题目 1:MinPerimeterRectangle
An integer N is given, representing the area of some rectangle.
The area of a rectangle whose sides are of length A and B is A * B, and the perimeter is 2 * (A + B).
The goal is to find the minimal perimeter of any rectangle whose area equals N. The sides of this rectangle should be only integers.
For example, given integer N = 30, rectangles of area 30 are:
- (1, 30), with a perimeter of 62,
- (2, 15), with a perimeter of 34,
- (3, 10), with a perimeter of 26,
- (5, 6), with a perimeter of 22.
Write a function:
int solution(int N);
that, given an integer N, returns the minimal perimeter of any rectangle whose area is exactly equal to N.
For example, given an integer N = 30, the function should return 22, as explained above.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [1..1,000,000,000].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(sqrt(N));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(1).
// you can use includes, for example:
#include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N) {
// write your code in C++11
int i=0;
for(i=sqrt(N);i>0;i--)
{
if(N%i==0)
break;
}
return 2*(i+N/i);
}题目 2:CountFactors
A positive integer D is a factor of a positive integer N if there exists an integer M such that N = D * M.
For example, 6 is a factor of 24, because M = 4 satisfies the above condition (24 = 6 * 4).
Write a function:
int solution(int N);
that, given a positive integer N, returns the number of its factors.
For example, given N = 24, the function should return 8, because 24 has 8 factors, namely 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24. There are no other factors of 24.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [1..2,147,483,647].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(sqrt(N));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(1).
// you can use includes, for example:
#include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N) {
// write your code in C++11
// special case when N can square
int factornum=0;
for(int i=sqrt(N);i>0;i--)
{
if(i*i==N)
factornum++;
else if(N%i==0)
factornum+=2;
}
return factornum;
}题目 3:Peaks
A non-empty zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers is given.
A peak is an array element which is larger than its neighbors. More precisely, it is an index P such that 0 < P < N − 1, A[P − 1] < A[P] and A[P] > A[P + 1].
For example, the following array A:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 2 A[2] = 3 A[3] = 4 A[4] = 3 A[5] = 4 A[6] = 1 A[7] = 2 A[8] = 3 A[9] = 4 A[10] = 6 A[11] = 2has exactly three peaks: 3, 5, 10.
We want to divide this array into blocks containing the same number of elements. More precisely, we want to choose a number K that will yield the following blocks:
- A[0], A[1], ..., A[K − 1],
- A[K], A[K + 1], ..., A[2K − 1],
...- A[N − K], A[N − K + 1], ..., A[N − 1].
What's more, every block should contain at least one peak. Notice that extreme elements of the blocks (for example A[K − 1] or A[K]) can also be peaks, but only if they have both neighbors (including one in an adjacent blocks).
The goal is to find the maximum number of blocks into which the array A can be divided.
Array A can be divided into blocks as follows:
- one block (1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 2). This block contains three peaks.
- two blocks (1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4) and (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 2). Every block has a peak.
- three blocks (1, 2, 3, 4), (3, 4, 1, 2), (3, 4, 6, 2). Every block has a peak. Notice in particular that the first block (1, 2, 3, 4) has a peak at A[3], because A[2] < A[3] > A[4], even though A[4] is in the adjacent block.
However, array A cannot be divided into four blocks, (1, 2, 3), (4, 3, 4), (1, 2, 3) and (4, 6, 2), because the (1, 2, 3) blocks do not contain a peak. Notice in particular that the (4, 3, 4) block contains two peaks: A[3] and A[5].
The maximum number of blocks that array A can be divided into is three.
Write a function:
int solution(vector<int> &A);
that, given a non-empty zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers, returns the maximum number of blocks into which A can be divided.
If A cannot be divided into some number of blocks, the function should return 0.
For example, given:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 2 A[2] = 3 A[3] = 4 A[4] = 3 A[5] = 4 A[6] = 1 A[7] = 2 A[8] = 3 A[9] = 4 A[10] = 6 A[11] = 2the function should return 3, as explained above.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [1..100,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..1,000,000,000].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N*log(log(N)));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(N), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
/////////method 1 the time complexity is O(N^2) #include <algorithm>
#include <set>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code in C++11
int n=A.size();
vector<int> peaks;
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
if(A[i]>A[i-1]&&A[i]>A[i+1])
peaks.push_back(i);
}
int slicesize=peaks.size();
int sliceblock=0;
set<int> st;
