论文名称:Chain-of-Tools: Utilizing Massive Unseen Tools in the CoT Reasoning of Frozen Language Models
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.16779
机构:苏州大学
Github代码链接:https://github.com/fairyshine/Chain-of-Tools
背景
论文内容的介绍看之前的博客即可,本篇文章就是记录一下自己对其项目代码的解读,非教学用。
仓库初览
顶层结构
当前版本时间是20250517,看到作者也在README里面加了Tip:

项目整体分为四个部分:
-
README.md:项目说明文档,包含训练、评测流程和数据集链接。
-
requirements.txt:依赖库,主要以深度学习、NLP、数据处理为主(如transformers、torch、huggingface等)。
-
assets/:存放图片资源(如项目架构图)。
-
data/:存放各类数据集和中间数据。
-
config/:存放各类训练、测试的配置文件(yaml格式)。
-
src/:核心代码目录。
核心代码(src/)
① 主体功能模块
-
main.py:主入口,可能用于统一调度训练/推理/评测流程。
-
train.py:训练主程序,负责模型训练流程。
-
inference.py:推理主程序,负责模型的推理/预测。
-
evaluation.py、prompt_evaluation.py:评测相关代码。
-
model.py:模型结构定义,核心神经网络实现。
-
corpus.py:数据集加载与处理。
-
prompt.py:提示词(prompt)相关处理。
② 工具与脚本
-
script/:包含各类训练、测试脚本,按任务(如GSM8K、FuncQA)和角色(Judge、Retriever)细分,便于快速启动不同实验。
-
tool_hub/:如arithmetic.py,实现具体的工具函数,可能用于工具链推理。
-
dataset_processing/:数据预处理脚本,针对不同数据集格式转换、清洗等。
③ 其他
-
discard/:废弃或实验性代码,如自定义Llama模型实现。
-
WillMindS/:通用NLP/深度学习工具库,包含模型、损失函数、评测、工具函数等,支持多种LLM(如LLaMA、ChatGLM、Baichuan等)。
典型工作流
以GSM8K-XL数据集的训练与评测为例。
Tool Judge 训练
python ./src/script/train_gsm8k_judge.py --config_file config/train_judge.yaml
train_gsm8k_judge.py 的主体内容为:
from WillMindS.config import Config
from WillMindS.log import Log_Init
from model import LLM_with_tools
from train import tool_judge_train, tool_retriever_train
from inference import *
def main(config, logger):
model = LLM_with_tools(config)
model.tokenizer.pad_token = model.tokenizer.eos_token # LLaMA2 Mistral
dataset_dir_dict = {"gsm8k_xl":config.dataset_dir["gsm8k_xl"]}
# * 加载工具库
model.load_tool_database(dataset_dir_dict)
model.calculate_database([dataset_name for dataset_name in dataset_dir_dict])
# * 训练judge
tool_judge_train(config, logger, model, dataset_dir_dict, mode="train+test")
if __name__ == "__main__":
config = Config()
logger = Log_Init(config)
config.log_print_config(logger)
main(config, logger)
-
主流程:配置加载 → 模型初始化 → 工具库加载/向量化 → 工具调用判别器训练/评估。
-
模型初始化:model.py里面的LLM_with_tools 是一个集成了基础大模型(如 LLaMA2/Mistral)和工具判别/检索能力的模型类,继承自torch.nn.Module。
-
工具库加载与向量计算:
-
load_tool_database:加载每个数据集下的工具信息(如工具描述、参数等),并构建工具库。
-
calculate_database:对每个工具的描述文本进行编码,得到工具的向量表示,后续用于工具选择和判别。
-
-
训练工具调用判别器:
-
训练“工具调用判别器”模块(model.tool_judge),判断在给定输入下是否需要调用工具。
-
包含训练和验证两个阶段,训练时优化判别器参数,验证时评估判别准确率、F1等指标。
-
Tool Retriever 训练
python ./src/script/train_gsm8k_retriever.py --config_file config/train_gsm8k_retriever.yaml
train_gsm8k_retriever.py 的主体内容为:
from WillMindS.config import Config
from WillMindS.log import Log_Init
from model import LLM_with_tools
from train import tool_judge_train, tool_retriever_train
from inference import *
def main(config, logger):
model = LLM_with_tools(config)
model.tokenizer.pad_token = model.tokenizer.eos_token # LLaMA2 Mistral
dataset_dir_dict = {"gsm8k_xl":config.dataset_dir["gsm8k_xl"]}
# * 加载工具库
model.load_tool_database(dataset_dir_dict)
model.calculate_database([dataset_name for dataset_name in dataset_dir_dict])
