
**1. 背景 **
在代码开发过程中,编辑器或 IDE 会提供一些常见的“智能”功能,例如:
- 语法高亮 (Syntax Highlighting)
- 自动补全 (Autocomplete / IntelliSense)
- 跳转定义 (Go to Definition)
- 查找引用 (Find References)
- 代码诊断 (Diagnostics, Errors & Warnings)
早期,这些功能大多是编辑器自己实现的,导致:
- 重复造轮子:每个编辑器需要针对不同语言重复开发
- 功能差异大:不同 IDE 支持同一种语言时功能不一致
- 维护成本高:语言升级或语法变化时,需要多方适配
LSP (Language Server Protocol) 正是为了解决这些痛点而诞生的。
**2. 什么是 LSP **
Language Server Protocol (语言服务器协议) 是 微软 在 2016 年提出的一种开放协议,核心思想是:
👉 把“语言智能”功能从编辑器里抽离出来,统一由独立的语言服务器提供。
- 编辑器 (Client):负责 UI 展示与用户交互
- 语言服务器 (Server):负责分析代码,提供智能提示
- 协议 (Protocol):客户端与服务端通过 JSON-RPC 通信
这样,一个语言服务器可以服务多个编辑器,大大减少了重复开发。

**3. 工作原理 **
LSP 的工作机制可以类比为 前端调用后端 API:
- 客户端 (Client):VS Code
- 服务器 (Server):针对某个语言的实现(如 TypeScript Language Server、Pyright、gopls)
- 协议 (Protocol):定义了固定的请求和响应格式(基于 JSON-RPC)
常见交互流程:
- Client → Server:
textDocument/completion请求代码补全 - Server → Client: 返回候选补全项
- Client → Server:
textDocument/definition请求跳转定义 - Server → Client: 返回定义位置
**4. 应用场景 **
- 代码补全(智能提示)
- 跳转定义 / 查找引用
- 悬停提示(Hover Info)
- 诊断信息(编译错误、警告)
- 代码格式化(Format Document)
- 重构功能(Rename Symbol、Code Action)
TypeScript / JavaScript → TypeScript Server
**5. 优势与局限 **
优势
- 🔹 跨编辑器:一次开发,处处使用
- 🔹 易扩展:语言作者只需实现一个 Server
- 🔹 降低成本:IDE 开发者不用重复实现语言解析
**6.开发一个符合自己需求的 LSP **
**1. 需求背景 **
- 在修改代码时,有时会复制到旧 control flow 写的代码,由于粗心会将这块漏过去
- 开发一个 LSP 用于在 VS Code 中检查 Angular 模板文件,提醒开发者是否还有遗留的旧语法,并一键替换
2. 实现步骤
- 建立 VSCode 插件 + LSP 服务
- 插件部分只负责启动语言服务。
- 语言服务部分负责扫描 .html 文件,找出 *ngIf 和 *ngFor 并发出诊断信息。
- 核心逻辑
- 在 LSP 的 onDidChangeContent 事件里,读取文档内容。
- 利用正则截取对应的代码再拼接
- 读取文档
- 用 正则 找到有 *ngIf / *ngFor 的节点
- 构造 Quick Fix,把整个元素替换成 block 形式
- 返回 Diagnostic[],VS Code 就会在文件中打黄线。
- 项目结构
angular-lsp/ ├── src/ (VSCode 插件) ├── extension.ts/ (Client) ├── server/ (语言服务器) ├── server.ts/ (语言服务器) ├── package.json - 代码
Server
```
// 升级版的 Angular 模板分析函数
function analyzeAngularTemplate(document: TextDocument) {
const content = document.getText();
const diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
debugLog("开始分析 Angular 模板");
// 检测 *ngIf
const ngIfRegex = /\*ngIf\s*=\s*"([^"]+)"/g;
let match;
while ((match = ngIfRegex.exec(content)) !== null) {
const range = getElementRange(content, match);
const condition = match[1];
debugLog(`发现 *ngIf: ${match[0]} 在位置 ${match.index}`);
// 生成新的控制流语法
const elementContent = content.substring(
content.indexOf('>', match.index) + 1,
content.lastIndexOf('<', content.indexOf(`</${getTagName(content, match.index)}`, match.index))
).trim();
const newControlFlow = `@if (${condition}) {\n ${elementContent}\n}`;
