文章目录
概述
框架组成
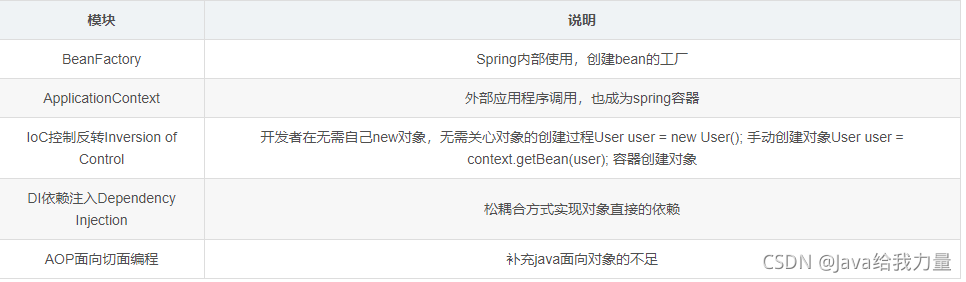
组成 Spring 框架的每个模块(或组件)都可以单独存在,或者与其他一个或多个模块联合实现。每个模块的功能如下:

核心概念
Spring框架可以和其他技术无缝衔接
BeanFactory: bean工厂, spring框架认为所有类都是bean. 从bean工厂可以获取每个bean
IOC: 控制反转, 不需要程序员来创建对象了,交给Spring框架来管理对象(从初始化…销毁).程序员可以直接从 Spring框架中获取Bean的对象
DI: 依赖注入,使用Spring框架明确两个对象间的依赖关系
AOP: 面向切面编程,是一种思想,解决了OOP的不足
三大核心组件的关系
Bean、Context、Core三大核心组件的关系:
Bean 包装的是 Object,而 Object 必然有数据,如何给这些数据提供生存环境就是 Context要解决的问题,对 Context 来说它就是要发现每个 Bean 之间的关系,为它们建立这种关系并且要维护好这种关系。所以 Context 就是一个Bean关系的集合,这个关系集合又叫 Ioc 容器,一旦建立起这个 Ioc 容器后 Spring 就可以为你工作了。那 Core 组件又有什么用武之地呢?其实Core 就是发现、建立和维护每个 Bean 之间的关系所需要的一些类的工具,从这个角度看来,Core 这个组件叫 Util 更能让你理解。
把Bean 比作一场演出中的演员的话,那 Context 就是这场演出的舞台背景,而 Core应该就是演出的道具了。只有他们在一起才能具备能演出一场好戏的最基本的条件。当然有最基本的条件还不能使这场演出脱颖而出,还要他表演的节目足够的精彩,这些节目就是 Spring 能提供的特色功能了。
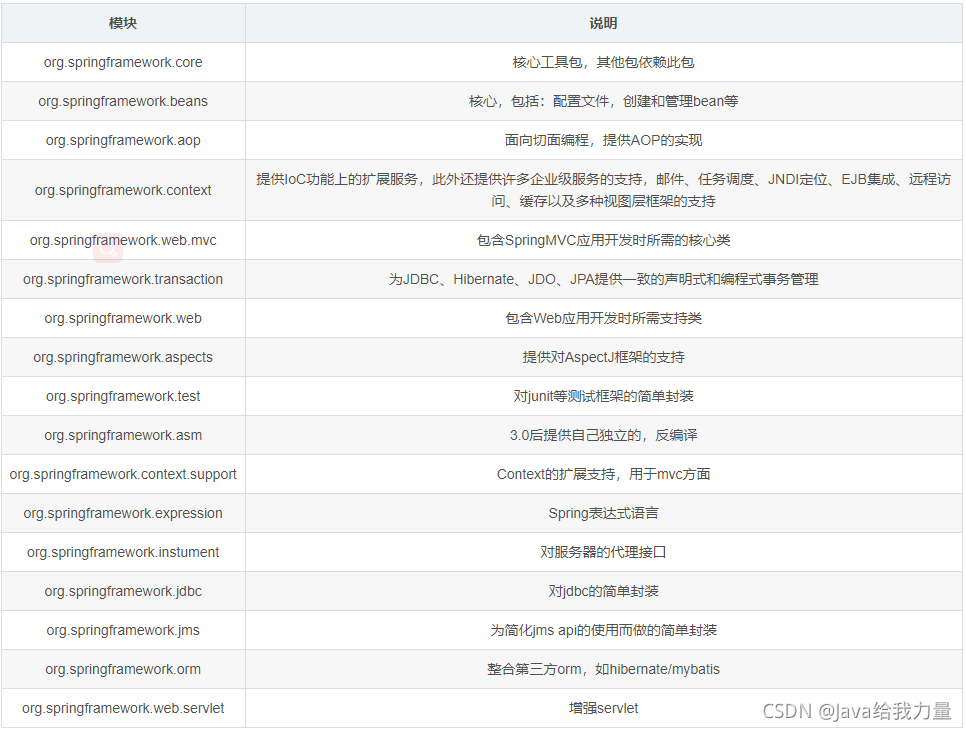
主要jar组成
Spring框架两大核心:IoC和DI
概念
- IoC(Inversion of Control)简单来说就是将对象Object的创建的权力及对象的生命周期的管理过程交由Spring框架来处理,从此在开发过程中不在需要关注对象的创建和生命周期的管理,而是在需要的时候由Spring框架提供,这个由Spring框架管理对象创建和生命周期的机制称之为控制反转。
- 在创建对象的过程中Spring可以依据对象的关系,自动把其它对象注入(无需创建对象,直接拿着使用)进来,这个过程称之为DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入。
总结下Spring核心就干了两件事:
1.创建对象
2.设置对象的关联关系
IoC
IOC(Inversion of Control),控制反转。
就是指将对象的创建,对象的存储(map),对象的管理(依赖查找,依赖注入)交给了spring容器。
常用的IOC注解有四个: 功能都一样,都是交给spring框架创建对象
@Component @Service @Controller @Repository
总结:
1, 创建类, 并且一定要使用IOC注解(@Component @Controller @Service @Repository)
2, 配置包扫描, 需要指定包的路径, 包的扫描范围越小越好, 合理的定范围就可以
3, IOC本质就是, 把你创建的类,Spring框架创建对象,存入Map集合里.
key是类名(首字母小写) value是类的对象(框架利用反射来创建的对象)
Map -> { “hello” , Class.forName(“Hello类的全路径”).newInstance() }
DI
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入 。
相对于IoC而言,依赖注入(DI)更加准确地描述了IoC的设计理念。所谓依赖注入,即组件之间的依赖关系由容器在应用系统运行期来决定,也就是由容器动态地将某种依赖关系的目标对象实例注入到应用系统中的各个关联的组件之中。
总结
1,什么时候需要IOC? 需要把创建对象的权利交给Spring框架管理时
2,什么时候需要DI?
当A类想用B类的属性或者方法时,直接把B类依赖注入到A类就可以
@Component
class A{
@Autowired //di注解,前提是先完成IOC
B b ;
}
@Component
class B{ }
3,DI的前提是完成IOC
IOC的XML方式实现
- 创建Hello类
package cn.tedu.spring;
public class Hello {
public void show(){
System.out.println("show()被调用成功!");
}
}
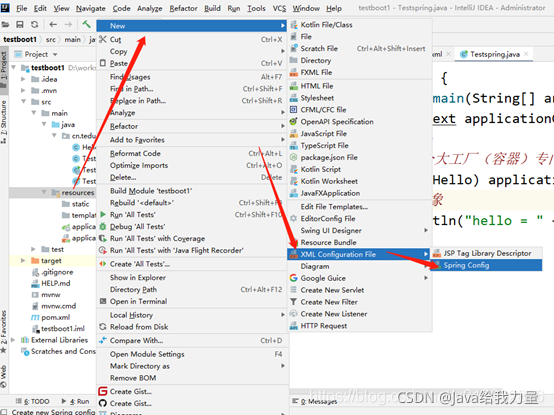
