目录
修改low值与缩点 ----------------->见这里
简介




流程
//有向图强连通分支的Tarjan算法
void tarjan()
{
dfn[u]=low[u]=++index;
stack.push(u);
for each(u,v) in E{
if(v is not visted){
tarjan(v);
low[n]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}
else if(v in stack){
low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
if(dfn[u]==low[u])//u是一个强连通分量的根
{
repeat
v=stack.pop;
print v;
until(u==v)
}//退栈,把整个强连通分量都弹出来
}//复杂度是O(E+V)的
模拟过程
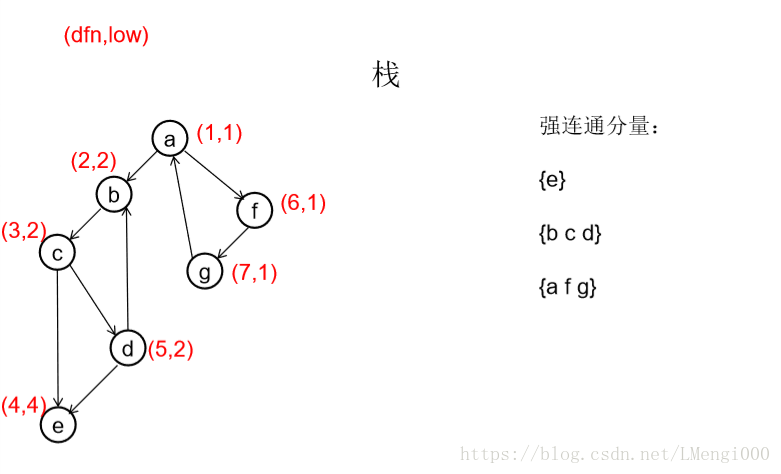
修改low值与缩点 ----------------->见这里
POJ 2186 Popular Cows
Description
Every cow's dream is to become the most popular cow in the herd. In a herd of N (1 <= N <= 10,000) cows, you are given up to M (1 <= M <= 50,000) ordered pairs of the form (A, B) that tell you that cow A thinks that cow B is popular. Since popularity is transitive, if A thinks B is popular and B thinks C is popular, then A will also think that C is
popular, even if this is not explicitly specified by an ordered pair in the input. Your task is to compute the number of cows that are considered popular by every other cow.
Input
* Line 1: Two space-separated integers, N and M
* Lines 2..1+M: Two space-separated numbers A and B, meaning that A thinks B is popular.
Output
* Line 1: A single integer that is the number of cows who are considered popular by every other cow.
Sample Input
3 3
1 2
2 1
2 3
Sample Output
1
Hint
Cow 3 is the only cow of high popularity.
Source
缩点就是在求出图的所有的强连通分量之后,把强连通分量都看成一个点,这样形成的一个先用tarjan求出每个强连通分量,再缩点,统计每个点的出度,如果有且只有1个出度为0的点,就输出这个点包含的节点数,否则输出0.
证明:
1.如果有强连通分量被孤立(即和其他强连通分量无边相连),那么答案一定是0,此时由于缩点后是一个DAG图,出度为0的点的个数一定大于1.
2.如果没有点被孤立,当出度为0的点多于1个时,由DAG图的性质可得,一定不存在一个点能从其他所有点到达。只有当出度为0的点的个数等于1时,这个出度为0的点才能被其他所有点到达。
还是应多做题目,加深理解过程。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=11000;
vector<int>mp[maxn];
int vis[maxn];
int dfn[maxn],low[maxn],S[maxn],color[maxn],sum[maxn],out0[maxn];
int n,m,cnt,tt,sig;
void Tarjan(int u)
{
vis[u]=1;
dfn[u]=low[u]=++cnt;
S[++tt]=u;
for(int i=0;i<mp[u].size();i++)
{
int v=mp[u][i];
if(vis[v]==0)
{
Tarjan(v);
}
if(vis[v]!=0)
{
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}
}
if(dfn[u]==low[u])
{
int len=tt;
sig++;
do
{
color[S[tt]]=sig;
}while(S[tt--]!=u);
sum[sig]=len-tt;
}
}
void Solve()
{
tt=-1,sig=0,cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(vis[i]==0)
{
Tarjan(i);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<mp[i].size();j++)
{
int v=mp[i][j];
if(color[i]!=color[v])
{
out0[color[i]]++;
}
}
}
int p=0;
for(int i=0;i<=sig;i++)
{
if(!out0[i])
{
if(p>0)
{
puts("0");
return ;
}
p=sum[i];
}
}
printf("%d\n",p);
}
void init()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(dfn,0,sizeof(dfn));
memset(low,0,sizeof(low));
memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp));
memset(out0,0,sizeof(out0));
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
init();
int u,v;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
mp[u].push_back(v);
}
Solve();
return 0;
}#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
int n,m;
int dfn[maxn],low[maxn],f[maxn],c[maxn],out0[maxn],sum[maxn];
int l=0,cnt=0,start=0;
vector<int>g[maxn];
void tarjan(int u)
{
dfn[u]=low[u]=++start;
c[++l]=u;
for(int i=0;i<g[u].size();i++)
{
int v=g[u][i];
if(!dfn[v])
{
tarjan(v);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}else if(!f[v])
{
low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
if(low[u]==dfn[u])
{
int len=l;
cnt++;
while(c[l]!=u)
{
f[c[l--]]=cnt;
}
f[c[l--]]=cnt;
sum[cnt]=len-l;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
g[x].push_back(y);
}
memset(dfn,0,sizeof(dfn));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!dfn[i])
tarjan(i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<g[i].size();j++)
{
int v=g[i][j];
if(f[i]!=f[v])
out0[f[i]]++;
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
if(!out0[i])
{
if(ans>0)
{
printf("0\n");
return 0;
}
ans=sum[i];
}
}
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}








 博客介绍了有向图强连通分支的Tarjan算法,给出了算法代码,复杂度为O(E+V)。还通过POJ 2186 Popular Cows问题展示应用,介绍缩点方法,即求出强连通分量后将其看成点,统计出度判断结果,强调多做题加深理解。
博客介绍了有向图强连通分支的Tarjan算法,给出了算法代码,复杂度为O(E+V)。还通过POJ 2186 Popular Cows问题展示应用,介绍缩点方法,即求出强连通分量后将其看成点,统计出度判断结果,强调多做题加深理解。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








