词法分析的核心在于,将文法转换为NFA再转换为DFA,根据DFA识别出单词的种别码。
下面给出RL/0文法的词汇表:
1.基本字:
begin, call, const, do, end,if, odd, procedure, read,then, var, while, write
对应的种别码:
beginsym, callsym, constsym, dosym, endsym,ifsym, oddsym, proceduresym, readsym,thensym, varsym, whilesym, writesym
2.标识符对应的种别码:ident
3.常数对应的种别码:number
4.运算符:
+, -, *, /, odd,=, <>, <, <=, >, >=, :=
对应的种别码:
plus, minus, times, slash,oddsym,eql, neq, lss, leq, gtr, geq,becomes
5.界符
( ) , ;.
对应的种别码:
Lapren,raplen,comma,semicolon,period
下面是简易的定义,注重过程,不在具体问题上纠结。
标识符对应的正规式为:(a|…|z)星(0|…|9)星 (暂时不考虑下划线)
而常数对应的正规式为:(1|…|9)(0|…|9)* (只考虑无符号的整数)
可以画出NFA
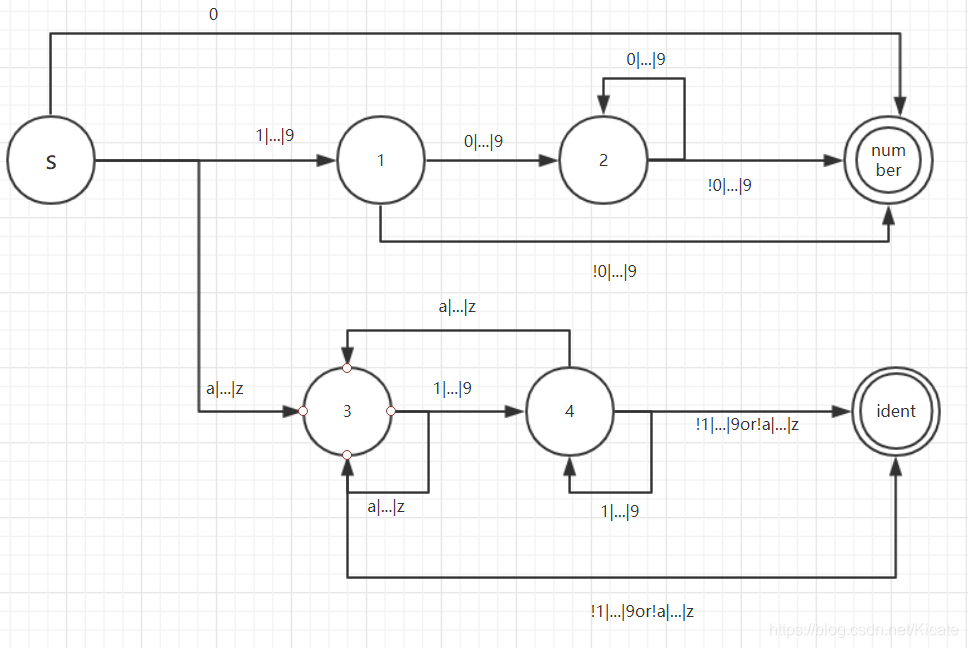
由于很接近dfa,直接给出状态转换表:
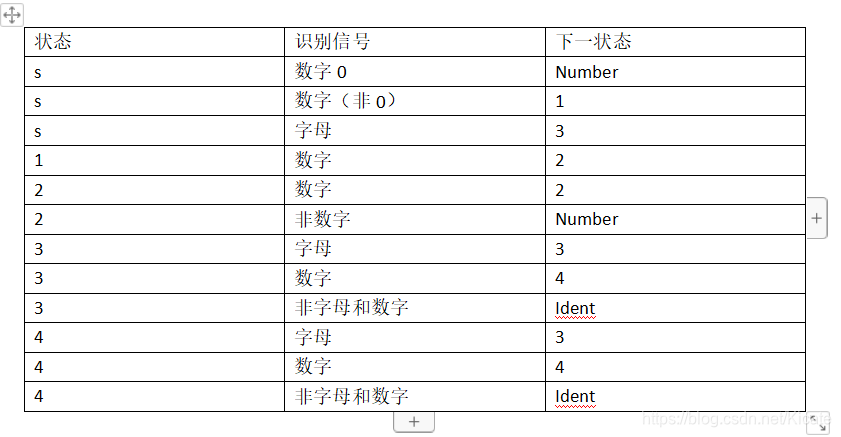
据此可以完成编码。
词法分析流程图:
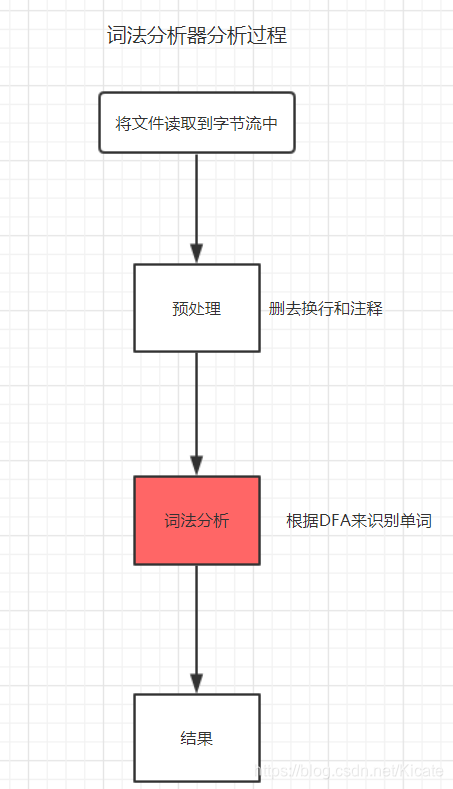
词法分析程序:
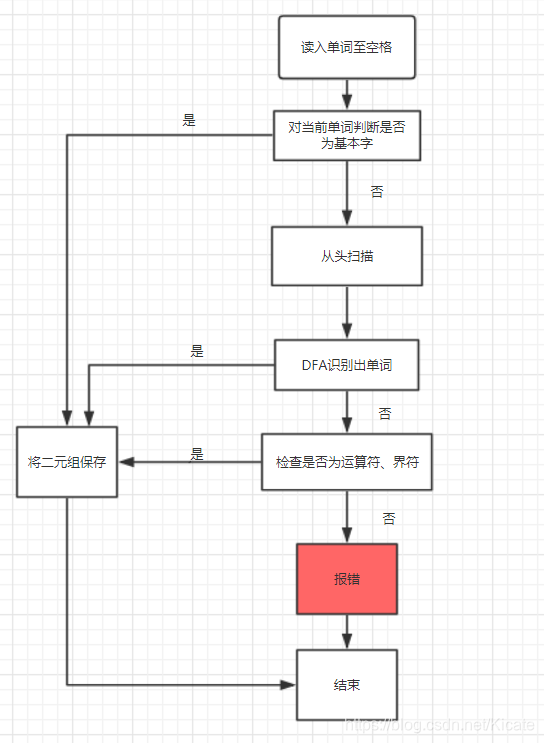
据此就可以编写程序:
public class Main {
//主程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(sc.nextLine());
while(sc.hasNextLine()) {
String s=sc.nextLine();
if(s.isEmpty()) break;
else sb.append(s+" ");
}
//词法分析返回二元组
sb=new la().g(sb);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
public class la {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
StringBuffer tF=new StringBuffer();
private void sw() {
map.put("begin","beginsym");
map.put("call","callsym");
map.put("const","constsym");
map.put("do","dosym");
map.put("end","endsym");
map.put("if","ifsym");
map.put("odd","oddsym");
map.put("procedure","proceduresym");
map.put("read","readsym");
map.put("then","thensym");
map.put("var","varsym");
map.put("while","whilesym");
map.put("write","writesym");
map.put("read","readsym");
map.put("+","plus");
map.put("-","minus");
map.put("*","times");
map.put("/","slash");
map.put("=","eql");
map.put("<>","neq");
map.put("<","lss");
map.put("<=","leq");
map.put(">","neq");
map.put("<=","gtr");
map.put("<=","geq");
map.put(":=","becomes");
map.put("(","lparen");
map.put(")","rparen");