- 创建配置文件,配置类的信息,进行IOC
在resources文件夹位置,右键-new-XML config…-Spring config-输入文件名
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
spring认为万物都是bean,只要你的类,交给spring框架,spring就能IOC
IOC是控制反转:是指Spring框架会帮你创建对象,你来获取对象
id属性是每个bean标签的唯一标识,class属性是用来指定类的全路径
IOC底层Map的数据结构{类,类的对象}
-->
<bean id="hello" class="cn.tedu.spring.Hello"></bean>
</beans>
- 创建测试类,直接获取对象
package cn.tedu.ioc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test1 {
//junit单元测试方法:测试一段代码的结果@Test
@Test
public void get(){
//1,读取配置文件--参数是配置文件的名字
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext spring =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"spring.xml");
//2,获取对象--参数是配置文件里,bean标签的id的属性值
Object o = spring.getBean("hello");
//cn.tedu.spring.Hello@4550bb58
System.out.println(o);
}
}
小结
这就是spring框架的IoC,控制反转。之前我们自己new出新类。new User();变成由一个初始化的xml配置文件来创建,也就是由spring容器来创建。遍历xml配置文件,读取到<bean>,获取到class属性的类的全路径,利用反射创建这个类。
在java范畴中万物皆Object,在Spring中万物皆Bean。Bean是Spring的核心、基础、根源。
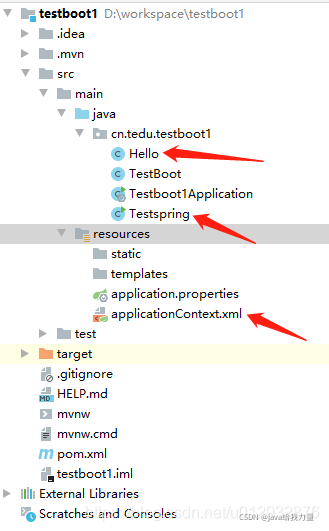
IoC的注解方式
- 创建springboot工程
- pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.tedu</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 集中定义依赖版本号 -->
<properties>
<junit.version>4.10</junit.version>
<spring.version>4.1.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- Hello.java
package spring;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component//让spring容器认识
public class Hello {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("Hello Spring.");
}
}
- applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描, 用注解的方式,配置bean
会扫描 指定包下,带@Component注解的类
并注入spring容器中,key是类名小写,value是类的对象
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu" />
</beans>
- TestIoC.java
package spring;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestIoC {
@Test
public void bean() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//根据id获取bean,beanname就是类名,首字母变小写
Hello hello = (Hello) ac.getBean("hello");
System.out.println(hello);
hello.hi();
}
}
DI依赖注入
- 创建Maven工程
- pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.tedu</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 集中定义依赖版本号 -->
<properties>
