本文研究 hotspot 虚拟机运行在 Win32 程序时: Java 线程的创建到操作系统线程创建的内存分配过程 Win32 线程栈虚拟内存释放过程 如果你不了解 win32 的内存管理相关知识,可以先看 Windows 内存管理知识总结
Java 线程 & JVM & 操作系统的关系
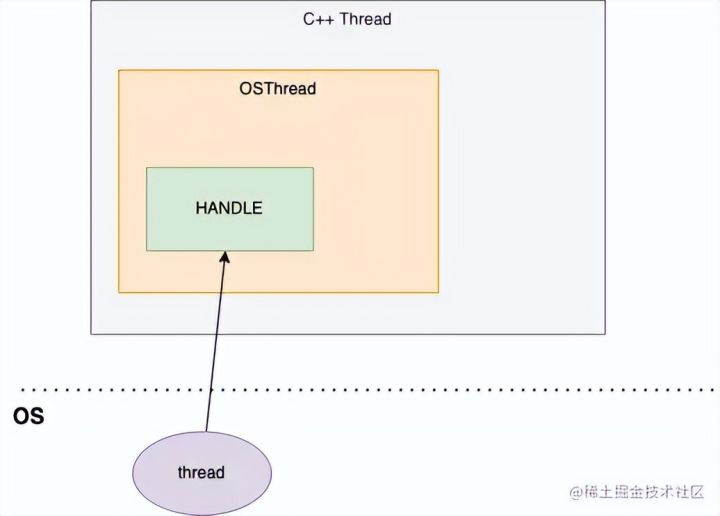
结论
Java 的线程对象实际是个空壳,真正逻辑在 native 层 Java 层通过 JNI 调用到 jvm.cpp,会创建一个 C++ Thread 对象 C++ Thread 对象会持有一个 OSThread 对象 OSThread 会持有具体操作系统创建线程的 HANDLE 想最终释放线程栈占进程的虚拟内存,需要释放 HANDLE
下面会按照一条 Java 线程从创建到销毁、内存从分配到释放的顺序分析核心代码。
Java 线程内存分配
Java new Thead -> thread.start()
/** * Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine * calls the <code>run</code> method of this thread. * <p> * The result is that two threads are running concurrently: the * current thread (which returns from the call to the * <code>start</code> method) and the other thread (which executes its * <code>run</code> method). * <p> * It is never legal to start a thread more than once. * In particular, a thread may not be restarted once it has completed * execution. * * @exception IllegalThreadStateException if the thread was already * started. * @see #run() * @see #stop() */ public synchronized void start() { /** * This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system" * group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added * to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM. * * A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW". */ if (threadStatus != 0) throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); /* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started * so that it can be added to the group's list of threads * and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */ group.add(this); boolean started = false; try { start0(); started = true; } finally { try { if (!started) { group.threadStartFailed(this); } } catch (Throwable ignore) { /* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then it will be passed up the call stack */ } } } private native void start0(); 复制代码
-
Java 层调用到 start() 时,实际是通过 JNI 调用了 native 方法 start0
Thread JNI 方法注册表
// jdk/src/share/native/java/lang/Thread.c:43 static JNINativeMethod methods[] = { {"start0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_StartThread}, {"stop0", "(" OBJ ")V", (void *)&JVM_StopThread}, {"isAlive", "()Z", (void *)&JVM_IsThreadAlive}, {"suspend0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_SuspendThread}, {"resume0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_ResumeThread}, {"setPriority0", "(I)V", (void *)&JVM_SetThreadPriority}, {"yield", "()V", (void *)&JVM_Yield}, {"sleep", "(J)V", (void *)&JVM_Sleep}, {"currentThread", "()" THD, (void *)&JVM_CurrentThread}, {"countStackFrames", "()I", (void *)&JVM_CountStackFrames}, {"interrupt0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_Interrupt}, {"isInterrupted", "(Z)Z", (void *)&JVM_IsInterrupted}, {"holdsLock", "(" OBJ ")Z", (void *)&JVM_HoldsLock}, {"getThreads", "()[" THD, (void *)&JVM_GetAllThreads}, {"dumpThreads", "([" THD ")[[" STE, (void *)&JVM_DumpThreads}, {"setNativeName", "(" STR ")V", (void *)&JVM_SetNativeThreadName}, }; // jdk/src/share/javavm/export/jvm.h:254 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL JVM_Interrupt(JNIEnv *env, jobject thread); 复制代码
-
上述代码标明了 Java 方法和 C++ 函数的映射关系
JVM_StartThread
start0() 实际调用到了 JVM_StartThread 函数中
JVM_ENTRY(void, JVM_StartThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject jthread)) JavaThread *native_thread = NULL; { // Ensure that the C++ Thread and OSThread structures aren't freed before // we operate. MutexLocker mu(Threads_lock); // Since JDK 5 the java.lang.Thread threadStatus is used to prevent // re-starting an already started thread, so we should usually find // that the JavaThread is null. However for a JNI attached thread // there is a small window between the Thread object being created // (with its JavaThread set) and the update to its threadStatus, so we // have to check for this if (java_lang_Thread::thread(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread)) != NULL) { throw_illegal_thread_state = true; } else { // We could also check the stillborn flag to see if this thread was already stopped, but // for historical reasons we let the thread detect that itself when it starts running