map.put(",","comma");
map.put(";","semicolon");
map.put(".","period");
}
public la() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
sw();
}
public int getBlank(String a)
{
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++)
{
if(a.charAt(i)==' ') return i;
}
return a.length();
}
public int dfa(int p,String a)
{
int l=p;
//l扫描指针
int flag=0; //状态
while(true)
{
if(l>=a.length())
{
if(flag==5||flag==1||flag==2)
{
tF.append("(");
tF.append("number");
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a.substring(p,l));
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
}
else if(flag==6||flag==3||flag==4)
{
if(map.containsKey(a.substring(p,l))) //识别为标准字
{
tF.append("(");
tF.append(map.get(a.substring(p,l)));
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a.substring(p,l));
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
break;
}
else {
tF.append("(");
tF.append("ident");
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a.substring(p,l));
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
break;
}
}
else
{
}
break;
}
if(flag==5)
{
tF.append("(");
tF.append("number");
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a.substring(p,l));
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
break;
}
else if(flag==6)
{
if(map.containsKey(a.substring(p,l))) //识别为标准字
{
tF.append("(");
tF.append(map.get(a.substring(p,l)));
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a.substring(p,l));
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
break;
}
else {
tF.append("(");
tF.append("ident");
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a.substring(p,l));
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
break;
}
}
else if(flag==0)
{
char x=a.charAt(l);
if(x=='0') flag=5;
else if(x<='9'&&x>='1')
{
flag=1;
l++;
}
else if(x<='z'&&x>='a')
{
flag=3;
l++;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
else if(flag==1||flag==2)
{
char x=a.charAt(l);
