1. priority_queue的介绍和使用
1.1 priority_queue的介绍
- 优先队列是一种容器适配器,根据严格的弱排序标准,它的第一个元素总是它所包含的元素中最大的。
- 此上下文类似于堆,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先队列中位于顶部的元素)。
- 优先队列被实现为容器适配器,容器适配器即将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类,queue提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的“尾部”弹出,其称为优先队列的顶部。
- 底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他特定设计的容器类。容器应该可以通过随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下操作:
- empty():检测容器是否为空
- size():返回容器中有效元素个数
- front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
- push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
- pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
- 标准容器类vector和deque满足这些需求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector。
- 需要支持随机访问迭代器,以便始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器通过在需要时自动调用算法函数make_heap、push_heap和pop_heap来自动完成此操作。
1.2 priority_queue的使用
优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用priority_queue。
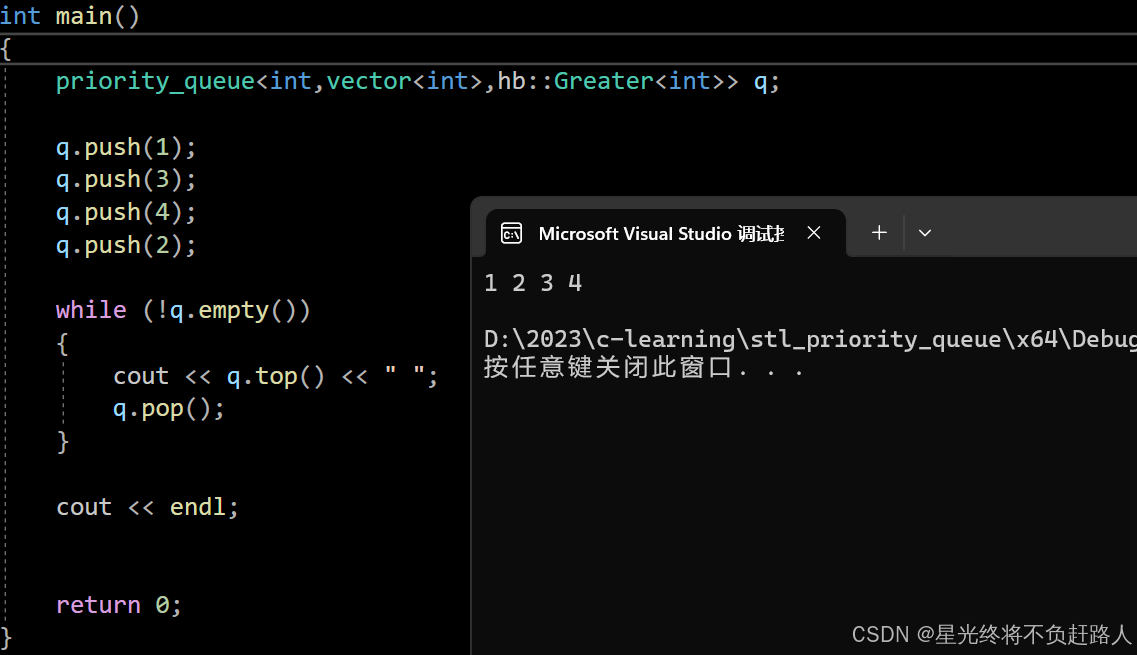
注意:默认情况下priority_queue是大堆。
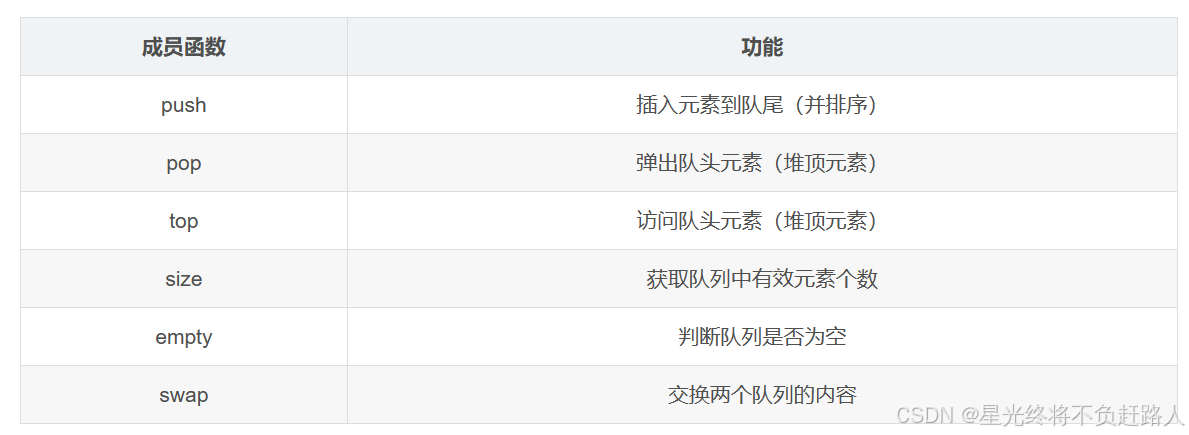

运行结果如图:
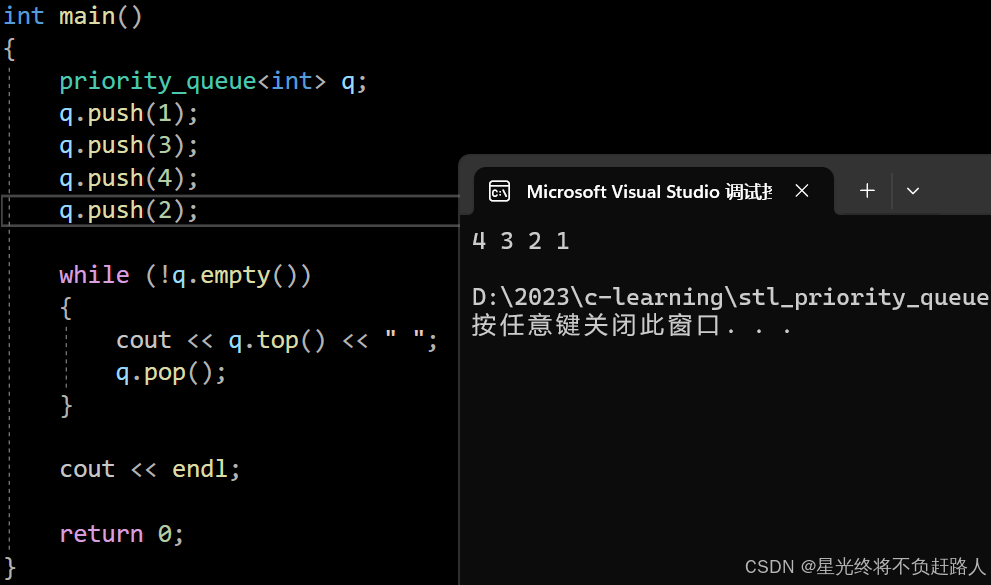