jlong size = java_lang_Thread::stackSize(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread)); // Allocate the C++ Thread structure and create the native thread. The // stack size retrieved from java is signed, but the constructor takes // size_t (an unsigned type), so avoid passing negative values which would // result in really large stacks. size_t sz = size > 0 ? (size_t) size : 0; native_thread = new JavaThread(&thread_entry, sz); // At this point it may be possible that no osthread was created for the // JavaThread due to lack of memory. Check for this situation and throw // an exception if necessary. Eventually we may want to change this so // that we only grab the lock if the thread was created successfully - // then we can also do this check and throw the exception in the // JavaThread constructor. if (native_thread->osthread() != NULL) { // Note: the current thread is not being used within "prepare". native_thread->prepare(jthread); } } } if (native_thread->osthread() == NULL) { // No one should hold a reference to the 'native_thread'. delete native_thread; if (JvmtiExport::should_post_resource_exhausted()) { JvmtiExport::post_resource_exhausted( JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_OOM_ERROR | JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_THREADS, "unable to create new native thread"); } THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_OutOfMemoryError(), "unable to create new native thread"); } Thread::start(native_thread); JVM_END 复制代码
-
JavaThread 是最开始图中的 C++ Thread 一方面是对操作系统线程做封装,可以看到其持有了 osthread 另一方面是绑定了 Java 层的 thread 对象 jthread,通过 thread_entry 调用到了 Java 层 Thread 类的 run()
-
C++ Thread 的对象内存会分配到 Heap 中
new JavaThread
JavaThread::JavaThread(ThreadFunction entry_point, size_t stack_sz) : Thread() #if INCLUDE_ALL_GCS , _satb_mark_queue(&_satb_mark_queue_set), _dirty_card_queue(&_dirty_card_queue_set) #endif // INCLUDE_ALL_GCS { if (TraceThreadEvents) { tty->print_cr("creating thread %p", this); } initialize(); _jni_attach_state = _not_attaching_via_jni; set_entry_point(entry_point); // Create the native thread itself. // %note runtime_23 os::ThreadType thr_type = os::java_thread; thr_type = entry_point == &compiler_thread_entry ? os::compiler_thread : os::java_thread; os::create_thread(this, thr_type, stack_sz); _safepoint_visible = false; // The _osthread may be NULL here because we ran out of memory (too many threads active). // We need to throw and OutOfMemoryError - however we cannot do this here because the caller // may hold a lock and all locks must be unlocked before throwing the exception (throwing // the exception consists of creating the exception object & initializing it, initialization // will leave the VM via a JavaCall and then all locks must be unlocked). // // The thread is still suspended when we reach here. Thread must be explicit started // by creator! Furthermore, the thread must also explicitly be added to the Threads list // by calling Threads:add. The reason why this is not done here, is because the thread // object must be fully initialized (take a look at JVM_Start) } 复制代码
-
将 entry_point 保存在 C++ Thread 中
-
执行 os::create_thread,真正线程由操作系统函数创建
os::create_thread
// Allocate and initialize a new OSThread bool os::create_thread(Thread* thread, ThreadType thr_type, size_t stack_size) { unsigned thread_id; // Allocate the OSThread object OSThread* osthread = new OSThread(NULL, NULL); if (osthread == NULL) { return false; } // Initialize support for Java interrupts HANDLE interrupt_event = CreateEvent(NULL, true, false, NULL); if (interrupt_event == NULL) { delete osthread; return NULL; } osthread->set_interrupt_event(interrupt_event); osthread->set_interrupted(false); thread->set_osthread(osthread); if (stack_size == 0) { switch (thr_type) { case os::java_thread: // Java threads use ThreadStackSize which default value can be changed with the flag -Xss if (JavaThread::stack_size_at_create() > 0) stack_size = JavaThread::stack_size_at_create(); break; case os::compiler_thread: if (CompilerThreadStackSize > 0) { stack_size = (size_t)(CompilerThreadStackSize * K); break; } // else fall through: // use VMThreadStackSize if