# * 训练retriever
tool_retriever_train(config, logger, model, dataset_dir_dict, mode="train+test")
if __name__ == "__main__":
config = Config()
logger = Log_Init(config)
config.log_print_config(logger)
main(config, logger)
-
主流程:配置 → 日志 → 模型初始化 → 工具库加载 → 工具向量计算 → 工具检索器训练与评测。
-
模型初始化与工具库加载与向量计算不变,不赘述。
-
训练工具检索器:
-
优化器与数据准备:构建优化器,准备数据集(读取 train.jsonl)。
-
训练循环:对每个 batch,分别编码 query 和 tool,抽取向量;计算 query/tool 向量后,归一化,做相似度(内积或归一化后内积);用 NLL Loss 训练,使得正确工具得分最高;定期记录 loss 和准确率。
-
评测与保存:在 dev 集合上评测,记录 top - 1/top - k 准确率;每隔若干 epoch 保存模型参数。
-
效果评测
python ./src/script/test_gsm8k.py --config_file config/test.yaml
test_gsm8k.py的主体内容为:
from WillMindS.config import Config
from WillMindS.log import Log_Init
from model import LLM_with_tools
from train import tool_judge_train, tool_retriever_train
from inference import *
def main(config, logger):
model = LLM_with_tools(config)
model.tokenizer.pad_token = model.tokenizer.eos_token # LLaMA2 Mistral
# * 加载模型参数
if config.load_toolcalling_checkpoint:
model.sl_judge(config.judge_checkpoint_dir, "load")
model.sl_retriever(config.retriever_checkpoint_dir, "load")
dataset_dir_dict = {"gsm8k_xl":config.dataset_dir["gsm8k_xl"]}
# * 加载工具库
model.load_tool_database(dataset_dir_dict)
model.calculate_database([dataset_name for dataset_name in dataset_dir_dict])
# * 评测
infer_with_tools(config, logger, model, "gsm8k_xl", "./data/gsm8k_xl/test.jsonl")
def multiple_run(config, logger):
model = LLM_with_tools(config)
model.tokenizer.pad_token = model.tokenizer.eos_token # LLaMA2专供
model.sl_judge("./output/gsm8k_xl_judge_checkpoint_dir/epoch_3/", "load")
checkpoint_list = ["./output/gsm8k_xl_retriever_checkpoint_dir/epoch_{}/".format(epoch) for epoch in range(3,11)]
for checkpoint in checkpoint_list:
logger.info(checkpoint)
model.sl_retriever(checkpoint, "load")
model.load_tool_database(config.dataset_dir)
model.calculate_database(["gsm8k_xl"])
if config.tensor_weighting and config.tensor_filtering:
model.get_tensor_filtering_index()
infer_with_tools(config, logger, model, "gsm8k_xl", "./data/gsm8k_xl/test.jsonl")
if __name__ == "__main__":
config = Config()
logger = Log_Init(config)
config.log_print_config(logger)
# main(config, logger)
multiple_run(config, logger)
-
主流程:配置加载 → 模型初始化 → 加载权重 → 工具库加载与预处理 → 推理评测
-
模型初始化与工具库加载与向量计算不变,不赘述,但增加了对 judge(工具选择器)和 retriever(工具召回器)的加载选项。
-
推理评测:使用infer_with_tools函数进行推理并评测,multiple_run是多轮评测的逻辑。
论文3.1节Tool Judge代码逻辑
工具使用判别器
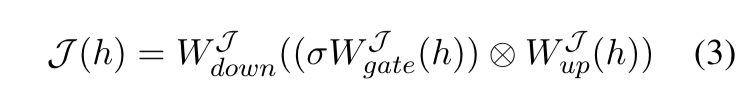
# 在src/model.py里面
class MLPLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, intermediate_size, output_size):
super().__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.input_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False)
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.input_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False)
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.output_size, bias=False)
self.act_fn = ACT2FN["silu"]
def forward(self, x):
down_proj = self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x))
return down_proj
其中:

