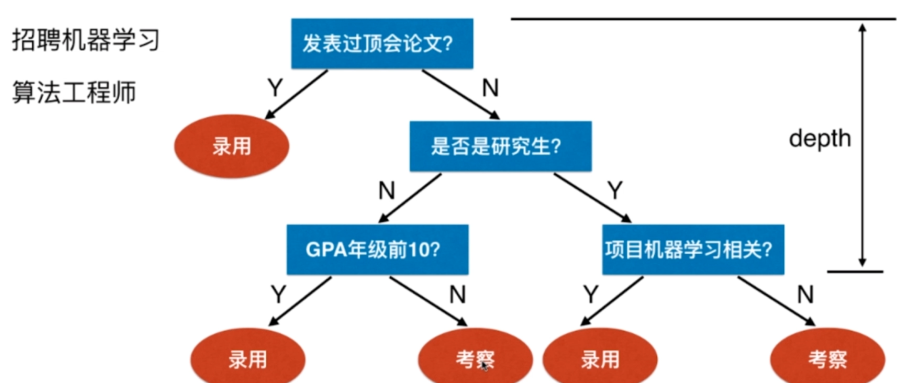
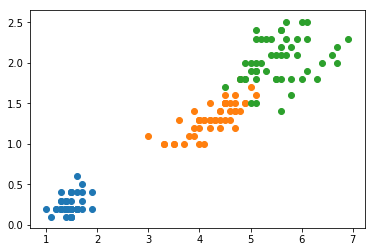
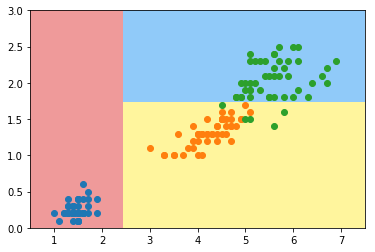
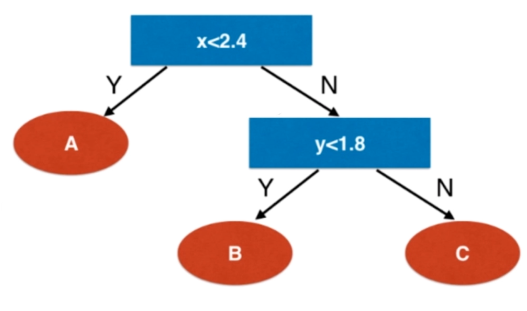
决策树
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, cmap=custom_cmap)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
非参数学习算法
可以解决分类问题
天然可以解决多分类问题
也可以解决回归问题
非常好的可解释性
信息熵
熵在信息论中代表 随机变量不确定度的度量
熵越大,数据的不确定性越高
熵越小,数据的不确定性越低
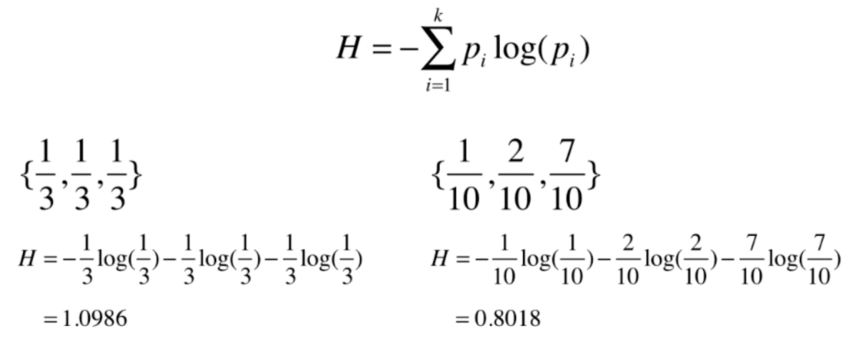
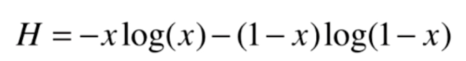
可视化
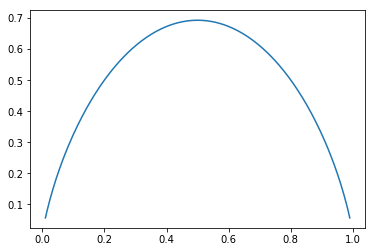
使用信息熵寻找最优划分
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:,2:]
y = iris.target
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
dt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, criterion="entropy", random_state=42)
dt_clf.fit(X, y)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, cmap=custom_cmap)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
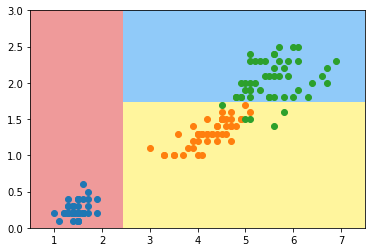
模拟使用信息熵进行划分
from collections import Counter
from math import log
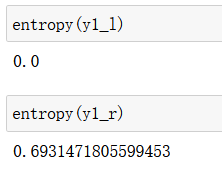
def entropy(y):
counter = Counter(y)
res = 0.0
for num in counter.values():
p = num / len(y)
res += -p * log(p)
return res
def try_split(X, y):
best_entropy = float('inf')
best_d, best_v = -1, -1
for d in range(X.shape[1]):
sorted_index = np.argsort(X[:,d])
for i in range(1, len(X)):
if X[sorted_index[i], d] != X[sorted_index[i-1], d]:
v = (X[sorted_index[i], d] + X[sorted_index[i-1], d])/2
X_l, X_r, y_l, y_r = split(X, y, d, v)
p_l, p_r = len(X_l) / len(X), len(X_r) / len(X)
