目录
回顾:
上篇学习了
二叉树的核心操作
把所有的节点,按一定的次序,全部访问(针对这个数据,进行各种操作如:打印,修改,判定,计算......)一遍,访问过程中“不重不漏”。二叉树的4种遍历方式:先序,中序,后序,层序
前三者都是基于递归实现的:为了方便理解给出了其各的递归展开图,本片也会借助图像为大家展现代码执行过程,方便理解方法实现。
二叉树的基本操作 :
| 1. int size ( Node root ) ; | 获取树中的节点 |
| 2. int getLeafNode( Node root ); | 获取叶子节点的个数 |
| 3. int getKLevelNodeCount ( Node root , int k); | 获取第K层节点的个数 |
| 4. int getHeight ( Node root ); | 获取树的深度 |
| 5. Node find ( Node root, int val ); | 检测值为 val 的元素是否存在 |
| 6. boolean isCompleteTree ( Node root ); | 判断完全二叉树 |
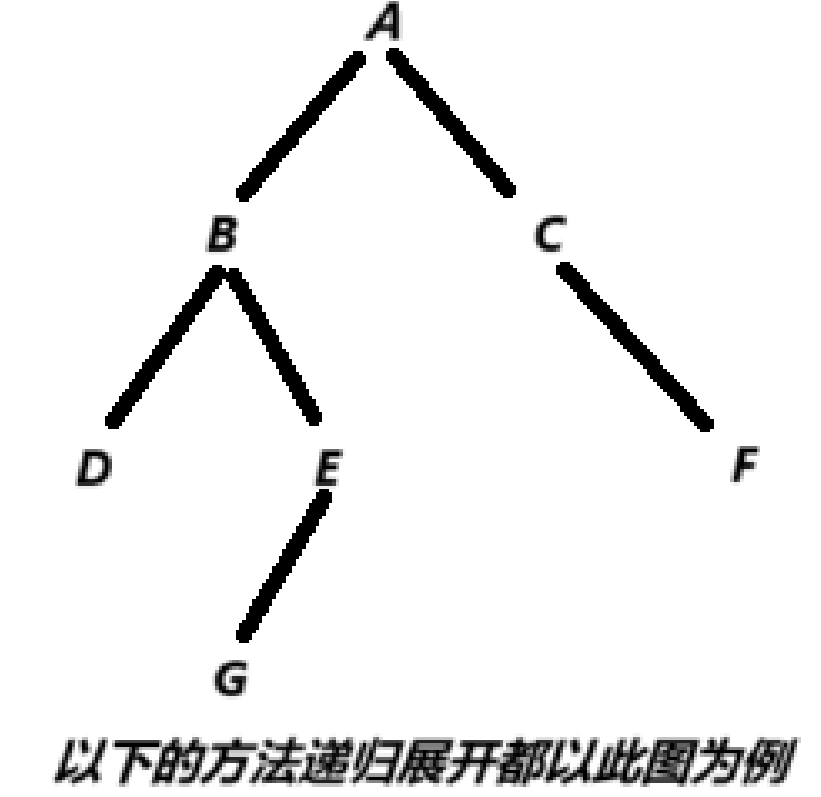
1.获取树中的节点
一棵树的个数:
根的个数(非空即为1)+ 左子树的节点个数 + 右子树的个数
❌写法
// 获取节点个数
public static int size (Node root){
// 遍历 先、中、后、层都可以
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int size = 0;
size++;
size(root.left);
size(root.right);
return size;
}int size = 0; 局部变量,每次递归时,在对应的函数栈帧中都会有一个全新的size 变量;
