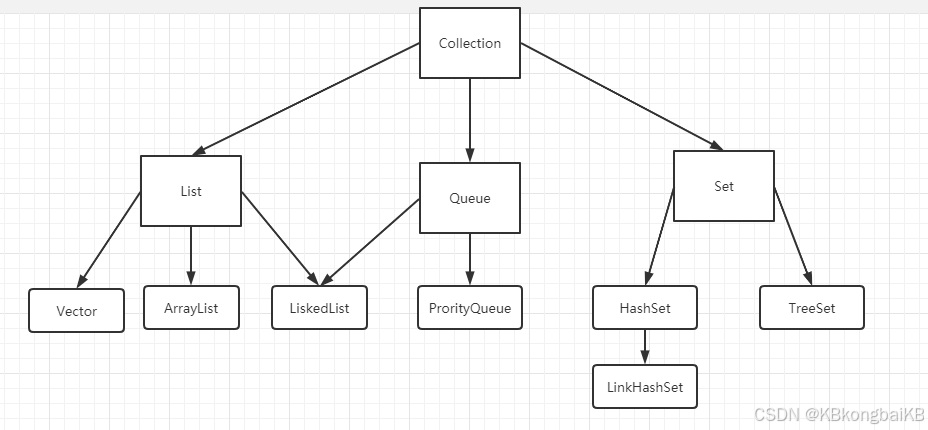
Collection集合
常用方法:
1.public boolean add(E e): 添加元素 添加成功返回true 2.public void clear(): 清空集合元素 3.public boolean isEmpty(): 判断集合是否为空,是空返回true,反之 4.public int size(): 获取集合的大小 5.public boolean contains(Object obj): 判断集合中是否包含某个元素 6.public boolean remove(E e): 删除某个元素:如果有多个重复元素默认删除前面的第一个 7.public Object[] toArray(): 把集合转换成数组
遍历集合:
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("张三");
c.add("李四");
c.add("王五");
c.add("赵六");
使用迭代器遍历集合:
1.从集合对象中获取迭代器对象
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
2.我们应该使用循环结合迭代器遍历集合
while (it.hasNext()){
String ele = it.next();
System.out.println(ele);
}
使用增强for遍历集合或者数组:
for (String ele : c){
System.out.println(ele);
}
String[] names = {"迪丽热巴","古力娜扎","嘻嘻哈哈"};
for (String name : names){
System.out.println(name);
}
结合Lambda表达式遍历集合:
c.forEach(System.out::println);
List集合
特点:添加的元素有序、可重复、有索引
ArrayList(基于数组)
特点:查询快、增删慢、
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
常用方法:
1.public void add(int index,E element):在某个索引位置插入元素 2.public E remove(int index):根据索引删除元素,返回呗删除元素 3.public E get(int index):返回集合中指定位置元素 4.public E set(int index,E element):修改索引位置处的元素,修改成功后,会返回原来的数据
LinkedList(基于双链表)
特点:查询慢、增删快、
Set集合
特点:添加的元素无序、不重复、无索引
Set<Integer> set = new HasgSet<>();
HashSet
哈希表 = 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
(先创建一个数组,通过元素的哈希值对数组长度求余后存入对应位置,有数据,判断是否相等,相等不存,不想等链表)
LinkedHashSet
基于哈希表,但是引用了双链表
TreeSet
通过红黑树实现排序
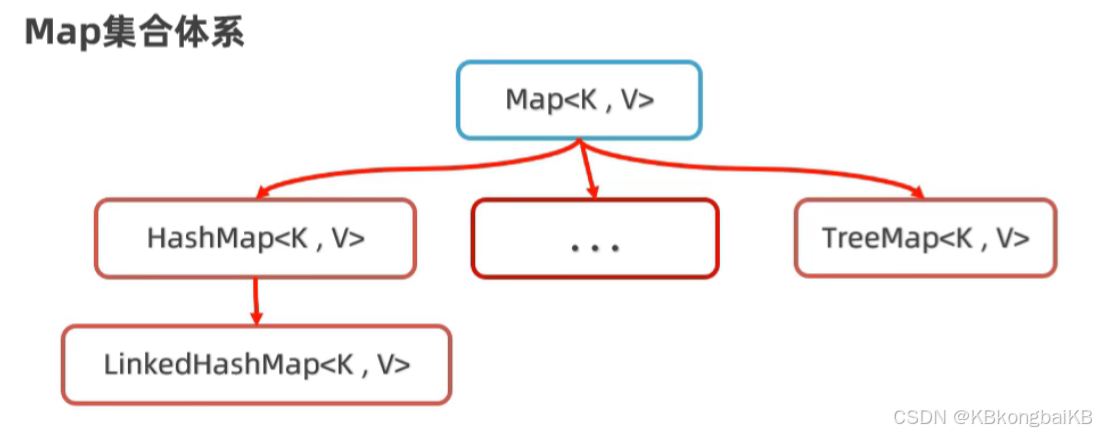
Map集合
常用方法:
1.public int size():获取集合的大小 2.public void clear():清空集合 3.public boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空,为空返回true,反之! 4.public V get(Object key):根据键获取对应值 5.public V remove(Object key):根据键删除整个元素(删除键会返回键的值) 6.public boolean containKey(Object key):判断是否包含某个键,包含返回true,反之! 7.public boolean containValue(Object value):判断是否包含某个值
遍历集合:
Map<String,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("手表",100);
map.put("电脑",220);
map.put("手机",20);
map.put("Java",30);
map.put("书",40)
键找值:
//1.获取Map集合的全部键
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
//2.遍历全部的键,根据键获取其所对应的值
for (String key : keys){
//根据键获取对应的值
double value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "====>" + value);
}
键值对:
Set<Map.Entry<String,Double>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String,Double> entry : entries){
String key = entry.getKey();
double value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "====>" + value);
}
Lambda:
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "====>" + v);
});
HashMap(HashSet)
Map<String Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
LinkedHashMap(LinkedHashSet)
TreeMap
特点:可排序




















 1252
1252

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