e = p_l * entropy(y_l) + p_r * entropy(y_r)
if e < best_entropy:
best_entropy, best_d, best_v = e, d, v
return best_entropy, best_d, best_v- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
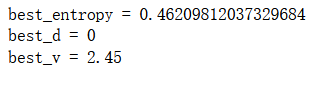
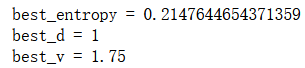
基尼系数
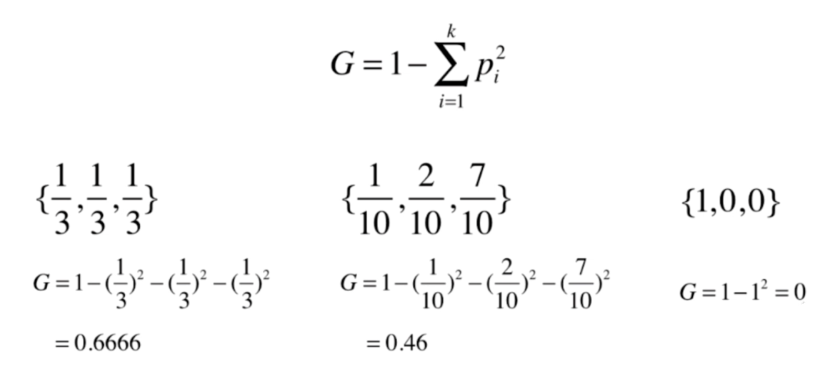
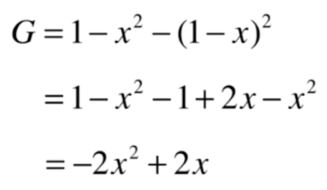
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*200)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*200)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, cmap=custom_cmap)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
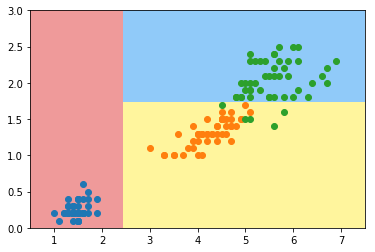
模拟使用基尼系数划分
from collections import Counter
from math import log
def split(X, y, d, value):
index_a = (X[:,d] <= value)
index_b = (X[:,d] > value)
return X[index_a], X[index_b], y[index_a], y[index_b]
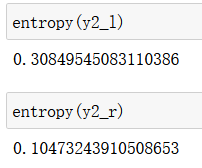
def gini(y):
counter = Counter(y)
res = 1.0
for num in counter.values():
p = num / len(y)
res -= p**2
return res
def try_split(X, y):
best_g = float('inf')
best_d, best_v = -1, -1
for d in range(X.shape[1]):
sorted_index = np.argsort(X[:,d])
for i in range(1, len(X)):
if X[sorted_index[i], d] != X[sorted_index[i-1], d]:
v = (X[sorted_index[i], d] + X[sorted_index[i-1], d])/2
X_l, X_r, y_l, y_r = split(X, y, d, v)
p_l, p_r = len(X_l) / len(X), len(X_r) / len(X)
g = p_l * gini(y_l) + p_r * gini(y_r)
if g < best_g:
best_g, best_d, best_v = g, d, v
return best_g, best_d, best_v- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.




