.findAll();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
// 获取分页相关数据
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(userList);
System.out.println("总记录数:"+pageInfo.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页数:"+pageInfo.getPages());
System.out.println("每页显示的记录数:"+pageInfo.getPageSize());
System.out.println("当前页码:"+pageInfo.getPageNum());
}
知识小结
MyBatis核心配置文件常用标签:
1、properties标签:该标签可以加载外部的properties文件
2、typeAliases标签:设置类型别名
3、environments标签:数据源环境配置标签
4、typeHandlers标签:配置自定义类型处理器
5、plugins标签:配置MyBatis的插件
4.Mybatis多表查询
1.1 一对一查询
1.1.1 一对一查询的模型
用户表和订单表的关系为,一个用户有多个订单,一个订单只从属于一个用户
一对一查询的需求:查询一个订单,与此同时查询出该订单所属的用户
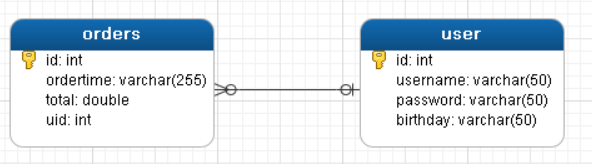
1.1.2一对一查询的语句
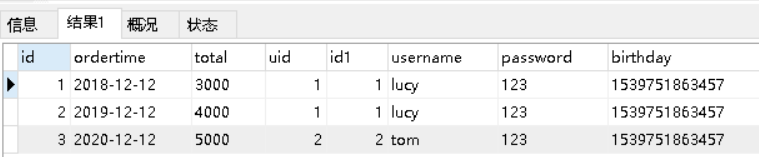
对应的sql语句:select * from orders o,user u where o.uid=u.id;
查询的结果如下:
1.1.3 创建Order和User实体
public class Order {
private int id;
private Date ordertime;
private double total;
//代表当前订单从属于哪一个客户
private User user;
}
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
}
1.1.4 创建OrderMapper接口
public interface OrderMapper {
List<Order> findAll();
}
1.1.5 配置OrderMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.OrderMapper">
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.itheima.domain.Order">
<result column="uid" property="user.id"></result>
<result column="username" property="user.username"></result>
<result column="password" property="user.password"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="user.birthday"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="orderMap">
select * from orders o,user u where o.uid=u.id
</select>
</mapper>
其中<resultMap>还可以配置如下:
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.itheima.domain.Order">
<result property="id" column="id"></result>
<result property="ordertime" column="ordertime"></result>
<result property="total" column="total"></result>
<association property="user" javaType="com.itheima.domain.User">
<result column="uid" property="id"></result>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
1.1.6 测试结果
OrderMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OrderMapper.class);
List<Order> all = mapper.findAll();
for(Order order : all){
System.out.println(order);
}
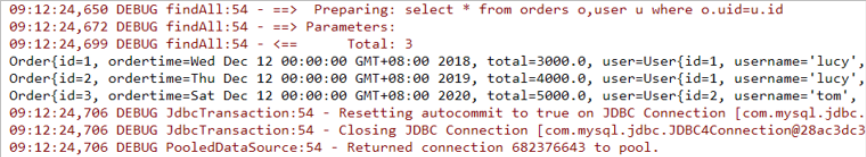
1.2 一对多查询
1.2.1 一对多查询的模型
用户表和订单表的关系为,一个用户有多个订单,一个订单只从属于一个用户
一对多查询的需求:查询一个用户,与此同时查询出该用户具有的订单
1.2.2 一对多查询的语句
对应的sql语句:select *,o.id oid from user u left join orders o on u.id=o.uid;
查询的结果如下:
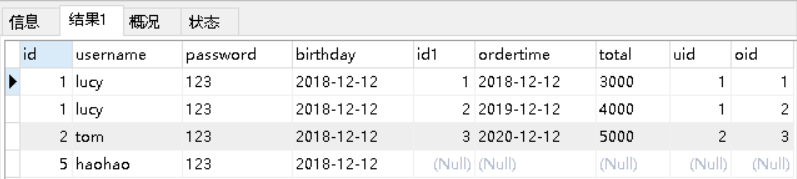
1.2.3 修改User实体
public class Order {
private int id;
private Date ordertime;
private double total;
//代表当前订单从属于哪一个客户
private User user;
}
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
//代表当前用户具备哪些订单
private List<Order> orderList;
}
1.2.4 创建UserMapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> findAll();
}
1.2.5 配置UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.itheima.domain.User">
<result column="id" property="id"></result>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result>