解决方案 1. 将size 改为成员变量 public static int size = 0;
2. 递归过程中,通过返回值把当前子树的递归结果返回到上层方法,上层方法再 进行累加
✅写法(2)
public static int size (Node root){
// 遍历 先、中、后、层都可以
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int rootSize = 1;
int leftSize = size(root.left);
int rightSize = size(root.right);
return rootSize + leftSize + rightSize;
}
// 简化
public static int size (Node root){
// 遍历 先、中、后、层都可以
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return rootSize + size(root.left) + size(root.right);
}递归展开
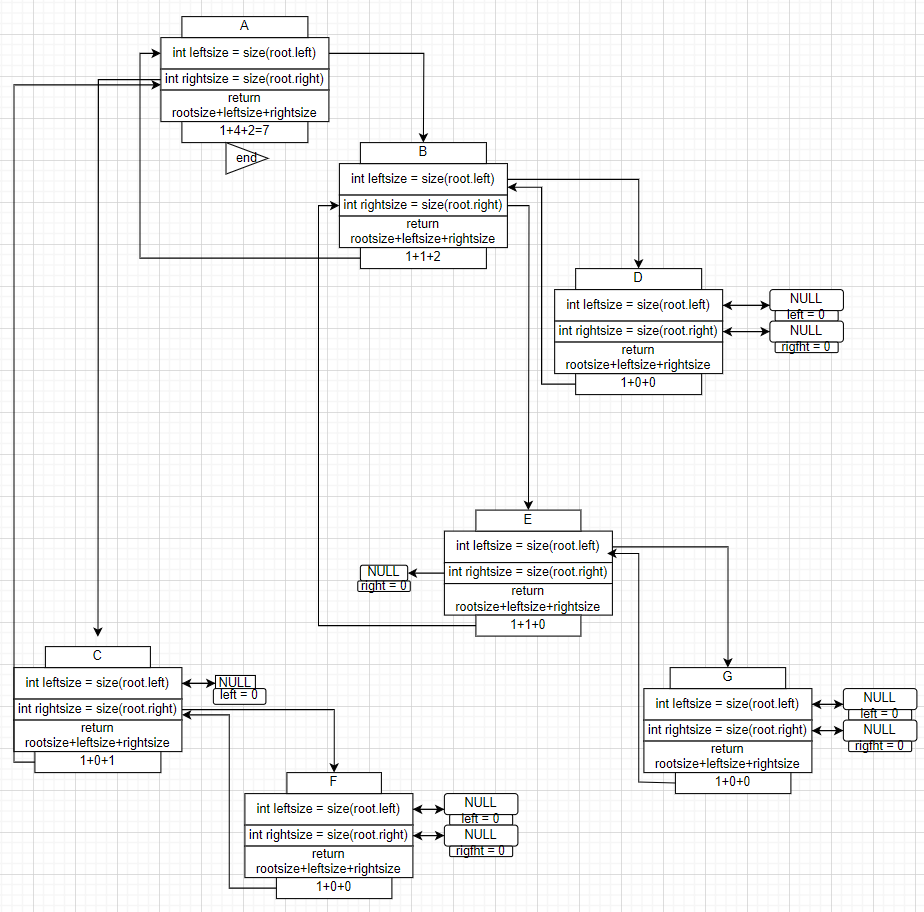
2.获取叶子节点的个数
叶子节点个数 = 左子树的叶子节点个数 + 右子树的叶子节点个数
✅写法
// 获取叶子节点个数
public static int getLeafSize(Node root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
// 判定当前根节点是否是叶子
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return 1;
}
// 如果当前根节点不是叶子,分别求左右子树的叶子节点个数,再作和
return getLeafSize(root.left) + getLeafSize(root.right);