默认是大堆,传的是less\如果我们希望使用小堆就要自己传一个仿函数
运行结果如图:
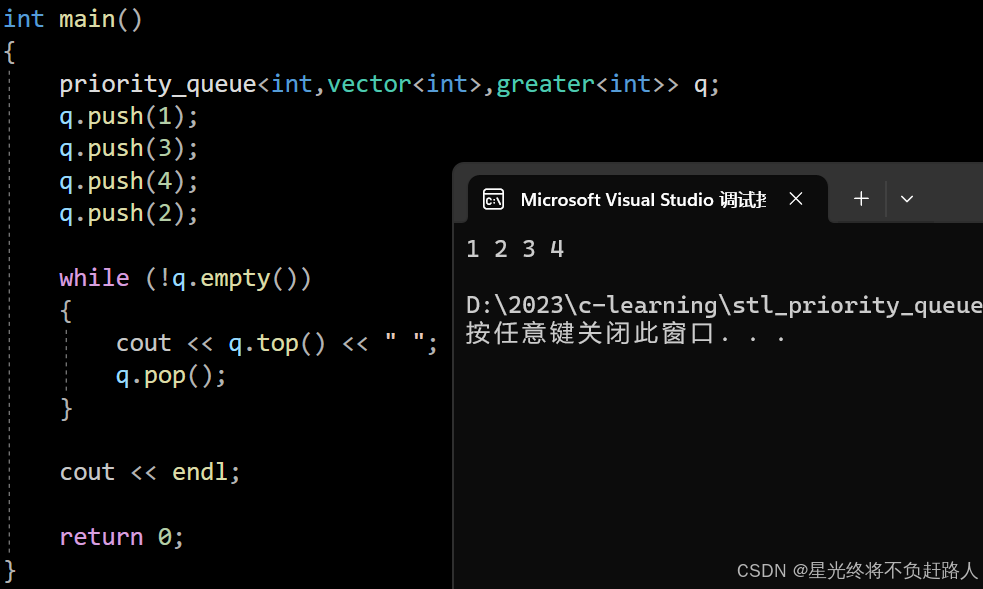
2. priority_queue的模拟实现
通过对priority_queue的底层结构就是堆,因此此处只需对对进行通用的封装即可
代码测试:
运行结果如图:
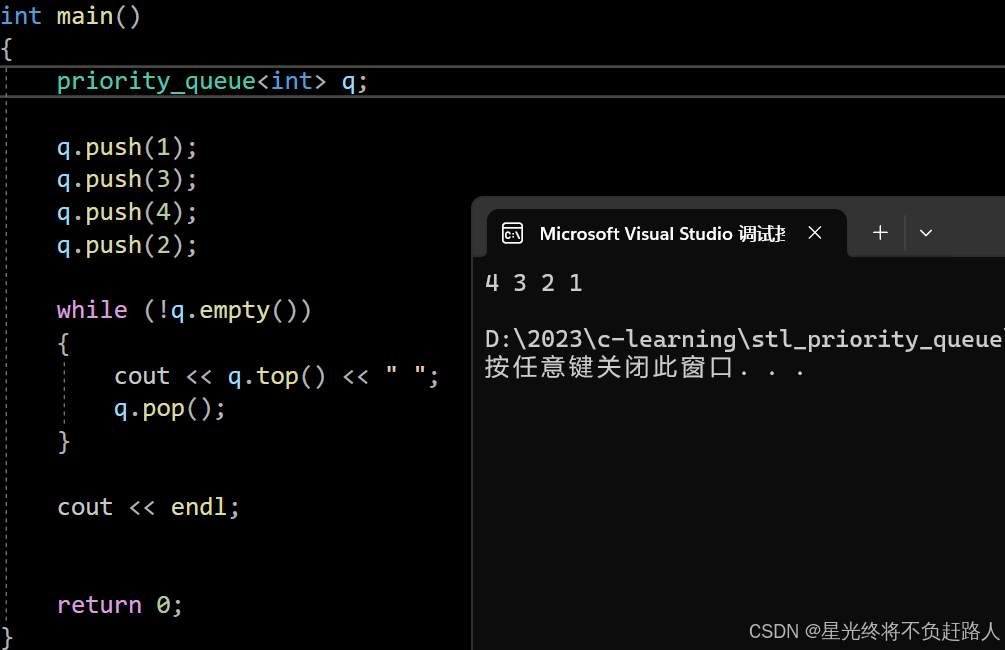
但是如果我们希望把大堆变成小堆就需要改变代码的比较方式,所以这里我们我们可以增加一个模板参数,通过这个模板参数来控制比较的方式,所以这里就要用到仿函数。
代码测试:
运行结果如图:
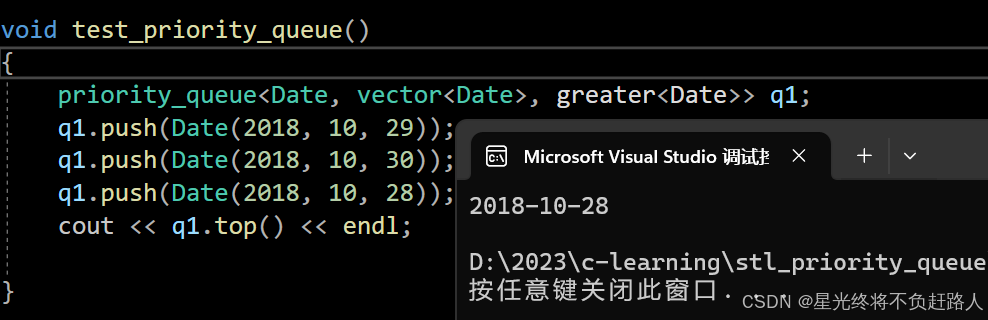
如果在priority_queue中放自定义类型的数据,用户需要在自定义类型中提供> 或者< 的重载。