diagnostics.push({
message: `💡 建议迁移到新的控制流: @if (${condition}) { ... }`,
range,
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
source: "angular-control-flow",
code: "MIGRATE_NGIF",
data: {
condition,
originalText: match[0],
suggestedText: newControlFlow,
elementRange: range,
replacementText: newControlFlow
}
});
}
return diagnostics;
}
function createNgIfCodeAction(document: TextDocument, diagnostic: Diagnostic, data: any): CodeAction {
const content = document.getText();
const elementRange = data.elementRange;
// 获取元素的完整内容
const elementText = document.getText(elementRange);
// 解析元素结构
const tagMatch = elementText.match(/<(\w+)([^>]*?)(\*ngIf="[^"]+")([^>]*?)>(.*?)<\/\1>/s);
if (!tagMatch) {
// 处理自闭合标签或简单情况
const simpleMatch = elementText.match(/<(\w+)([^>]*?)(\*ngIf="[^"]+")([^>]*?)\/?>/);
if (simpleMatch) {
const [, tagName, beforeAttr, ngIfAttr, afterAttr] = simpleMatch;
const condition = ngIfAttr.match(/\*ngIf="([^"]+)"/)?.[1] || data.condition;
const cleanAttrs = (beforeAttr + afterAttr).trim();
const newElement = cleanAttrs ? `<${tagName} ${cleanAttrs} />` : `<${tagName} />`;
const replacement = `@if (${condition}) {\n ${newElement}\n}`;
return {
title: `🔄 替换为 @if (${condition})`,
kind: CodeActionKind.QuickFix,
diagnostics: [diagnostic],
edit: {
changes: {
[document.uri]: [{
range: elementRange,
newText: replacement
}]
}
}
};
}
} else {
const [, tagName, beforeAttr, ngIfAttr, afterAttr, innerContent] = tagMatch;
const condition = data.condition;
const cleanAttrs = (beforeAttr + afterAttr).trim();
const newElement = cleanAttrs
? `<${tagName} ${cleanAttrs}>${innerContent}</${tagName}>`
: `<${tagName}>${innerContent}</${tagName}>`;
const replacement = `@if (${condition}) {\n ${newElement}\n}`;
return {
title: `🔄 替换为 @if (${condition})`,
kind: CodeActionKind.QuickFix,
diagnostics: [diagnostic],
edit: {
changes: {
[document.uri]: [{
range: elementRange,
newText: replacement
}]
}
}
};
}
// 默认回退
return {
title: `🔄 替换为新的 @if 控制流`,
kind: CodeActionKind.QuickFix,
diagnostics: [diagnostic],
edit: {
changes: {
[document.uri]: [{
range: diagnostic.range,
newText: `@if (${data.condition})`
}]
}
}
};
}
```
完整代码 https://github.com/Xiaohang0316/Blog/tree/master/LSP/angular-lsp
- 效果图
展示下划线,提出建议
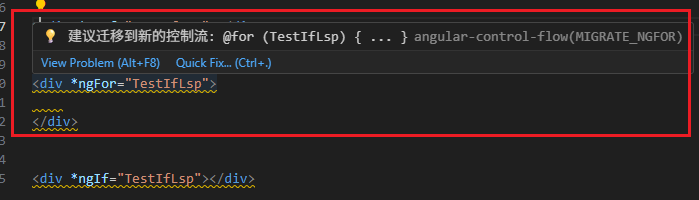
一键替换 旧 control flow
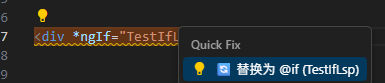
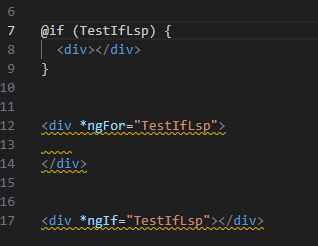
替换效果
**💡 延伸阅读 **





















 1085
1085

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








