单链表概述
单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存放线性表中的数据元素。链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素(数据元素的映象) + 指针(指示后继元素存储位置),元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。
单链表的实现原理
在单链表中,我们定义一个节点Node 包括两个部分:元数据和下一个节点的地址。节点和节点之间 通过next(即下一个节点的地址)来进行关联,这样就形成了一个链式结构。我们很轻易的就能从头(head)结点一直遍历到最后边的节点。这种结构有点像铁锁一样环环相扣。
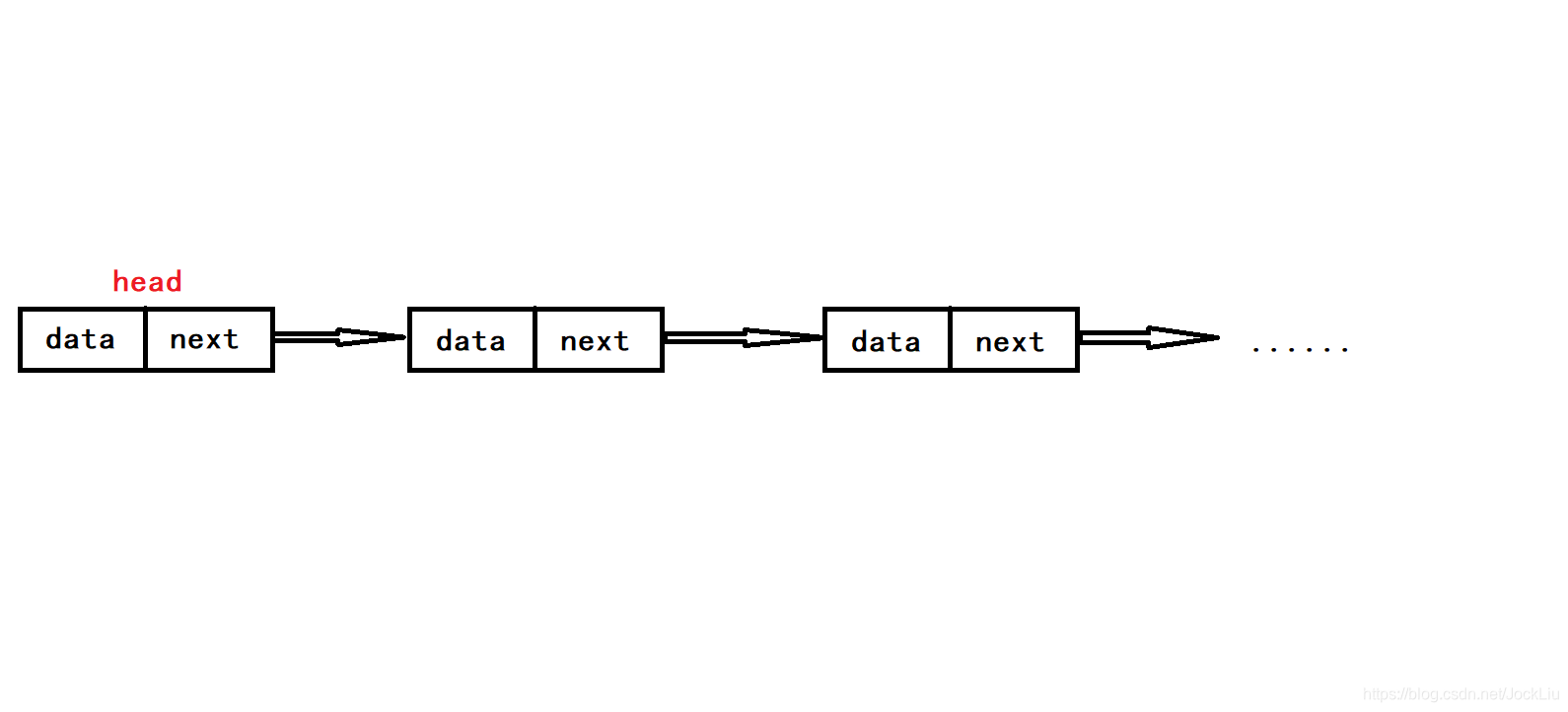
单链表操作(java实现)
节点类(需要定义,两种方式)
class Node{
Object data;//链表中的数据
Node next;//下一节点的索引
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;//取的元素
}
}
Node head;//链表的头结点
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
向链表对象中添加节点对象的功能
/*
* 添加节点
*/
public void add(Object data) {
// 构建节点对象
Node node = new Node(data);
// 判断链表是否为空,若为空,则头节点为空
if (head == null) {
head = node;
// 若不为空,则执行函数,判断下一节点
} else {
Node arr = listNode();
arr.next = node;
}
}
private Node listNode() {
// 从头开始遍历
// 定义一个临时变量,让它等于头
Node temp = head;
// 不为空的话继续遍历
while (temp != null) {
// 若下一节点为空,则中断遍历
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// 遍历下一个
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
在链表对象中删除指定元素
/*
* 删除
*/
public void delete(int index) {
if (index < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("无效索引");
}
Node p = head;
int i = 0;
while (i < index-1 && p != null) {
p = p.next;
i++;
}
if(p == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("无效链表");
}
p.next = p.next.next;
}
向链表中插入指定元素
/*
* 插入节点
*/
public void insert(int value, int index) {
Node p = head;
int i = 0;
while (i < index) {
i++;
}
Node temp = new Node(value);
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
}
向链表中修改指定元素
/*
* 修改结点
*/
public void update(int data, int index) {
if (index<0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("无效链表");
}
int i = 0;
Node p = head;
while (i < index) {
p = p.next;
i++;
}
p.data = data;
}
查询链表中的指定元素
/*
* 查找元素
*/
public Object find(int index) {
int i = 0;
Node p = head;
while (i < index) {
i++;
p = p.next;
}
System.out.println(p.data);
return p.data;
}
增加打印机制(这个主要是为了方便查看链表结构)
/*
* 定义打印函数
*/
public void print() {
Node p = head;
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.data + "->");
p = p.next;
}
}
实现功能的全部代码:
//定义节点对象
class Node {
