es6中promise 实现原理
以下是学习promise 原理时看到的比较好的版本:
版本一
/**
* index.js
* @author monkeywang
* Date: 2018/3/5
*/
var PENDING = 0;
var FULFILLED = 1;
var REJECTED = 2;
function PPromise(fn) {
// store state which can be PENDING, FULFILLED or REJECTED
var state = PENDING;
// store value once FULFILLED or REJECTED
var value = null;
// store sucess & failure handlers
var handlers = [];
function fulfill(result) {
state = FULFILLED;
value = result;
handlers.forEach(handle);
handlers = null;
}
function reject(error) {
state = REJECTED;
value = error;
handlers.forEach(handle);
handlers = null;
}
function resolve(result) {
try {
var then = getThen(result);
if (then) {
doResolve(then.bind(result), resolve, reject)
return
}
fulfill(result);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}
function handle(handler) {
if (state === PENDING) {
handlers.push(handler);
} else {
if (state === FULFILLED &&
typeof handler.onFulfilled === 'function') {
handler.onFulfilled(value);
}
if (state === REJECTED &&
typeof handler.onRejected === 'function') {
handler.onRejected(value);
}
}
}
this.done = function (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// ensure we are always asynchronous
setTimeout(function () {
handle({
onFulfilled: onFulfilled,
onRejected: onRejected
});
}, 0);
}
this.then = function (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
var self = this;
return new PPromise(function (resolve, reject) {
return self.done(function (result) {
if (typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
try {
return resolve(onFulfilled(result));
} catch (ex) {
return reject(ex);
}
} else {
return resolve(result);
}
}, function (error) {
if (typeof onRejected === 'function') {
try {
return resolve(onRejected(error));
} catch (ex) {
return reject(ex);
}
} else {
return reject(error);
}
});
});
}
doResolve(fn, resolve, reject);
}
function getThen(value) {
var t = typeof value;
if (value && (t === 'object' || t === 'function')) {
var then = value.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
return then;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Take a potentially misbehaving resolver function and make sure
* onFulfilled and onRejected are only called once.
*
* Makes no guarantees about asynchrony.
*
* @param {Function} fn A resolver function that may not be trusted
* @param {Function} onFulfilled
* @param {Function} onRejected
*/
function doResolve(fn, onFulfilled, onRejected) {
var done = false;
try {
fn(function (value) {
if (done) return
done = true
onFulfilled(value)
}, function (reason) {
if (done) return
done = true
onRejected(reason)
})
} catch (ex) {
if (done) return
done = true
onRejected(ex)
}
}
使用例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
<script src="./index.js"></script>
<script>
function getUserId() {
return new PPromise(function (resolve) {
// 异步请求
resolve(123)
});
}
getUserId().then(function (id) {
return new PPromise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve(23123)
}, 1000)
})
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(value)
})
</script>
</html>
打印结果:
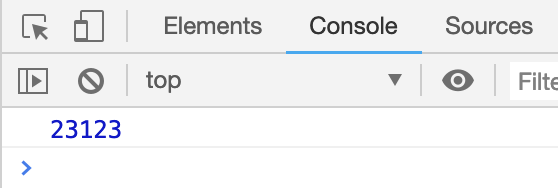
版本二
/**
* 我们要满足状态只能三种状态:PENDING,FULFILLED,REJECTED三种状态,
* 且状态只能由PENDING=>FULFILLED,或者PENDING=>REJECTED
*/
var PENDING = 0;
var FULFILLED = 1;
var REJECTED = 2;
/**
* value状态为执行成功事件的入参,deferreds保存着状态改变之后的需要处理的
* 函数以及promise子节点,构造函数里面应该包含这三个属性的初始化
* @param {*} callback
*/
function Promise(callback) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.defferd = [];
// 这里setTimeout 很关键,绑定完作用域要执行一次
setTimeout(callback.bind(this, this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this)), 0);
}
Promise.prototype = {
constructor: Promise,
resolve: function(result) {
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = result;
this.done();
},
reject: function(error) {
this.status = REJECTED;
this.value = error;
},
handle: function(fn) {
if (!fn) {
return;
}
var value = this.value;
var t = this.status;
var p;
if (t == PENDING) {
this.defferd.push(fn);
} else {
if (t == FULFILLED && typeof fn.onfulfiled == 'function') {
p = fn.onfulfiled(value);
}
if (t == REJECTED && typeof fn.onrejected == 'function') {
p = fn.onrejected(value);
}
var promise = fn.promise;
if (promise) {
if (p && p.constructor == Promise) {
p.defferd = promise.defferd;
} else {
p = this;
p.defferd = promise.defferd;
this.done();
}
}
}
},
done: function() {
var status = this.status;
if (status == PENDING) {
return;
}
var defferd = this.defferd;
for (var i = 0; i < defferd.length; i++) {
this.handle(defferd[i]);
}
},
then: function(success, fail) {
var o = {
onfulfiled: success,
onrejected: fail
};
var status = this.status;
o.promise = new this.constructor(function() {
});
if (status == PENDING) {
this.defferd.push(o);
} else if (status == FULFILLED || status == REJECTED) {
this.handle(o);
}
return o.promise;
}
};
使用示例:
// 使用示例
var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// ... some code
if (true) {
resolve('value');
} else {
reject(error);
}
});
promise.then(function(v) {
console.log('resolved.');
}, function(error) {
console.error('reject 出错了', error);
});
打印结果:

至此,结束。








 本文详细解析了ES6中Promise的实现原理,包括状态管理、异步处理和链式调用机制,通过两个版本的代码示例展示了如何手动实现Promise。
本文详细解析了ES6中Promise的实现原理,包括状态管理、异步处理和链式调用机制,通过两个版本的代码示例展示了如何手动实现Promise。
















 1015
1015

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