for(int i=slicesize;i>0;i--)
{
if(n%i==0)
{
st.clear();
sliceblock=n/i;
for(int j=0;j<peaks.size();j++)
st.insert(peaks[j]/sliceblock);
if(st.size()==i)
break;
}
}
return st.size();
}//////method 2 the time complexity is O(n)// you can use includes, for example:
#include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code in C++11
int n=A.size();
if(n<3)
return 0;
vector<int> peaks(n,0);
int last=-1,D=0;
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
peaks[i]=peaks[i-1];
if(A[i]>A[i-1]&&A[i]>A[i+1])
{
++peaks[i];
D=max(D,i-last);
last=i;
}
}
D=max(D,n-last);
if((peaks[n-1]=peaks[n-2])==0)
return 0;
for(int i=(D>>1)+1;i<D;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
{
int left=0;int j=0;
for(j=i;j<=n;j+=i)
{
if(peaks[j-1]>left)
left=peaks[j-1];
else
break;
}
if(j>n)
return n/i;
}
}
int block=0;
for(block=D;n%block;block++);
return n/block;
}method 3: the complexity is O(n*log(logn))
<pre name="code" class="cpp">// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code in C++11
int n=A.size();
if(n<3)
return 0;
vector<int> peaks(n,0);
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
peaks[i]=peaks[i-1];
if(A[i]>A[i-1]&&A[i]>A[i+1])
++peaks[i];
}
if((peaks[n-1]=peaks[n-2])==0)
return 0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
{
int left=0;
int j=0;
for(j=i;j<=n;j+=i)
{
if(peaks[j-1]>left)
left=peaks[j-1];
else
break;
}
if(j>n)
return n/i;
}
}
return 0;
}题目 4:Flags
A non-empty zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers is given.
A peak is an array element which is larger than its neighbours. More precisely, it is an index P such that 0 < P < N − 1 and A[P − 1] < A[P] > A[P + 1].
For example, the following array A:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 5 A[2] = 3 A[3] = 4 A[4] = 3 A[5] = 4 A[6] = 1 A[7] = 2 A[8] = 3 A[9] = 4 A[10] = 6 A[11] = 2has exactly four peaks: elements 1, 3, 5 and 10.
You are going on a trip to a range of mountains whose relative heights are represented by array A, as shown in a figure below. You have to choose how many flags you should take with you. The goal is to set the maximum number of flags on the peaks, according to certain rules.
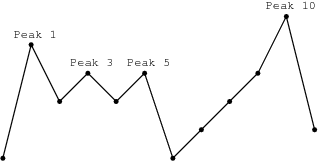
Flags can only be set on peaks. What's more, if you take K flags, then the distance between any two flags should be greater than or equal to K. The distance between indices P and Q is the absolute value |P − Q|.
For example, given the mountain range represented by array A, above, with N = 12, if you take:
- two flags, you can set them on peaks 1 and 5;
- three flags, you can set them on peaks 1, 5 and 10;
- four flags, you can set only three flags, on peaks 1, 5 and 10.
You can therefore set a maximum of three flags in this case.
Write a function:
int solution(vector<int> &A);
that, given a non-empty zero-indexed array A of N integers, returns the maximum number of flags that can be set on the peaks of the array.
For example, the following array A:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 5 A[2] = 3 A[3] = 4 A[4] = 3 A[5] = 4 A[6] = 1 A[7] = 2 A[8] = 3 A[9] = 4 A[10] = 6 A[11] = 2the function should return 3, as explained above.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [1..400,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..1,000,000,000].
Complexity:
代码1:(time complexity is O(n^2))
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N);
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(N), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
int solution(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code in C++11
int n=A.size();
vector<int>peaks;
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
if(A[i]>A[i-1]&&A[i]>A[i+1])
peaks.push_back(i);
}
int slicesize=peaks.size();
if(slicesize<1) return 0;
if(slicesize==1) return 1;
// int flags=0;
int count=0;int i=slicesize;
for(;i>0;i--)
{
int left=0,right=1;count=0;
for(;right<slicesize;right++)
{
if(peaks[right]-peaks[left]>=i)
{
left=right;
count++;
}
}
if((count+1)>=i)
break;
}
return i;
}代码 2: (time complexity is O(n))
// you can use includes, for example:
#include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
// find the nearlist element the distance is greater than or equal to dis.
int binarySearch(vector<int>&a,int from,int dis)
{
int left=from+1,last=a.size()-1;
while(left<=last)
{
int mid=(left+last)>>1;
if((a[mid]-a[from])>=dis)
last=mid-1;
else
left=mid+1;
}
return last+1;
}
int solution(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code in C++11
int n=A.size();
vector<int> a;
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
if(A[i]>A[i-1]&&A[i]>A[i+1])
a.push_back(i);
}
if(a.size()<2)
return a.size();
int D=a.back()-a.front();
// k*(k-1)<=D;
//(k-1)(k-1)<=D;
int left=2,right=sqrt(D)+1;
while(left<=right)
{
int mid=(left+right)/2;
int last=0;int i=0;
for(i=1;i<mid;</span>++i)
{
last=binarySearch(a,last,mid);
if(last>=a.size())
break;
}
if(i>=mid)
left=mid+1;</span>
else
right=mid-1;
}
return left-1;
}




 本文深入探讨了算法与编程技术的关键概念与实践应用,涵盖了从基础数据结构到高级AI处理等多个层面,旨在为读者提供全面的技术指导与实战经验。
本文深入探讨了算法与编程技术的关键概念与实践应用,涵盖了从基础数据结构到高级AI处理等多个层面,旨在为读者提供全面的技术指导与实战经验。
















 1132
1132

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