信息熵 vs 基尼系数
熵信息的计算比基尼系数稍慢
scikit-learn中默认为基尼系数
大多数时候二者没有特别的效果优劣
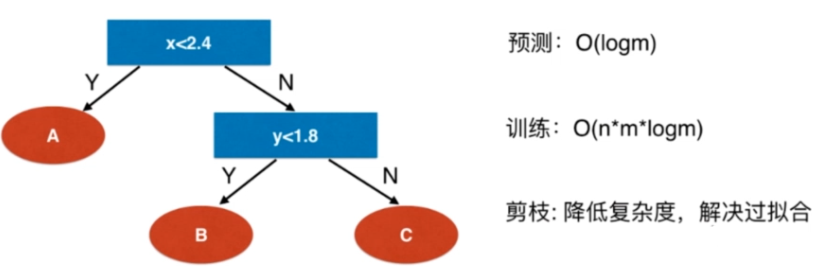
CART与决策树中的超参数
CART
Classification And Regression Tree
根据某一个维度d和某一个阈值v进行二分
scikit-learn的决策树实现:CART
ID3, C4.5, C5.0
复杂度
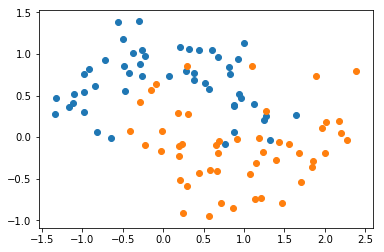
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
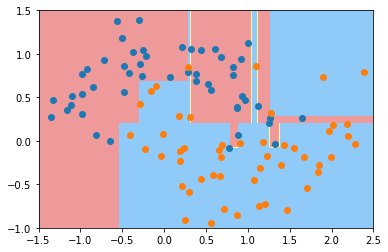
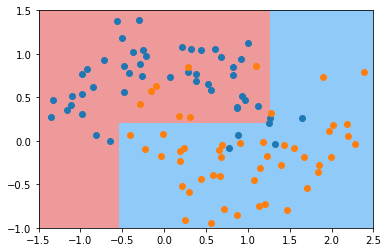
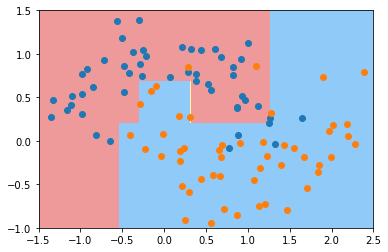
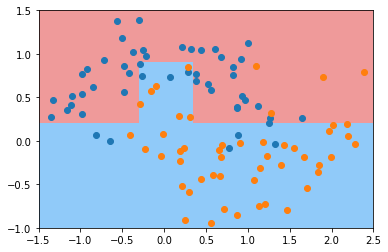
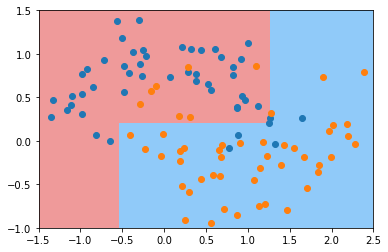
min_samples_split
min_samples leaf
min_weight fraction leaf
max depth
max leaf nodesmin features
决策树解决回归问题

模型复杂度曲线
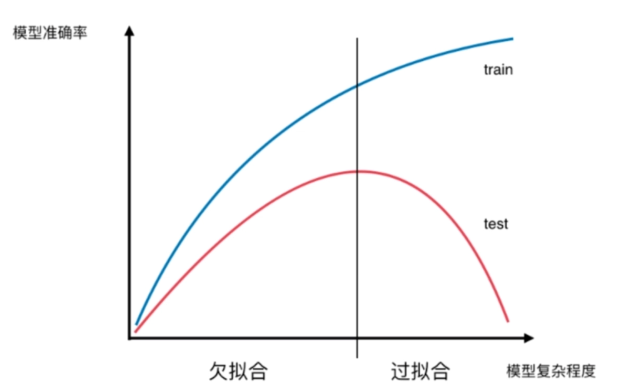
决策树的局限性
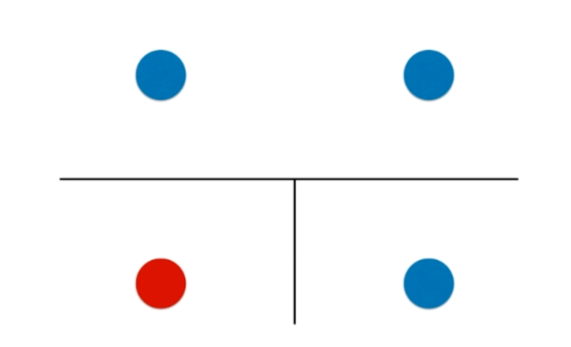
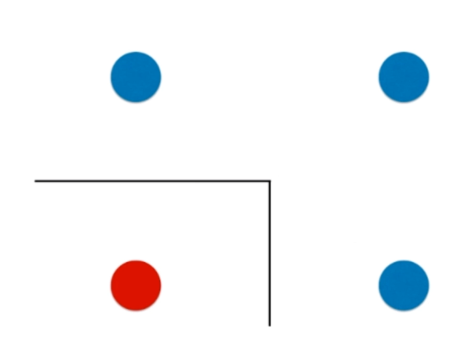
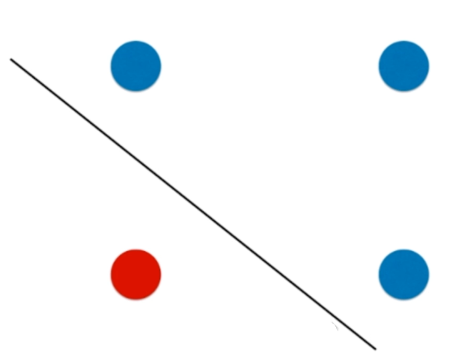
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*200)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*200)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
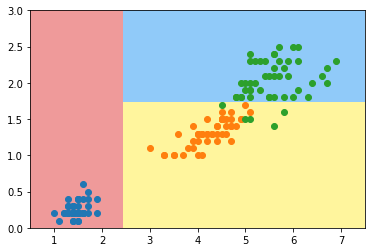
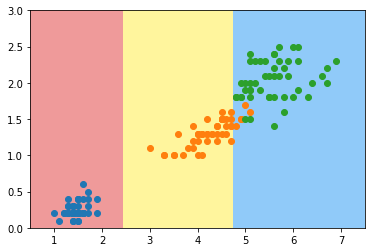




















 6万+
6万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