CompilerThreadStackSize is not defined case os::vm_thread: case os::pgc_thread: case os::cgc_thread: case os::watcher_thread: if (VMThreadStackSize > 0) stack_size = (size_t)(VMThreadStackSize * K); break; } } // Create the Win32 thread // // Contrary to what MSDN document says, "stack_size" in _beginthreadex() // does not specify stack size. Instead, it specifies the size of // initially committed space. The stack size is determined by // PE header in the executable. If the committed "stack_size" is larger // than default value in the PE header, the stack is rounded up to the // nearest multiple of 1MB. For example if the launcher has default // stack size of 320k, specifying any size less than 320k does not // affect the actual stack size at all, it only affects the initial // commitment. On the other hand, specifying 'stack_size' larger than // default value may cause significant increase in memory usage, because // not only the stack space will be rounded up to MB, but also the // entire space is committed upfront. // // Finally Windows XP added a new flag 'STACK_SIZE_PARAM_IS_A_RESERVATION' // for CreateThread() that can treat 'stack_size' as stack size. However we // are not supposed to call CreateThread() directly according to MSDN // document because JVM uses C runtime library. The good news is that the // flag appears to work with _beginthredex() as well. #ifndef STACK_SIZE_PARAM_IS_A_RESERVATION #define STACK_SIZE_PARAM_IS_A_RESERVATION (0x10000) #endif HANDLE thread_handle = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL, (unsigned)stack_size, (unsigned (__stdcall *)(void*)) java_start, thread, CREATE_SUSPENDED | STACK_SIZE_PARAM_IS_A_RESERVATION, &thread_id); if (thread_handle == NULL) { // perhaps STACK_SIZE_PARAM_IS_A_RESERVATION is not supported, try again // without the flag. thread_handle = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL, (unsigned)stack_size, (unsigned (__stdcall *)(void*)) java_start, thread, CREATE_SUSPENDED, &thread_id); } if (thread_handle == NULL) { // Need to clean up stuff we've allocated so far CloseHandle(osthread->interrupt_event()); thread->set_osthread(NULL); delete osthread; return NULL; } Atomic::inc_ptr((intptr_t*)&os::win32::_os_thread_count); // Store info on the Win32 thread into the OSThread osthread->set_thread_handle(thread_handle); osthread->set_thread_id(thread_id); // Initial thread state is INITIALIZED, not SUSPENDED osthread->set_state(INITIALIZED); // The thread is returned suspended (in state INITIALIZED), and is started higher up in the call chain return true; } 复制代码
-
分配 OSThread 对象
-
CreateEvent(interrupt_event),信号量机制,具体参考learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windo…
-
初始化 stack_size
-
通过 _beginthreadex 创建 Windows 线程,并将 HANDLE 设置到 OSThread 中
C++ Thread 开始执行
上一节 _beginthreadex 的第 3 个参数表示 Windows 线程跑起来后要执行的函数地址
// Thread start routine for all new Java threads static unsigned __stdcall java_start(Thread* thread) { // Try to randomize the cache line index of hot stack frames. // This helps when threads of the same stack traces evict each other's // cache lines. The threads can be either from the same JVM instance, or // from different JVM instances. The benefit is especially true for // processors with hyperthreading technology. static int counter = 0; int pid = os::current_process_id(); _alloca(((pid ^ counter++) & 7) * 128); OSThread* osthr = thread->osthread(); assert(osthr->get_state() == RUNNABLE, "invalid os thread state"); if (UseNUMA) { int lgrp_id = os::numa_get_group_id(); if (lgrp_id != -1) { thread->set_lgrp_id(lgrp_id); } } // Install a win32 structured exception handler around every thread created // by VM, so VM can genrate error dump when an exception occurred in non- // Java thread (e.g. VM thread). __try { thread->run(); } __except(topLevelExceptionFilter( (_EXCEPTION_POINTERS*)_exception_info())) { // Nothing to do. } // One less thread is executing // When the VMThread gets here, the main thread may have already exited // which frees the CodeHeap containing the Atomic::add code if (thread != VMThread::vm_thread() && VMThread::vm_thread() != NULL) { Atomic::dec_ptr((intptr_t*)&os::win32::_os_thread_count); } return 0; } 复制代码
