基本介绍
- 职责链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern),又叫责任链模式,为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链(简单示意图)。这种模式对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。
- 职责链模式通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,以此类推。
- 这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
### 原理类图 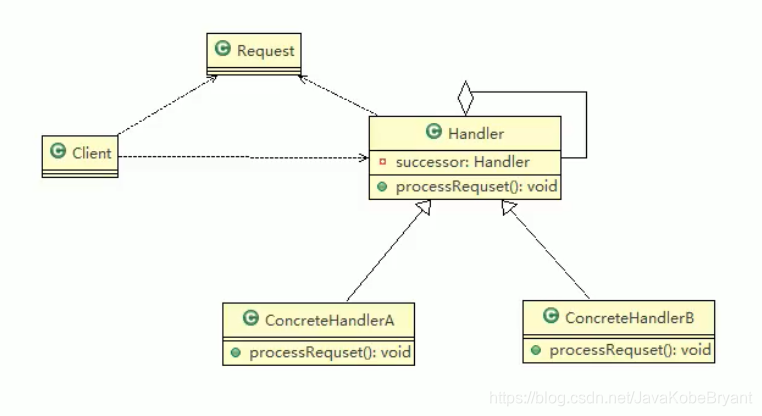 **职责链模式(Chain Of Responsiblity)** 使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系,将这个对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。 **对原理类图的说明-即(职责链模式的角色及职责)** 1. Handler:抽象的处理者,定义了一个处理请求的接口,同时含有另外一个Handler对象 2. ConcreteHandlerA,B是具体的处理者,处理它自己负责的请求,可以访问它的后继者(即下一个处理者),如果可以处理当前请求则自己处理,否则就将该请求交给下一个后继者去处理,从而形成一个职责链 3. Request,含有很多属性,表示一个请求。
职责链模式的实例类图

职责链模式的实例代码
//请求类
public class PurchaseRequest {
private int type; //请求类型
private int number;
private float price = 0.0f;//请求的金额
private int id = 0;
public PurchaseRequest(int type, float price, int id) {
this.type = type;
this.price = price;
this.id = id;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
}
//请求类
public class PurchaseRequest {
private int type; //请求类型
private int number;
private float price = 0.0f;//请求的金额
private int id = 0;
public PurchaseRequest(int type, float price, int id) {
this.type = type;
this.price = price;
this.id = id;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
}
public class DepartmentApprover extends Approver {
public DepartmentApprover(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void processRequest(PurchaseRequest purchaseRequest) {
if (purchaseRequest.getPrice() <= 5000) {
System.out.println("请求编号 id=" + purchaseRequest.getId() + " 被 " + this.name + " 处理");
} else {
approver.processRequest(purchaseRequest);
}
}
}
public class CollegeApprover extends Approver {
public CollegeApprover(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void processRequest(PurchaseRequest purchaseRequest) {
if (purchaseRequest.getPrice() > 5000 && purchaseRequest.getPrice() <= 10000) {
System.out.println("请求编号 id=" + purchaseRequest.getId() + " 被 " + this.name + " 处理");
} else {
approver.processRequest(purchaseRequest);
}
}
}
public class ViceSchoolMasterApprover extends Approver {
public ViceSchoolMasterApprover(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void processRequest(PurchaseRequest purchaseRequest) {
if (purchaseRequest.getPrice() > 10000 && purchaseRequest.getPrice() <= 30000) {
System.out.println("请求编号 id=" + purchaseRequest.getId() + " 被 " + this.name + " 处理");
} else {
approver.processRequest(purchaseRequest);
}
}
}
public class SchoolMasterApprover extends Approver {
public SchoolMasterApprover(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void processRequest(PurchaseRequest purchaseRequest) {
if (purchaseRequest.getPrice() > 30000) {
System.out.println("请求编号 id=" + purchaseRequest.getId() + " 被 " + this.name + " 处理");
} else {
approver.processRequest(purchaseRequest);
}
}
}
职责链模式在SpringMvc的源码分析

源码分析

说明
- springmvc请求的流程图中,执行了拦截器相关方法interceptor.preHandler等等。
- 在处理SpringMvc请求时,使用到职责链模式还使用到适配器模式
- HandlerExecutionChain 主要负责的是请求拦截器的执行和请求处理,但是它本身不处理请求,只是将请求分配给链上注册的处理器执行,这是职责链的实现方式,减少职责链本身与处理逻辑之间的耦合,规范了处理流程
- HandlerExecutionChain 维护了HandlerInterceptor的集合,可以向其中注册相应的拦截器。
职责链模式的注意事项和细节
- 将请求和处理分开,实现解耦,提高系统的灵活性
- 简化了对象,使对象不需要知道链的结构
- 性能会受到影响,特别在链比较长的时候,因此需要控制链中最大节点数量,一般通过在Handler中设置一个最大节点数量,在setNext()方法中判断是否已经超过阈值,超过则不允许该链建立,避免出现超长链无意识地破坏系统性能
- 调试不方便,采用了类似递归的方式,调试时逻辑可能比较复杂
- 最佳应用场景:有多个对象可以处理同一个请求时,比如:多级请求、请假/加薪等审批流程、java Web中Tomcat对Encoding 的处理、拦截器





 本文深入讲解职责链模式的基本概念、工作原理与应用实例,通过具体代码演示如何在系统设计中运用此模式,达到解耦的目的。
本文深入讲解职责链模式的基本概念、工作原理与应用实例,通过具体代码演示如何在系统设计中运用此模式,达到解耦的目的。
















 1592
1592

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