<junit.version>4.10</junit.version>
<spring.version>4.1.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
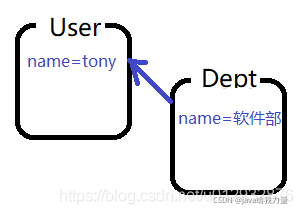
- Dept.java
package spring.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Dept {
String name = "java开发部";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- User.java
package spring.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
String name = "jack";
@Autowired //相当于框架完成了:new User().setDept(new Dept());
Dept dept;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", dept=" + dept +
'}';
}
}
- applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 扫描包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.pojo" />
</beans>
- TestDI.java
package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import spring.pojo.Dept;
import spring.pojo.User;
public class TestDI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Dept d = (Dept)ac.getBean("dept");
User u = (User)ac.getBean("user");
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(u);
System.out.println(u.dept.name);
}
}
小结
面试:IoC和DI
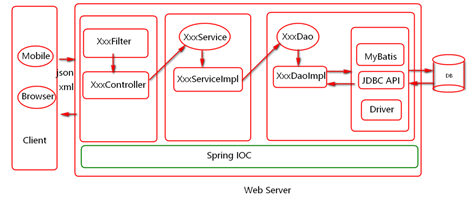
在平时的java应用开发中,我们要实现某一个功能或者说是完成某个业务逻辑时可能需要多个对象来协作完成,在没有使用Spring的时候,每个对象在需要使用他的合作对象时,自己均要使用像new object() 这样的语法来将合作对象创建出来,这个合作对象是由自己主动创建出来的,创建合作对象的主动权在自己手上,自己需要哪个合作对象,就主动去创建,创建合作对象的主动权和创建时机是由自己把控的,而这样就会使得对象间的耦合度高了,A对象需要使用合作对象B来共同完成一件事,A要使用B,那么A就对B产生了依赖,也就是A和B之间存在一种耦合关系,并且是紧密耦合在一起,而使用了Spring之后就不一样了,创建合作对象B的工作是由Spring来做的,Spring创建好B对象,然后存储到一个容器里面,当A对象需要使用B对象时,Spring就从存放对象的那个容器里面取出A要使用的那个B对象,然后交给A对象使用,至于Spring是如何创建那个对象,以及什么时候创建好对象的,A对象不需要关心这些细节问题(你是什么时候生的,怎么生出来的我可不关心,能帮我干活就行),A得到Spring给我们的对象之后,两个人一起协作完成要完成的工作即可。
所以控制反转IoC(Inversion of Control)是说创建对象的控制权进行转移,以前创建对象的主动权和创建时机是由自己把控的,而现在这种权力转移到第三方,比如转移交给了IoC容器,它就是一个专门用来创建对象的工厂,你要什么对象,它就给你什么对象,有了 IoC容器,依赖关系就变了,原先的依赖关系就没了,它们都依赖IoC容器了,通过IoC容器来建立它们之间的关系。
DI(依赖注入)其实就是IOC的另外一种说法,DI是由Martin Fowler 在2004年初的一篇论文中首次提出的。他总结:控制的什么被反转了?就是:获得依赖对象的方式反转了。
IoC是设计思想,IoC有三个核心:BeanFactory、反射、DI。BeanFactory利用反射实现对象的创建,DI实现对象关系管理。
总结:
1, 创建类, 并且一定要使用IOC注解(@Component @Controller @Service @Repository)
2, 配置包扫描, 需要指定包的路径, 包的扫描范围越小越好, 合理的定范围就可以
3, IOC本质就是, 把你创建的类,Spring框架创建对象,存入Map集合里.