-
调用了 thread -> run(),请继续看下一节
JavaThread::run
// The first routine called by a new Java thread void JavaThread::run() { // initialize thread-local alloc buffer related fields this->initialize_tlab(); // used to test validitity of stack trace backs this->record_base_of_stack_pointer(); // Record real stack base and size. this->record_stack_base_and_size(); // Initialize thread local storage; set before calling MutexLocker this->initialize_thread_local_storage(); this->create_stack_guard_pages(); this->cache_global_variables(); // Thread is now sufficient initialized to be handled by the safepoint code as being // in the VM. Change thread state from _thread_new to _thread_in_vm ThreadStateTransition::transition_and_fence(this, _thread_new, _thread_in_vm); assert(JavaThread::current() == this, "sanity check"); assert(!Thread::current()->owns_locks(), "sanity check"); DTRACE_THREAD_PROBE(start, this); // This operation might block. We call that after all safepoint checks for a new thread has // been completed. this->set_active_handles(JNIHandleBlock::allocate_block()); if (JvmtiExport::should_post_thread_life()) { JvmtiExport::post_thread_start(this); } EventThreadStart event; if (event.should_commit()) { event.set_javalangthread(java_lang_Thread::thread_id(this->threadObj())); event.commit(); } // We call another function to do the rest so we are sure that the stack addresses used // from there will be lower than the stack base just computed thread_main_inner(); // Note, thread is no longer valid at this point! } 复制代码
-
record_stack_base_and_size 中会查询具体栈内存地址,分别调用 current_stack_base 和 current_stack_size
current_stack_base & current_stack_size
// os::current_stack_base() // // Returns the base of the stack, which is the stack's // starting address. This function must be called // while running on the stack of the thread being queried. address os::current_stack_base() { MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION minfo; address stack_bottom; size_t stack_size; VirtualQuery(&minfo, &minfo, sizeof(minfo)); stack_bottom = (address)minfo.AllocationBase; stack_size = minfo.RegionSize; // Add up the sizes of all the regions with the same // AllocationBase. while( 1 ) { VirtualQuery(stack_bottom+stack_size, &minfo, sizeof(minfo)); if ( stack_bottom == (address)minfo.AllocationBase ) stack_size += minfo.RegionSize; else break; } #ifdef _M_IA64 // IA64 has memory and register stacks // // This is the stack layout you get on NT/IA64 if you specify 1MB stack limit // at thread creation (1MB backing store growing upwards, 1MB memory stack // growing downwards, 2MB summed up) // // ... // ------- top of stack (high address) ----- // | // | 1MB // | Backing Store (Register Stack) // | // | / \ // | | // | | // | | // ------------------------ stack base ----- // | 1MB // | Memory Stack // | // | | // | | // | | // | \ / // | // ----- bottom of stack (low address) ----- // ... stack_size = stack_size / 2; #endif return stack_bottom + stack_size 复制代码
size_t os::current_stack_size() { size_t sz; MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION minfo; VirtualQuery(&minfo, &minfo, sizeof(minfo)); sz = (size_t)os::current_stack_base() - (size_t)minfo.AllocationBase; return sz; } 复制代码
-
通过 Windows Api VirtualQuery 查询当前线程栈内存信息
-
JVM C++ Thread 记录 stack_size 的目的是为了处理 stack overflow 异常
thread_main_inner
void JavaThread::thread_main_inner() { assert(JavaThread::current() == this, "sanity check"); assert(this->threadObj() != NULL, "just checking"); // Execute thread entry point unless this thread has a pending exception // or has been stopped before starting. // Note: Due to JVM_StopThread we can have pending exceptions already! if (!this->has_pending_exception() && !java_lang_Thread::is_stillborn(this->threadObj())) { { ResourceMark rm(this); this->set_native_thread_name(this->get_thread_name()); } HandleMark hm(this); this->entry_point()(this, this); } DTRACE_THREAD_PROBE(stop, this); this->exit(false); delete this; } 复制代码
-
重点是最后一行 delete this,会进一步调用 C++ Thread 的析构函数
thread_entry
