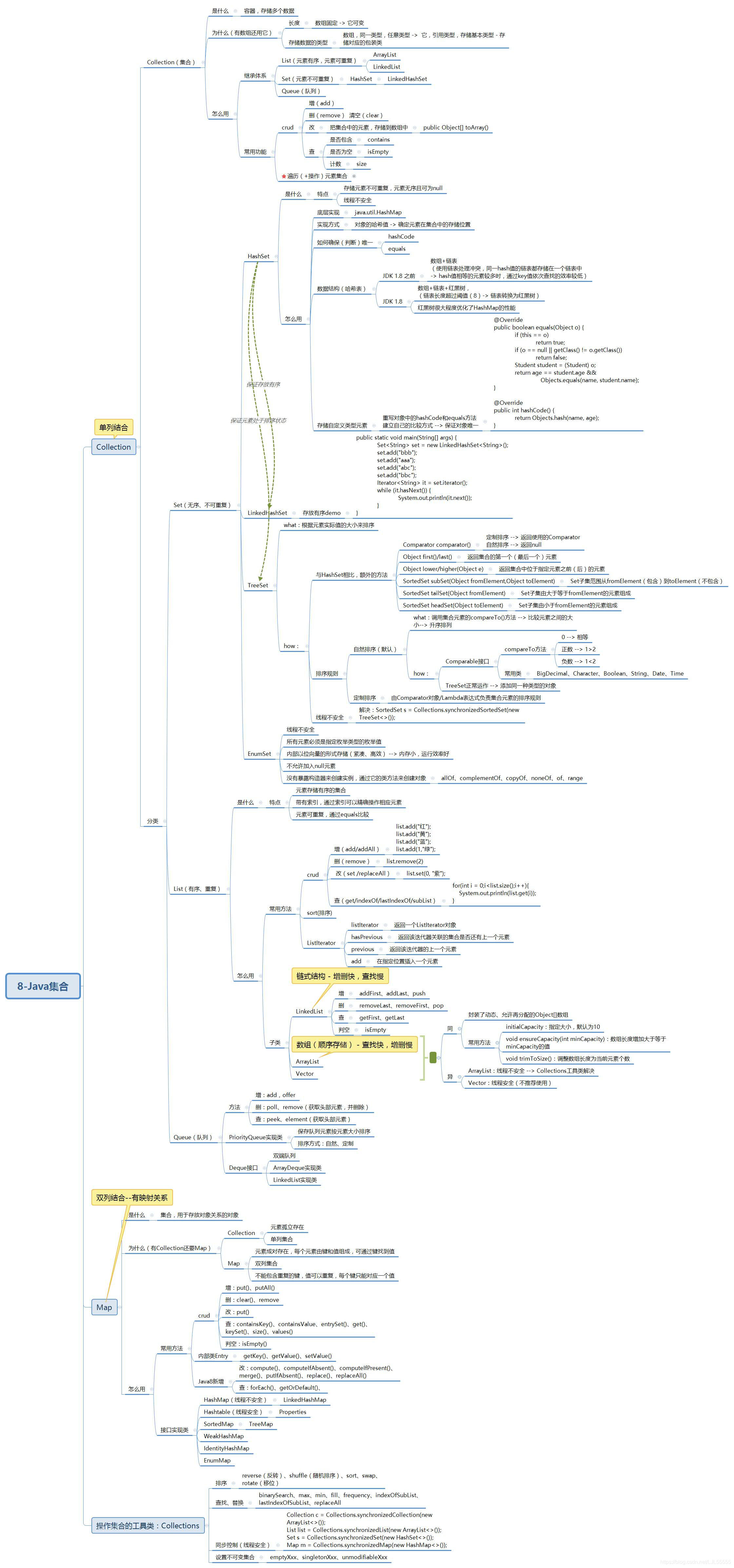
遍历(+操作)元素集合
1.Lambda表达式
// 创建集合
Collection<String> coll = new HashSet<>();
coll.add("C");
coll.add("C++");
coll.add("Java");
coll.add("Python");
(1)遍历集合
coll.forEach(obj -> System.out.println(obj));
(2)遍历Iterator
// 获取coll集合对应的迭代器
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
it.forEachRemaining(obj-> System.out.println(obj));
2.Java8增强的Iterator
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String str = it.next();
System.out.println(str);
if (str.equals("Java")) {
// 从集合中删除上一次next()返回的元素
it.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(coll);
3.foreach
for(String str:coll){
System.out.println(str);
}
4.Java8新增的Predicate
// 计算集合中字符串长度大于3的数量
System.out.println(calAll(coll, ele ->((String)ele).length()>3));
// 计算集合中包含“C”子串的数量
System.out.println(calAll(coll, ele ->((String)ele).contains("C")));
public static int calAll(Collection books, Predicate p) {
int total = 0;
for (Object obj : books) {
if (p.test(obj)) {
total++;
}
}
return total;
}
5.Java8新增的Stream(可对集合元素进行批量操作)
// 计算集合中字符串长度大于3的数量
System.out.println(coll.stream()
.filter(ele -> ele.length() > 3)
.count());
// 计算集合中包含“C”子串的数量
System.out.println(coll.stream()
.filter(ele -> ele.contains("C"))
.count());

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