key是类名(首字母小写) value是类的对象(框架利用反射来创建的对象)
Map -> { “hello” , Class.forName(“Hello类的全路径”).newInstance() }
自动装配
利用注解方式,我们只需要写@Autowired注解,底层就会去容器中找对应的对象,如果有获取到,反射调用其对应的set方法,设置。而这个调用过程都是自动,我们没有手工去写set方法。所以这个过程也称为自动装配。
AOP面向切面编程
概念
Spring核心特征中除了IoC控制反转、DI依赖注入,还有一个核心就是强大的面向切面编程AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)的实现。
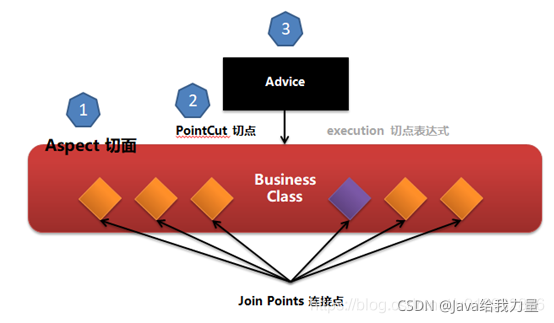
Spring AOP有三要素:
- Aspect定义切面;
- 通过通知(Advice)来指定具体做什么事情。如方法执行前做什么,方法执行后做什么,抛出异常做什么,从而实现对象行为(方法)的增强;
- 具体通过切点(PointCut)配置切点表达式(expression)来指定在哪些类的哪些方法上织入(ware)横切逻辑;被切的地方叫连接点(JoinPoint);
概述
是面向切面编程的思想.好处是: 把一些共性代码,提取形成切面,提供丰富的通知,聚焦了程序员的关注点,只关注业务本身.
1, 切面Aspect: 就是一个类
2, 通知Advice: 类里的方法,分类:
前置通知, 是指调用业务方法前会被执行的功能(适用于权限管理,缓存管理)
后置通知, 是指调用业务方法后会被执行的功能(适用于释放资源)
环绕通知, 是指调用业务方法的前 后 会被执行的功能(适用于事务管理,性能分析)
返回后通知, 是指调用业务方法并返回了结果后 会被执行的功能
异常通知, 是指调用业务方法并抛出异常后 会被执行的功能
3,切点PointCut: 触发通知执行的那个方法的时间点
通知的执行顺序
Spring框架实现了AOP面向切面,其引入了第三方AspectJ框架来具体实现。AspectJ提供了五种切入方式,术语称为通知advice。
具体五种为:
- 前置通知before
- 后置通知after
- 环绕通知around
- 返回后通知afterReturning
- 异常通知afterThrowing。
- 异常通知特殊,这里暂不讨论。
可以看到,分别在业务方法(Business Method)的执行前后进行拦截,执行指定的代码。
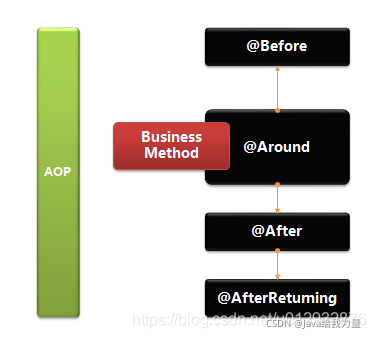
多切面执行顺序
下面是 两个切面 各通知的执行顺序:
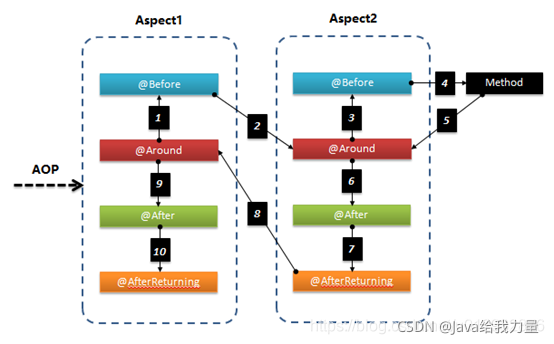
使用步骤
1, 加入jar包
<dependencies>
<!--添加aop依赖包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2, 创建切面,提供通知和切点
3, 测试
- 创建切面
package cn.tedu;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect//切面:由切点和通知组成
public class AspectD {
//切点表达式: *表示1个 ..表示多个 *依次代表方法返回值,类名,方法名,(..)是参数列表
@Pointcut("execution(* cn.tedu.service.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
@Before("pointcut()")//前置通知,在每一个方法开始之前被调用
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("我是前置通知");
}
@After("pointcut()")//后置通知,在每一个方法结束后被调用
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("我是后置通知");
}
@Around("pointcut()")//环绕通知,方法执行前后都被调用,必须有返回值
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object o = joinPoint.proceed();//放行,执行目标方法
time= System.currentTimeMillis()-time;
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();//方法名
System.out.print("我是环绕通知");
System.out.println(methodName+"===耗时:"+time+"===");
return o;
}
}
- 测试
创建启动类,打开浏览器访问以下程序即可观察到控制台的输出效果
package cn.tedu;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("c")
public class ControllerImpl {
@RequestMapping("a")
public void add(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("~");
}
}
}
OOP与AOP测试方法性能案例
OOP
package cn.tedu.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("time")
public class TimeController {
//TODO 提供丰富的方法,并统计性能
@RequestMapping("get")
public void get(){