if(x<='9'&&x>='0')
{
flag=2;
l++;
}
else
{
flag=5;
}
}
else if(flag==3||flag==4)
{
char x=a.charAt(l);
if(x<='z'&&x>='a')
{
flag=3;
l++;
}
else if(x<='9'&&x>='0')
{
flag=4;
l++;
}
else
{
flag=6;
}
}
}
return l;
}
public int jy(int l,String a)
{
//System.out.println("66666:"+l);
String s=Character.toString(a.charAt(l));
//System.out.println(s);
if(s.equals("<")&&l<a.length()-1)
{
if(a.charAt(l+1)=='>'||a.charAt(l+1)=='=')
s=s+Character.toString(a.charAt(l+1));
l++;
}
else if(s.equals(">")&&l<a.length()-1)
{
if(a.charAt(l+1)=='=')
s=s+Character.toString(a.charAt(l+1));
l++;
}
else if(s.equals(":")&&l<a.length()-1)
{
//System.out.println("7777777");
if(a.charAt(l+1)=='=')
{
s=s+Character.toString(a.charAt(l+1));
//System.out.println(s);
l++;
}
}
if(map.containsKey(s))
{
tF.append("(");
tF.append(map.get(s));
tF.append(",");
tF.append(s);
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
l++;
}
return l;
}
public void LL(String a)
{
if(map.containsKey(a)) //识别为标准字
{
tF.append("(");
tF.append(map.get(a));
tF.append(",");
tF.append(a);
tF.append(")");
tF.append("\r\n");
}
else {
int l=0; //扫描指针
int o=l;
int r=a.length();
while(true)
{
//dfa识别
l=dfa(l,a);
//System.out.println("l="+l+"r="+r);
if(l>=r) break;
l=jy(l,a);
//System.out.println("l="+l);
if(l>=r) break;
if(o==l) {
System.out.println("Error!");
break;
}
o=l;
}
}
}
public StringBuffer g(StringBuffer a)
{
String s=new String(a);
while(true)
{
//获得空格前的字符串
int k=getBlank(s);
//System.out.println(k);
//System.out.println(s.length()-1);
String ps=s.substring(0, k);
//如果读取到最后,则退出循环
//进入词法判断
//System.out.println(ps);
LL(ps);
if(k>=s.length()-1) break;
s=s.substring(k+1);
}
return tF;
}
}




 本文介绍了如何进行RL/0文法的词法分析,包括将文法转换为NFA和DFA的过程,详细列举了词汇表、种别码以及简易的定义。并提供了词法分析流程图和程序编写思路。
本文介绍了如何进行RL/0文法的词法分析,包括将文法转换为NFA和DFA的过程,详细列举了词汇表、种别码以及简易的定义。并提供了词法分析流程图和程序编写思路。
















 1757
1757

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