}递归展开
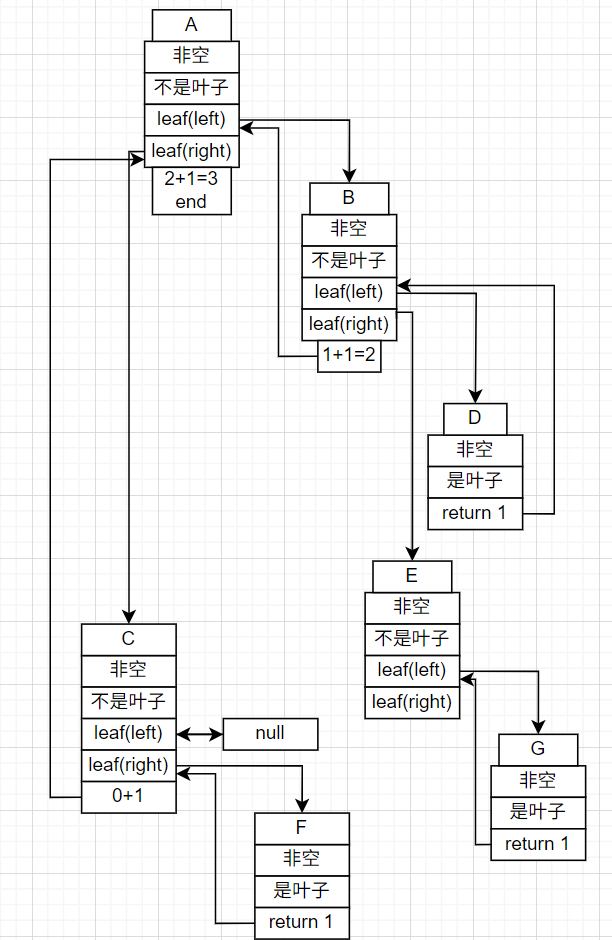
3. 获取第K层节点的个数
在二叉树的性质中:我们知道 k层树的节点个数最多有 2^(k-1)
此处要注意不能将获取第K层节点的个数和其混为一谈
思路
若 k < 1 非法
若 k = 1 求第一层节点个数 若是非空的树的,节点个数就是1若 k > 1 求第k层节点个数 ——> 求左子树k-1层的节点个数 + 求右子树k-1层的节点个数
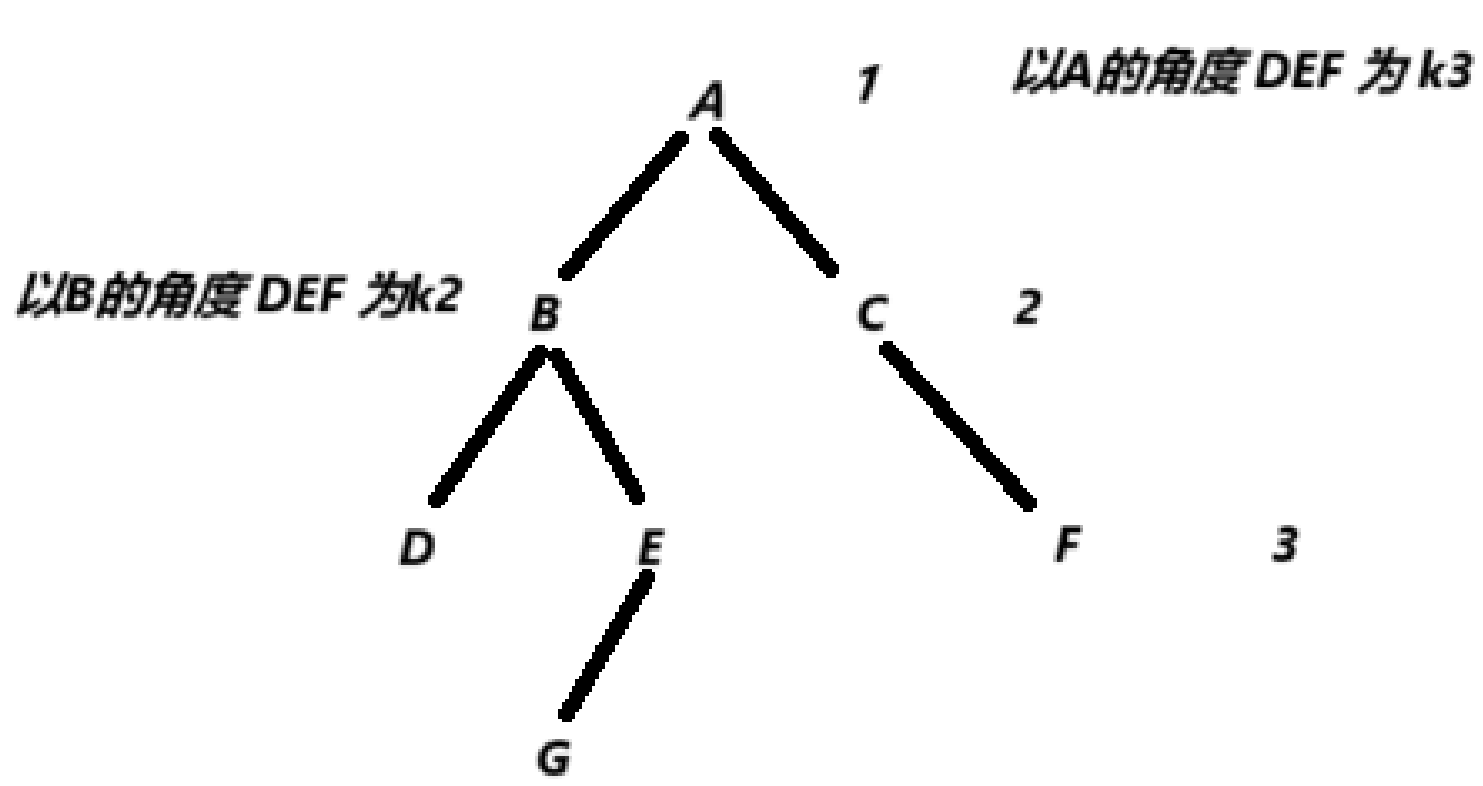
针对这个树 求k为3的节点个数
此问题等价于 求 B 这个子树的k 为2的节点个数 + C这个子树的k为2的节点个数
以B的视角:求 B 这个子树的k 为2的节点个数 = 求 D 这个子树的k 为1的节点个数 + E这个子树的k为1的节点个数
✅写法
// 获取第k层节点个数
public static int getKLevelNodeCount(Node root,int k){
if(root == null || k < 1){
return 0;
}
if(k == 1){
// 对于非空的树来说 k==1 表示根节点
return 1;
}
return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k-1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k-1);
}递归展开
4. 获取树的深度
根节点出发到任意节点,路径的最大长度
思路
max(左子树的高度 , 右子树的高度) + 1
✅写法
public static int getHeight(Node root){
// 当前树的高度 = max( 左子树的高度 , 右子树的高度 ) + 1