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时开始
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时结束
System.out.println();
System.out.println(end-time);//性能
}
@RequestMapping("find")
public void find(){
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时开始
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时结束
System.out.println();
System.out.println(end-time);//性能
}
}
AOP
问题: 每个方法都想统计性能,性能统计的代码需求写好多次.
解决方案:利用AOP,提取共性代码形成切面,并提供通知
package cn.tedu.spring;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component //ioc的注解,交给spring完成new
@Aspect//spring整合了aspectj提供了面向切面编程的方式
//切面就是一个类,由通知(就是方法) 和 切点组成
public class TimerAspect {
//切点:什么时候要触发通知的功能
//方法返回值 包名 类名 方法名(参数列表)
@Pointcut("execution(* cn.tedu.controller.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
//这是前置通知,在调用目标方法前 触发执行
@Before("pointcut()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//TODO 检查缓存,权限,日志
System.out.println("我是前置通知~~~");
}
//这是后置通知,在调用目标方法后 触发执行
@After("pointcut()")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//TODO 关流 ...
System.out.println("我是 后置通知~~~");
}
//这是环绕通知,在调用目标方法前后 触发执行
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint)
throws Throwable {
//TODO 事务管理 性能分析 日志管理
//统计每个方法的执行性能
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时开始
Object o = joinPoint.proceed();//找到目标方法并执行
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); //计时结束
System.out.println("aop统计的结果表示,方法的耗时是:"+(end-start));
return o ;//放行,执行目标方法
}
}
测试AOP
就是打开浏览器,访问Controller层的各种方法,都会触发执行通知的功能.观察IDEA里控制台的输出语句就知道了.
http://localhost:8080/time/find
http://localhost:8080/time/get
修改服务器的端口号
- 在resources里创建application.yml文件
#语法规则比较严谨k: v,修改端口号8080(1025~65535)
server:
port: 8888
- 测试
端口号已经不再是8080了
http://localhost:8888/hello/show
Spring高级用法
1.1 Lombok用法
1.1.1 添加依赖
说明: 按照要求 添加lombok jar包文件
<!--引入插件lombok 自动的set/get/构造方法插件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.1.2 安装插件
1.1.3 POJO常用注解
package com.jt.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* POJO写法说明:
* 1.必须有get/set方法
* 2.必须实现序列化接口 数据流传输/socket通讯
*
* 注解说明:
* @Data 自动生成get/set/toString/equals/hashcode等方法
* @Accessors(chain = true) 重写了Set方法,使得写入后返回该对象
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
@NoArgsConstructor //无参构造
@AllArgsConstructor //全参构造
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
/* public void setId(Integer id){
this.id = id;
}
public User setId(Integer id){
this.id = id;
//this 代表当前对象 运行期有效
return this;
}*/
}
1.2 Spring容器管理对象用法
1.2.1 @Component注解说明
表示: 表示将User对象交给Spring容器管理
类似于: new User();
问题: 如果直接new User(), 其中的属性都为null.