判别器的调用
-
输入 hidden_states,输出经过sigmoid的概率。
-
超过0.5则判定需要调用工具。
# 在src/model.py里面
class LLM_with_tools(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
# ...
# 判别是否调用工具
self.tool_judge = MLPLayer(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, 1).to("cuda:0") #.to("cuda:{}".format(torch.cuda.device_count()-1))
def tool_judging(self, hidden_states):
probs = self.tool_judge(hidden_states.to(next(self.tool_judge.parameters()).device))
if list(probs.size()) == [1]:
single_probs = F.sigmoid(probs)[0]
if single_probs > 0.5:
return True, probs
else:
return False, probs
else:
probs = torch.squeeze(probs, dim=-1)
return probs
判别器的训练

-
用基础模型抽取hidden state,送入 tool_judging 得到概率。
-
用 F.binary_cross_entropy 计算损失,对应论文的 BCE 损失。
def tool_judge_train(config, logger, model, dataset_dir_dict, mode="train+test"):
# ...
for step, data in track(enumerate(train_dataloader),description='Training epoch {} ...'.format(epoch)):
all_steps = len(train_dataloader)
for key,_ in data.items():
data[key] = data[key].cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
foundation_output = model.foundation_model(data["input_ids"], output_hidden_states=True)
judge_logits = model.tool_judging(foundation_output.hidden_states[-1][0])
judge_logits = torch.sigmoid(judge_logits)
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(judge_logits, data["judge_labels"][0].float())
loss.backward()
# ...
论文3.2节Tool Retriever代码逻辑
查询向量构建
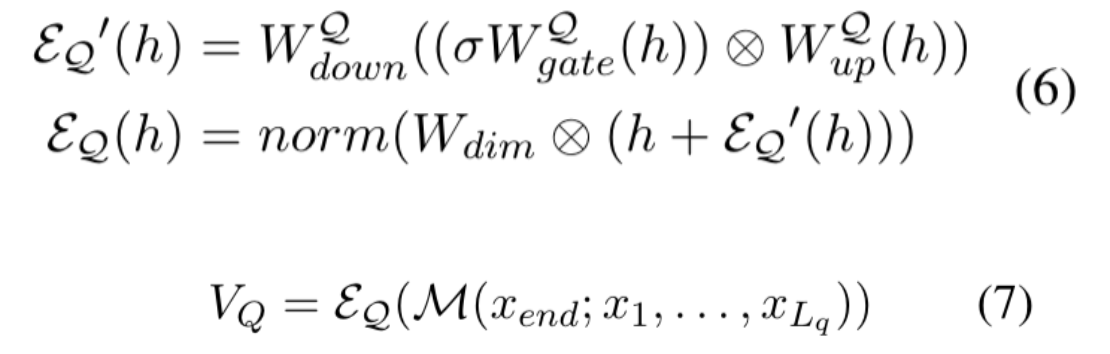
-
MLPLayer 实现了公式6的结构(门控、上投影、下投影、残差)
-
MLPLayer 用于 self.retriever_query,在 calculate_query_vector 中被调用。
-
self.retriever_query 是 MLPLayer,只有 self.config.cal_seq == False 时使用。如果 self.config.cal_seq == True,则用 MambaBlock 代替 MLPLayer,结构更复杂,但本质也是对 hidden state 做变换再加残差。
-
hidden_states 来源于 LLM最后token的hidden state。
# 在src/model.py里面
class MLPLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, intermediate_size, output_size):
super().__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.input_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False)
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.input_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False)
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.output_size, bias=False)
self.act_fn = ACT2FN["silu"]
def forward(self, x):
down_proj = self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x))
return down_proj
class LLM_with_tools(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
# ...
def calculate_query_vector(self, hidden_states, calculated_tensor=None):
if self.config.cal_seq:
query_vector = calculated_tensor + hidden_states.to(calculated_tensor.device)
else:
raw_dim = hidden_states.dim()
if raw_dim == 1:
hidden_states = hidden_states.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
elif raw_dim == 2:
hidden_states = hidden_states.unsqueeze(0)
else:
assert raw_dim == 3
query_vector = self.retriever_query(hidden_states.to(next(self.retriever_query.parameters()).device))
query_vector += hidden_states.to(query_vector.device)
query_vector = query_vector.squeeze()
if raw_dim == 2 and query_vector.dim() == 1:
query_vector = query_vector.unsqueeze(0)
if self.config.tensor_weighting:
query_vector = self.w_tensor(query_vector.to(self.w_tensor.weight.device))