<collection property="orderList" ofType="com.itheima.domain.Order">
<result column="oid" property="id"></result>
<result column="ordertime" property="ordertime"></result>
<result column="total" property="total"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select *,o.id oid from user u left join orders o on u.id=o.uid
</select>
</mapper>
1.2.6 测试结果
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> all = mapper.findAll();
for(User user : all){
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
List<Order> orderList = user.getOrderList();
for(Order order : orderList){
System.out.println(order);
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
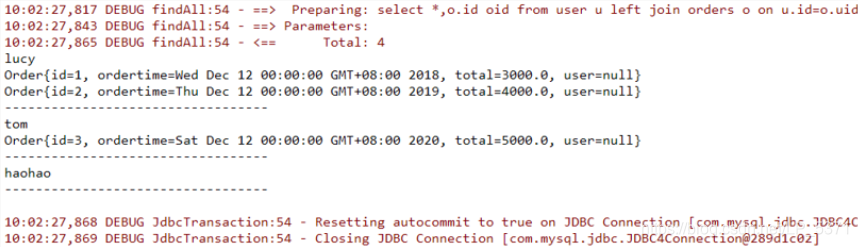
1.3 多对多查询
1.3.1 多对多查询的模型
用户表和角色表的关系为,一个用户有多个角色,一个角色被多个用户使用
多对多查询的需求:查询用户同时查询出该用户的所有角色
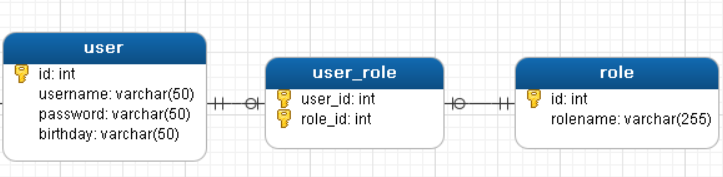
1.3.2 多对多查询的语句
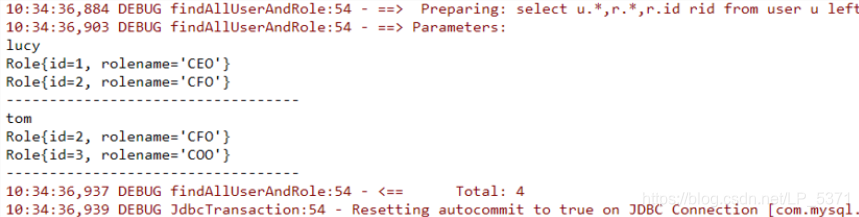
对应的sql语句:select u.,r.,r.id rid from user u left join user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join role r on ur.role_id=r.id;
查询的结果如下:
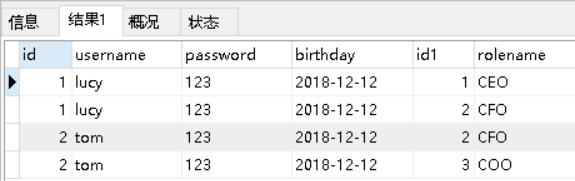
1.3.3 创建Role实体,修改User实体
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
//代表当前用户具备哪些订单
private List<Order> orderList;
//代表当前用户具备哪些角色
private List<Role> roleList;
}
public class Role {
private int id;
private String rolename;
}
1.3.4 添加UserMapper接口方法
List<User> findAllUserAndRole();
1.3.5 配置UserMapper.xml
<resultMap id="userRoleMap" type="com.itheima.domain.User">
<result column="id" property="id"></result>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result>
<collection property="roleList" ofType="com.itheima.domain.Role">
<result column="rid" property="id"></result>
<result column="rolename" property="rolename"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllUserAndRole" resultMap="userRoleMap">
select u.*,r.*,r.id rid from user u left join user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join role r on ur.role_id=r.id
</select>
1.3.6 测试结果
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> all = mapper.findAllUserAndRole();
for(User user : all){
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
List<Role> roleList = user.getRoleList();
for(Role role : roleList){
System.out.println(role);
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
1.4多表操作小结
多表模型分类:一对一、一对多、多对多。
<resultMap>:配置字段和对象属性的映射关系标签。
id 属性:唯一标识
type 属性:实体对象类型
<id>:配置主键映射关系标签。
<result>:配置非主键映射关系标签。
column 属性:表中字段名称
property 属性: 实体对象变量名称
<association>:配置被包含对象的映射关系标签。
property 属性:被包含对象的变量名
javaType 属性:被包含对象的数据类型
<collection>:配置被包含集合对象的映射关系标签。
property 属性:被包含集合对象的变量名
ofType 属性:集合中保存的对象数据类型




 本文详细介绍了Mybatis的Dao层实现,包括传统开发方式和代理方式,并探讨了动态SQL的使用,如<if>、<where>、<foreach>标签以及SQL片段抽取。此外,还讲解了一对一、一对多和多对多的多表查询实现,通过<resultMap>配置映射关系。
本文详细介绍了Mybatis的Dao层实现,包括传统开发方式和代理方式,并探讨了动态SQL的使用,如<if>、<where>、<foreach>标签以及SQL片段抽取。此外,还讲解了一对一、一对多和多对多的多表查询实现,通过<resultMap>配置映射关系。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