如果是以下这种情况呢
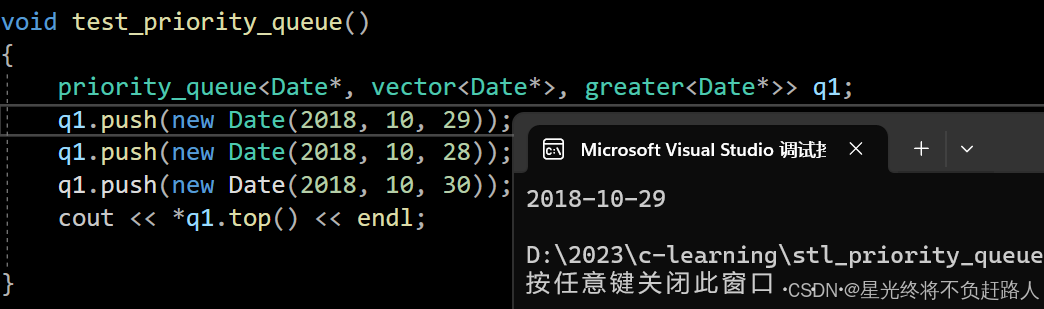
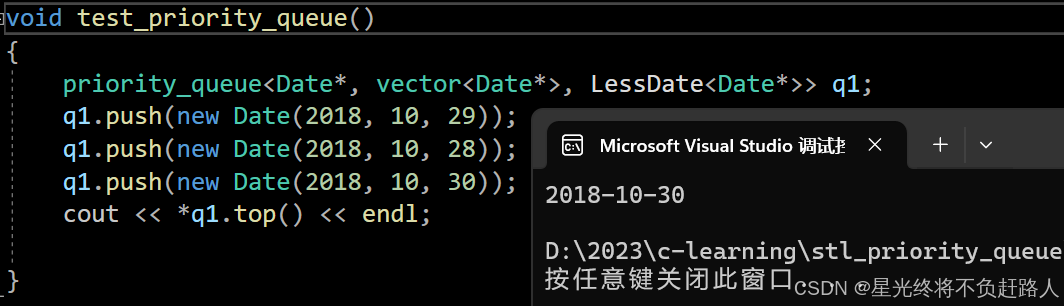
虽然指针也可以比较大小,但是指针比较大小的方式是按照地址的大小来比较,显然不符合我们的预期,我们希望的是比较指针解引用的内容。
所以再写一个专门用来比较指针解引用的仿函数

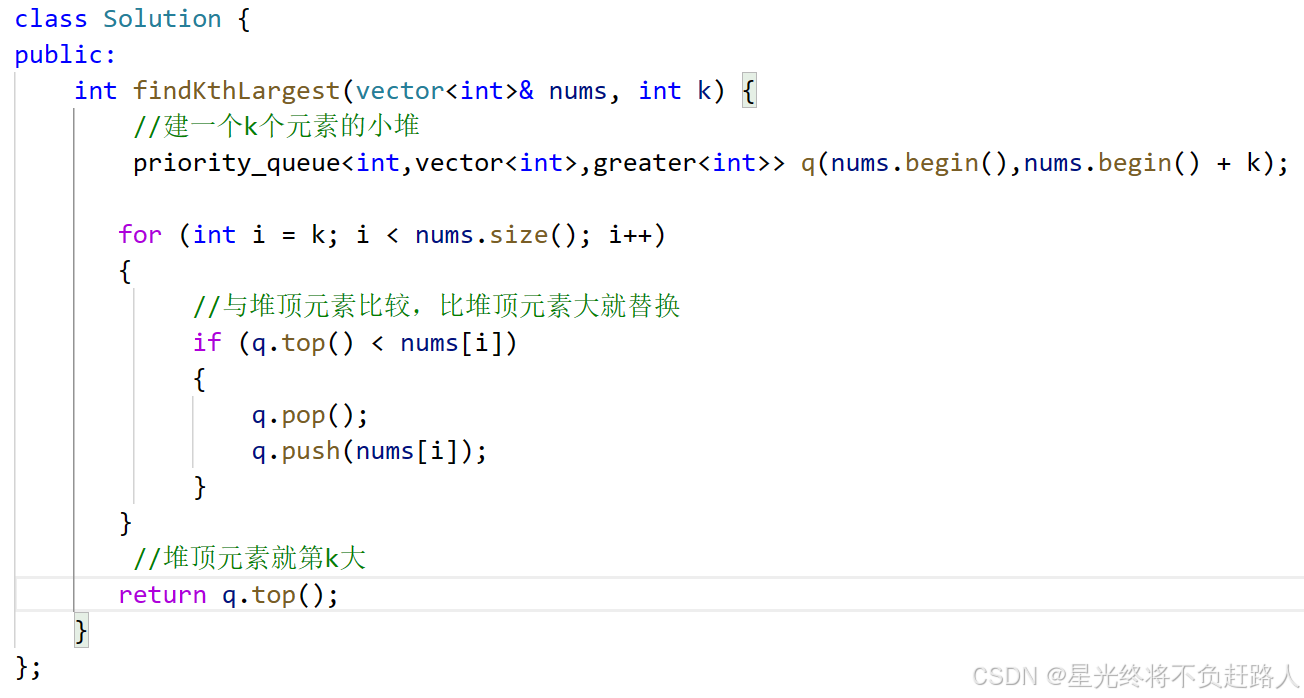
3. 堆排序
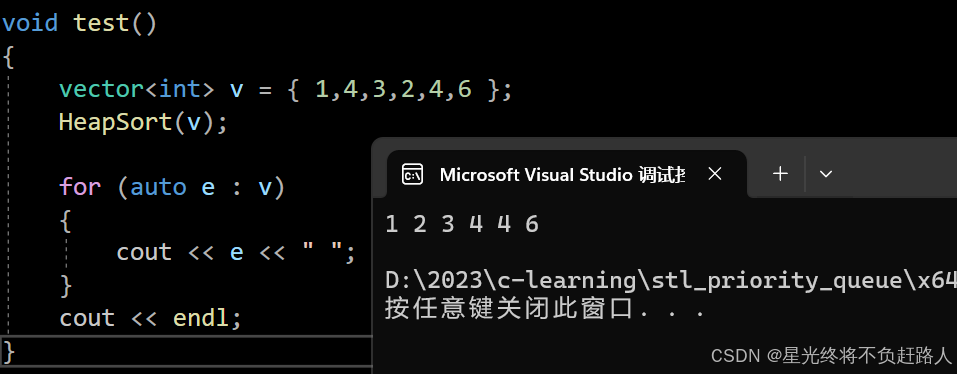
代码测试:
运行结果如图:




















 1206
1206

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