return query_vector
工具向量构建
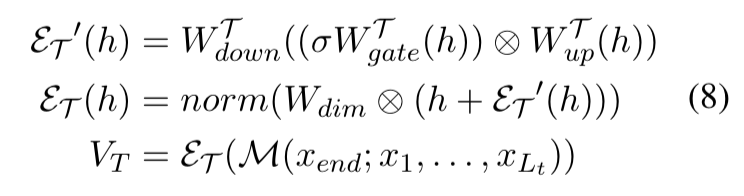
-
self.retriever_tool_selection 是 MLPLayer 或 MambaBlock,和 query vector分支一致。
-
只有 self.config.cal_seq == False 时用 MLPLayer,否则用 MambaBlock。
-
工具描述文本经过 LLM 得到 hidden state,再送入 calculate_tool_vector
# 在src/model.py里面
class LLM_with_tools(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
# ...
def calculate_tool_vector(self, hidden_states, calculated_tensor=None):
if self.config.cal_seq:
tool_vector = calculated_tensor + hidden_states.to(calculated_tensor.device)
else:
raw_dim = hidden_states.dim()
if raw_dim == 1:
hidden_states = hidden_states.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
elif raw_dim == 2:
hidden_states = hidden_states.unsqueeze(0)
else:
assert raw_dim == 3
tool_vector = self.retriever_tool_selection(hidden_states.to(next(self.retriever_tool_selection.parameters()).device))
tool_vector += hidden_states.to(tool_vector.device)
tool_vector = tool_vector.squeeze()
if raw_dim == 2 and tool_vector.dim() == 1:
tool_vector = tool_vector.unsqueeze(0)
if self.config.tensor_weighting:
tool_vector = self.w_tensor(tool_vector.to(self.w_tensor.weight.device))
return tool_vector
相似度计算与检索
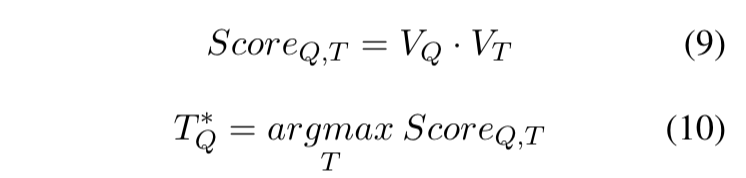
① 相似度分数计算(公式9)
- 在训练和推理时,query/tool向量归一化后会去做点积。
# 在src/train.py里面
def tool_retriever_train(config, logger, model, dataset_dir_dict, mode="train+test"):
# ...
query_vectors_out = query_vectors_out.to(tool_vectors_out.device)
if not config.similarity_norm:
# 原算法
scores = torch.matmul(query_vectors_out, torch.transpose(tool_vectors_out, 0, 1))
else:
# 考虑模长
q_norm_list = [torch.norm(query_vecotr) for query_vecotr in query_vectors_out]
t_norm_list = [torch.norm(tool_vector) for tool_vector in tool_vectors_out]
norm_matrix = torch.tensor([[((q_norm+t_norm)/2)**2 for t_norm in t_norm_list] for q_norm in q_norm_list]).to(tool_vectors_out.device)
scores = torch.matmul(query_vectors_out, torch.transpose(tool_vectors_out, 0, 1)).div(norm_matrix)
② 取得分最高的工具(公式10)
- 取最大分数的索引,即
tool_idx = probs.index(max(probs))的逻辑。
# 在src/model.py里面
class LLM_with_tools(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
# ...
def tool_selection(self, dataset_name, hidden_states):
# ...
# 限制工具检索的搜索范围
if self.tool_range > 0:
probs = probs[:self.tool_range]
tool_idx = probs.index(max(probs))
top_k = min(5, len(probs))
_ , top_k_indices = torch.topk(torch.tensor(probs), top_k)
return tool_name_list[tool_idx], probs[tool_idx], [tool_name_list[i] for i in top_k_indices]
检索器的训练
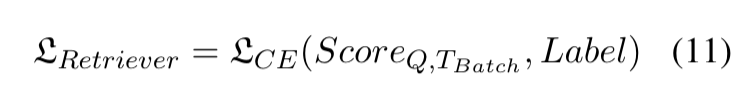
- 这里 scores 是每个 query 对 batch 内所有 tool 的分数,data[“gold_labels”] 是正确工具的索引。
# 在src/train.py里面
def tool_retriever_train(config, logger, model, dataset_dir_dict, mode="train+test"):
# ...
softmax_scores = F.log_softmax(scores, dim=1)
loss = F.nll_loss(softmax_scores.to(data["gold_labels"].device), data["gold_labels"], reduction="mean")
loss.backward()
论文3.3节Tool Calling代码逻辑
工具调用参数生成
-
输入:拼接好的“工具调用prompt”