Object data;// 链表中的数据
Node next;// 下一节点的索引
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;// 取的元素
}
}
public class SingleList {
Node head;// 链表的头结点
/*
* 定义打印函数
*/
public void print() {
Node p = head;
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.data + "->");
p = p.next;
}
}
/*
* 添加节点
*/
public void add(Object data) {
// 构建节点对象
Node node = new Node(data);
// 判断链表是否为空,若为空,则头节点为空
if (head == null) {
head = node;
// 若不为空,则执行函数,判断下一节点
} else {
Node arr = listNode();
arr.next = node;
}
}
private Node listNode() {
// 从头开始遍历
// 定义一个临时变量,让它等于头
Node temp = head;
// 不为空的话继续遍历
while (temp != null) {
// 若下一节点为空,则中断遍历
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// 遍历下一个
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
/*
* 删除
*/
public void delete(int index) {
if (index < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("无效索引");
}
Node p = head;
int i = 0;
while (i < index - 1 && p != null) {
p = p.next;
i++;
}
if (p == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("无效链表");
}
p.next = p.next.next;
}
/*
* 插入节点
*/
public void insert(int value, int index) {
Node p = head;
int i = 0;
while (i < index) {
i++;
}
Node temp = new Node(value);
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
}
/*
* 修改结点
*/
public void update(int data, int index) {
if (index<0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("无效链表");
}
int i = 0;
Node p = head;
while (i < index) {
p = p.next;
i++;
}
p.data = data;
}
/*
* 查找元素
*/
public Object find(int index) {
int i = 0;
Node p = head;
while (i < index) {
i++;
p = p.next;
}
System.out.println(p.data);
return p.data;
}
}
测试对象示例
public class TestSingleList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleList list = new SingleList();
list.add(10000);
list.add(10010);
list.add(10086);
list.add(12580);
list.add(12306);
list.delete(2);
list.insert(12586, 1);
list.update(12345, 4);
list.find(4);
list.print();
}
}







 本文介绍了单链表的概念和实现原理,详细讲解了如何使用Java实现单链表,包括节点类的定义、添加节点、删除元素、插入元素、修改元素、查询元素等功能,并提供了完整的代码示例和打印链表结构的方法。
本文介绍了单链表的概念和实现原理,详细讲解了如何使用Java实现单链表,包括节点类的定义、添加节点、删除元素、插入元素、修改元素、查询元素等功能,并提供了完整的代码示例和打印链表结构的方法。

















 75
75

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