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight) + 1;
// return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
// if(leftHeight > rightHeight){
// return leftHeight + 1;
// }else{
// return rightHeight + 1;
// }
}后面两种写法也可以,但三目运算符 要注意运算优先级
递归展开
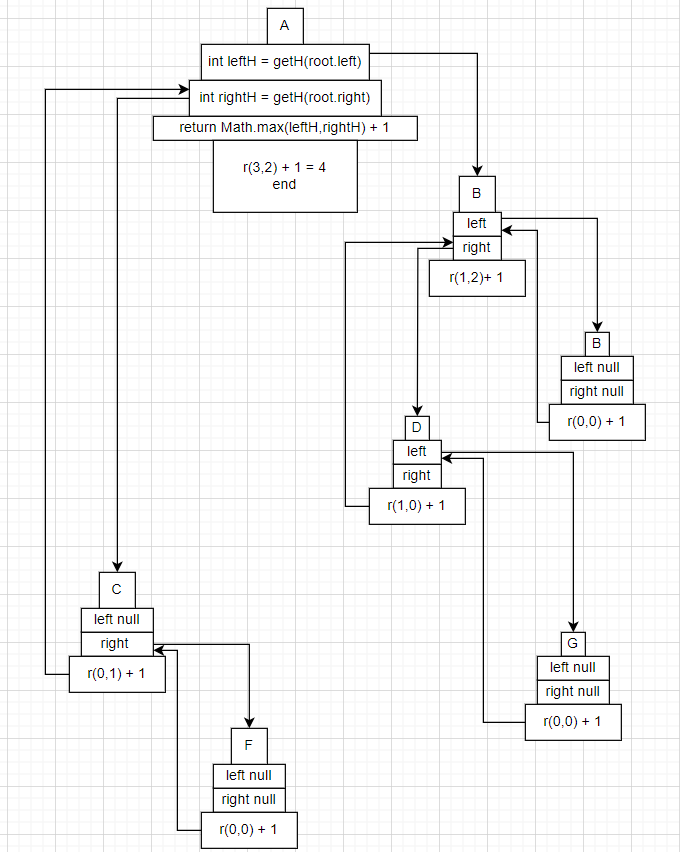
5. 检测值为 val 的元素是否存在
思路
判断跟节点是不是
是,返回根节点
不是,继续递归左子树找
如果也没找到
递归右子树找
✅写法
// 查找val是否存在
public static Node find(Node root,String val){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.val.equals(val)){
return root;
}
Node leftRes = find(root.left,val);
if(leftRes != null){
//找到了直接返回上述结果
return leftRes;
}
//没找到,继续在右子树中找
return find(root.right,val);
}递归展开
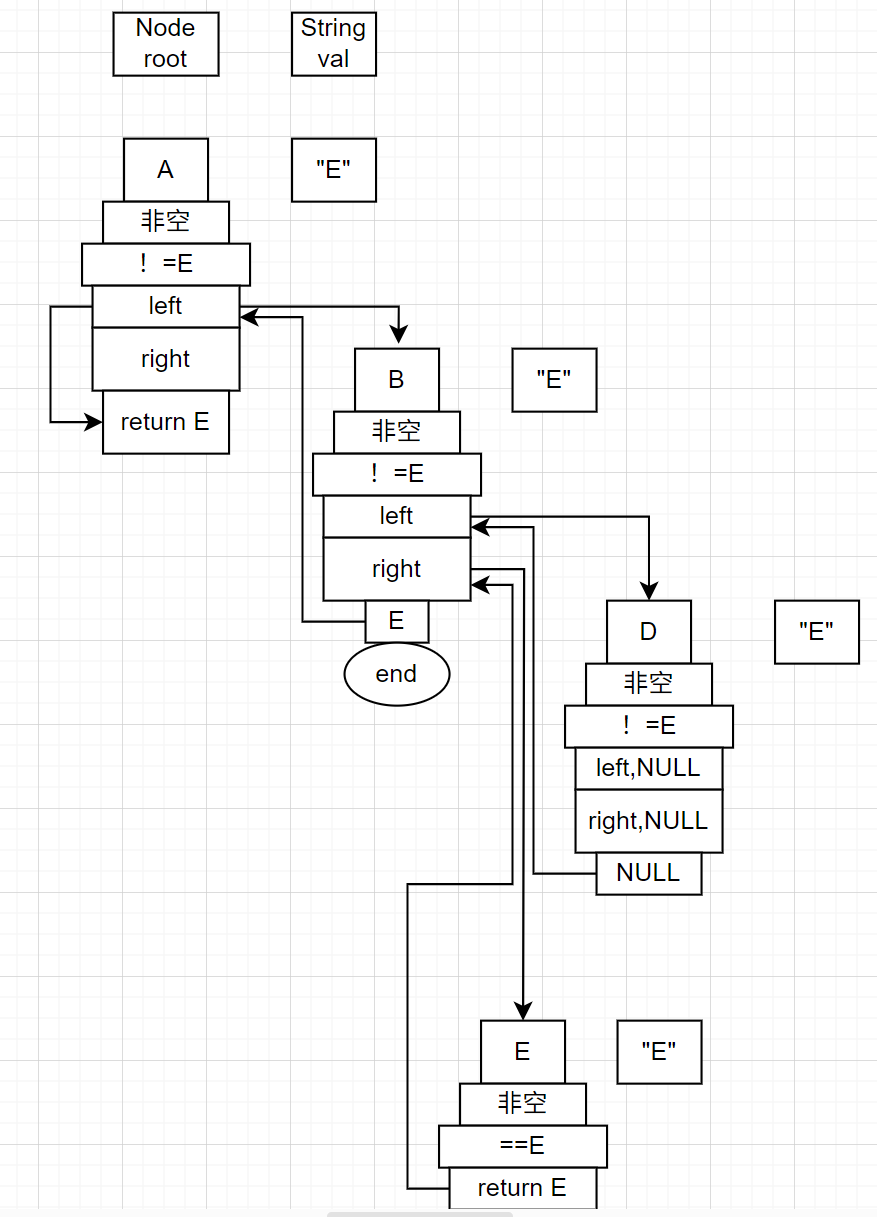
6.判断完全二叉树
思路
1.要求每个节点必须有两个子树
a ) 没有子树 进入二阶段
b)只有左子树 进入二阶段
c ) 只有右子树 false
2.要求每个节点必须没有子树
public static boolean isComplete(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return true; // 空树是完全二叉树
}
boolean isFirstStage = true;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node current = queue.poll();
if (isFirstStage) {
if (current.left == null && current.right == null) {
isFirstStage = false; // 进入第二阶段
} else if (current.left != null && current.right == null) {
isFirstStage = false; // 只有左子树,进入第二阶段
queue.offer(current.left); // 别忘了处理左子树
} else if (current.left == null && current.right != null) {
return false; // 只有右子树,违反完全二叉树规则
} else {
// 左右子树都有,继续正常遍历
queue.offer(current.left);
queue.offer(current.right);
}
} else {
// 第二阶段:所有节点必须无子节点
if (current.left != null || current.right != null) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true; // 遍历完所有节点都符合条件
}整条街都是恋爱的人 我独自走在暖风的夜
——寂寞的季节 DT
🌟💗🦀




















 1108
1108

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