-
输出:形如(参数1,参数2,…)的参数字符串
-
内部用正则/括号匹配提取参数
# 在src/model.py里面
class LLM_with_tools(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
# ...
@torch.no_grad()
def generate_tool_calling_with_query(self, query, max_length=200):
def find_tool_calling_parameters(input_text):
# ... 省略,作用是用括号和引号匹配,提取参数字符串 ...
# ... 省略,设置采样参数 ...
input_token_list = self.tokenizer(query,add_special_tokens=True).input_ids
generated_token_num = 0
while generated_token_num < max(max_length, len(query)):
# ... 省略,基础大模型生成下一个token ...
if generated_token_num%10==0:
output_text = self.tokenizer.decode(input_token_list, skip_special_tokens=True)[len(query):]
end_flag, parameter_text = find_tool_calling_parameters(output_text)
if end_flag:
return parameter_text
# ... 省略,最终返回参数字符串 ...
工具执行
- 用正则/字符串处理,拼接成可执行的Python表达式,执行工具,返回结果。
# 在src/inference.py里面
def call_arithmetic_tools(tool_name, parameter_text):
args = parameter_text.replace("((", "(").replace("))", ")").replace("$", "").replace("=","")
if ", " in args:
args = args.replace(", ", ";").replace(",", "").replace(";", ", ")
args = args.replace(" ", "")
# handle %
if '%' in args:
temp = args[1:-1].split(",")
for arg_i, arg in enumerate(temp):
# if have percentage, convert to decimal
if "%" in arg:
arg = remove_english_chars(arg.replace("%", "").split("/")[0].strip())
arg = str(float(arg) / 100)
temp[arg_i] = arg
args = f"({','.join(temp)})"
try:
res = eval(f"{tool_name[1:-1]}_{args}")
tool_calling = f"{tool_name}{args} = {res}"
return True, tool_calling, res
except Exception as e:
return False, str(e), None
期间所用Prompt
-
生成参数时,拼接成特定的格式,让模型补全缺失的参数部分。
-
还有不同任务的prompt(如funcqa、kamel等),本质都是“问题+已生成答案片段+工具名”的格式。
# 在src/prompt.py里面
def prompt_tool_retriever(tool_name, tool_description):
if tool_description != "":
return '''tool name: {}, tool description: {}'''.format(tool_name, tool_description)
else:
return '''tool name: {}'''.format(tool_name)
prompt_gsm8k_xl_infer = '''Answer the following questions step by step
Question: Mark has 3 tanks for pregnant fish. Each tank has 4 pregnant fish and each fish gives birth to 20 young. How many young fish does he have at the end?
Answer: He has 4*3=12 pregnant fish They give birth to 12*20=240 fish #### 240
Question: The math questions in a contest are divided into three rounds: easy, average, and hard. There are corresponding points given for each round. That is 2, 3, and 5 points for every correct answer in the easy, average, and hard rounds, respectively. Suppose Kim got 6 correct answers in the easy; 2 correct answers in the average; and 4 correct answers in the difficult round, what are her total points in the contest?
Answer: Kim got 6 points/round x 2 round = 12 points in the easy round. She got 2 points/round x 3 rounds = 6 points in the average round. She got 4 points/round x 5 rounds = 20 points in the difficult round. So her total points is 12 points + 6 points + 20 points = 38 points. #### 38
Question: A clothing store sells 20 shirts and 10 pairs of jeans. A shirt costs $10 each and a pair of jeans costs twice as much. How much will the clothing store earn if all shirts and jeans are sold?
Answer: Twenty shirts amount to $10 x 20 = $200. The cost of each pair of jeans is $10 x 2 = $20. So 10 pairs of jeans amount to $20 x 10 = $200. Therefore, the store will earn $200 + $200 = $400 if all shirts and jeans are sold. #### 400
Question: Arnold's collagen powder has 18 grams of protein for every 2 scoops. His protein powder has 21 grams of protein per scoop. And his steak has 56 grams of protein. If he has 1 scoop of collagen powder, 1 scoop of protein powder and his steak, how many grams of protein will he consume?
Answer: 2 scoops of collagen powder have 18 grams of protein and he only has 1 scoop so he consumes 18/2 = 9 grams of protein He has 9 grams collagen powder, 21 grams of protein powder and 56 grams in his steak for a total of 9+21+56 = 86 grams of protein #### 86
Question: {}
Answer:{}'''
prompt_gsm8k_xl_tool_mode = '''{} Let's think step by step.{}'''






















 1706
1706

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