// java.lang.Thread ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // In most of the JVM Thread support functions we need to be sure to lock the Threads_lock // to prevent the target thread from exiting after we have a pointer to the C++ Thread or // OSThread objects. The exception to this rule is when the target object is the thread // doing the operation, in which case we know that the thread won't exit until the // operation is done (all exits being voluntary). There are a few cases where it is // rather silly to do operations on yourself, like resuming yourself or asking whether // you are alive. While these can still happen, they are not subject to deadlocks if // the lock is held while the operation occurs (this is not the case for suspend, for // instance), and are very unlikely. Because IsAlive needs to be fast and its // implementation is local to this file, we always lock Threads_lock for that one. static void thread_entry(JavaThread* thread, TRAPS) { HandleMark hm(THREAD); Handle obj(THREAD, thread->threadObj()); JavaValue result(T_VOID); JavaCalls::call_virtual(&result, obj, KlassHandle(THREAD, SystemDictionary::Thread_klass()), vmSymbols::run_method_name(), vmSymbols::void_method_signature(), THREAD); } 复制代码
-
run_method_name() 实际就是 Java Thread 的 run(),template(run_method_name, "run")
Java 线程内存释放
void JavaThread::thread_main_inner() { delete this; } 复制代码
-
上一节提到 thread_main_inner 会调用 delete this 随后触发 C++ Thread 的析构函数,下面看看析构函数具体做了什么
Thread:~Thread()
Thread::~Thread() { // Reclaim the objectmonitors from the omFreeList of the moribund thread. ObjectSynchronizer::omFlush (this) ; EVENT_THREAD_DESTRUCT(this); // stack_base can be NULL if the thread is never started or exited before // record_stack_base_and_size called. Although, we would like to ensure // that all started threads do call record_stack_base_and_size(), there is // not proper way to enforce that. #if INCLUDE_NMT if (_stack_base != NULL) { address low_stack_addr = stack_base() - stack_size(); MemTracker::release_thread_stack(low_stack_addr, stack_size(), this); #ifdef ASSERT set_stack_base(NULL); #endif } #endif // INCLUDE_NMT // deallocate data structures delete resource_area(); // since the handle marks are using the handle area, we have to deallocated the root // handle mark before deallocating the thread's handle area, assert(last_handle_mark() != NULL, "check we have an element"); delete last_handle_mark(); assert(last_handle_mark() == NULL, "check we have reached the end"); // It's possible we can encounter a null _ParkEvent, etc., in stillborn threads. // We NULL out the fields for good hygiene. ParkEvent::Release (_ParkEvent) ; _ParkEvent = NULL ; ParkEvent::Release (_SleepEvent) ; _SleepEvent = NULL ; ParkEvent::Release (_MutexEvent) ; _MutexEvent = NULL ; ParkEvent::Release (_MuxEvent) ; _MuxEvent = NULL ; delete handle_area(); delete metadata_handles(); // osthread() can be NULL, if creation of thread failed. if (osthread() != NULL) os::free_thread(osthread()); delete _SR_lock; // clear thread local storage if the Thread is deleting itself if (this == Thread::current()) { ThreadLocalStorage::set_thread(NULL); } else { // In the case where we're not the current thread, invalidate all the // caches in case some code tries to get the current thread or the // thread that was destroyed, and gets stale information. ThreadLocalStorage::invalidate_all(); } CHECK_UNHANDLED_OOPS_ONLY(if (CheckUnhandledOops) delete unhandled_oops();) } 复制代码
-
析构函数核心是调用了 os::free_thread
os::free_thread
// Free Win32 resources related to the OSThread void os::free_thread(OSThread* osthread) { assert(osthread != NULL, "osthread not set"); CloseHandle(osthread->thread_handle()); CloseHandle(osthread->interrupt_event()); delete osthread; } 复制代码
-
重点是 CloseHandle,会释放 _beginthreadex 返回的 HANDLE,从而释放栈虚拟内存




 本文详细解析了Java线程在Windows环境中从创建到销毁,特别是线程栈内存的分配和释放过程。从Java层的start()方法开始,通过JNI调用到C++的JVM_StartThread,然后在C++层创建线程并分配内存。当线程执行完毕,析构函数会调用os::free_thread释放操作系统线程资源,包括关闭HANDLE,从而释放栈内存。
本文详细解析了Java线程在Windows环境中从创建到销毁,特别是线程栈内存的分配和释放过程。从Java层的start()方法开始,通过JNI调用到C++的JVM_StartThread,然后在C++层创建线程并分配内存。当线程执行完毕,析构函数会调用os::free_thread释放操作系统线程资源,包括关闭HANDLE,从而释放栈内存。
















 265
265

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