需求: 准备User对象 id=100,name=“tomcat” age=18 sex=“男” 交给Spring容器管理!!!
注意事项: 在进行测试时 将@Component删除
1.2.2 @Bean注解
注解说明: @Bean注解是Spring 专门为管理自定义对象 研发的注解.
用法区域: 在配置类文件中使用
用法说明:
package com.jt.config;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 需求: 自定义User对象,交给Spring容器管理
* 注解讲解:
* 1.@Configuration 该类是一个配置类
* 理解:该类是一块区域,在区域中编辑自定义对象
*/
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
/**
* 要求: 必须有返回值.
* 功能: 被@Bean修饰的方法,将方法名当做key--user,将返回值对象当做值value
* 根据Key-value 存储到Map集合中 交给Spring容器管理
* Map<user,User对象>
* @return
*/
@Bean
public User user(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(100).setName("tomcat猫").setSex("男").setAge(18);
return user;
}
}
1.2.3 对象测试
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//需求: 测试User对象是否交给Spring容器管理
@RestController
public class UserController {
//1.先管理对象,之后再注入对象
@Autowired
private User user;
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public User getUser(){
return user;
}
}
1.2.4 测试效果展现

Spring事务管理
事务特性
原子性: 原子不可分割.事务处理要么同时成功,要么同时失败.
一致性: 多线程条件下,数据应该保持一致.
隔离性: 多线程条件下,操作数据时,操作是独立互不干扰.
持久性: 将数据最终处理之后,持久化到数据库中.
谐音:日本名字 “原一隔持”
Spring中的事务
业务逻辑说明
说明: 下列代码运行时,会抛出异常.但是数据也会被删除.
结论: Spring不会默认添加事务控制.
//面试题: 常见运行时异常 常见检查异常(编译异常)
@Override
public void deleteUserById(Integer id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
int a = 1/0;
}
Spring控制事务
说明: Spring中提供了注解@Transactional 用来控制事务, 常见业务 增/删除/修改一般需要事务控制. 查询一般不用.
//面试题: 常见运行时异常 常见检查异常(编译异常)
@Transactional //事务的注解
@Override
public void deleteUserById(Integer id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
int a = 1/0;
}
Spring控制事务策略
规则:
- Spring中的事务注解 默认条件下只处理运行时异常.如果遇到检查异常(编译异常)事务控制没有效果.
- 注解的属性控制
rollbackFor = IOException.class , 遇到某种异常实现事务的回滚
noRollbackFor = 遇到某种异常事务不回滚.
readOnly = true 该操作是只读的,不能修改. 公告/合同等
Spring 全局异常处理机制
知识铺垫
说明:
- 后端业务执行时,无法保证 业务运行不出错. 所以一般添加try-catch进行异常的捕获.
- 捕获异常是为了按照特定的要求 返回用户可以识别的有效数据.
- 如果添加了try-catch 则会对代码的可读性造成影响.
- 如果通过try-catch控制异常,则所有的controller方法都必须添加, 导致代码繁琐.
全局异常处理机制
AOP 复习
说明: 面向切面编程
作用: 在代码结构中,实现了业务的松耦合.(解耦)
通知类型:
- before
- afterReturning
- afterTrowing
- after
- around 环绕通知 控制程序执行前后.
定义全局异常处理机制
编辑全局异常处理类
package com.jt.config;
import com.jt.vo.SysResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
//定义全局异常处理机制 内部封装了AOP
@RestControllerAdvice //标识Controller层 返回值JSON串
public class SystemException {
/**
* 业务说明: 如果后端服务器报错,问应该返回什么数据?
* 返回值: SysResult对象(status=201)
* 异常类型: 运行时异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = RuntimeException.class)
public SysResult fail(Exception e){
//输出异常
e.printStackTrace();
return SysResult.fail();
}
}




















 173万+
173万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








