1.传统JDBC的开发流程
加载数据库驱动
创建并获取数据库链接
创建jdbc statement对象
设置sql语句
设置sql语句中的参数(使用preparedStatement)
通过statement执行sql并获取结果
对sql执行结果进行解析处理
释放资源(resultSet、preparedstatement、connection)
缺点:
数据库链接创建、释放频繁造成系统资源浪费从而影响系统性能,如果使用数据库链接池可解决此问题。
Sql语句在代码中硬编码,造成代码不易维护,实际应用sql变化的可能较大,sql变动需要改变java代码。
使用preparedStatement向占有位符号传参数存在硬编码,因为sql语句的where条件不一定,可能多也可能少,修改sql还要修改代码,系统不易维护。
对结果集解析存在硬编码(查询列名),sql变化导致解析代码变化,系统不易维护,如果能将数据库记录封装成pojo对象解析比较方便。
2.Mybatis
MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis,基于java的持久层框架,它对jdbc的操作数据库的过程进行封装,使开发者只需要关注 SQL 本身,而不需要花费精力去处理例如注册驱动、创建connection、创建statement、手动设置参数、结果集检索等jdbc繁杂的过程代码。
对象关系映射(Object Relational Mapping,简称ORM)模式是一种为了解决面向对象与关系数据库存在的互不匹配的现象的技术。简单的说,ORM是通过使用描述对象和数据库之间映射的元数据,将程序中的对象自动持久化到关系数据库中。
3.Mybatis框架
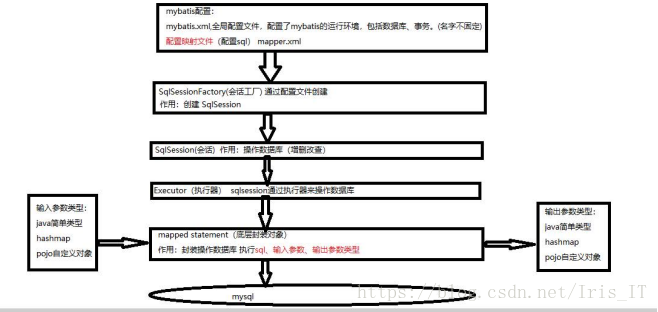
4.mybatis入门程序
4.1.mybatis的jar包
①mybatis-3.2.7.jar ------------ mybatis的核心包
②lib ------- mybatis的依赖包
③程序中可能需要junit-4.9.jar和mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar
4.2创建java工程,创建lib文件放jar包
4.3 配置log4j.properties日志文件----------src下
4.4 mybatis核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- mybatis的运行环境 default指加载的默认环境-->
<!-- 与spring整合后无序以下配置 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 事务 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- 配置数据库连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名?characterEncoding=utf-8" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!--resource1 加载映射文件 -->
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/> //也可以写全路径/
</mappers>
</configuration>
4.5 新建数据库表
4.6 新建pojo对象
Po类作为mybatis进行sql映射使用,po类通常与数据库表对应,User.java如下:
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;// 用户姓名
private String sex;// 性别
private Date birthday;// 生日
private String address;// 地址
// getter/setter此处省略。
// 重写toString方法,输出每个属性。
}
4.7 配置mapper.xml
创建sql映射文件 在src下创建sql映射文件UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace 命名空间 作用1 分割SQL -->
<mapper namespace="UserMapper">
<!-- 根据id查询 -->
<!-- id:标识映射文件中的SQL
被mapped statement封装的,statement的id
paramterType:输入参数类型,当前是int类型
#{}:表示一个占位符
#{id} : 通过参数名称来获取,但是传入的是java基本类型,则可以使用#{value}或者来获取参数
resultType:输出结果类型,指的是单条记录的类型
Select中的属性之间必须有空格
-->
<select id="selectUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="cn.pojo.User">
select * from user where id=#{value}
</select>
</mapper>
4.8 测试类
根据id查询单条记录
@Test
public void test() throws IOException{
//加载mybatis的运行环境
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//创建会话工厂
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//通过sqlSession来操作数据库
//statement 指的是statement的id = namespace.statement的id
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("UserMapper.selectUserById", 1);
System.err.println(user);
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
查询多条记录
<!-- 用户名模糊查询查询 -->
<!-- id:标识映射文件中的SQL
被mapped statement封装的,statement的id
paramterType:输入参数类型
${} :拼接到SQL
最好使用#{},可以防止SQL注入
resultType:输出结果类型,指的是单条记录的类型
-->
<select id="selectUserByName" parameterType="string" resultType="cn.pojo.User">
<!-- select * from user where username like #{value} -->
select * from user where username like "%${value}%"
</select>
测试类中:
@Test
public void selectUserByName() {
// 获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//根据名字模糊查询
//List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("UserMapper.selectUserByName", "%三");
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("UserMapper.selectUserByName", "三");
System.err.println(list);
sqlSession.close();
}
新增
<!-- 按照User类中去取 -->
<!--keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true":獲取生成的id -->
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="cn.pojo.User" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
修改
<!-- 修改用戶 -->
<!-- 按照User类中去取 -->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="cn.pojo.User">
update user set username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address} where id=#{id}
</update>
删除
<!-- 刪除用戶 -->
<delete id="delUser" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id = #{id}
</delete>
查询需要sqlSession.close();
增删改需要sqlSession.commit();和sqlSession.close();
5.SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession
SqlSessionFactory指的是会话工厂,开发它是单例的,只需要一个实例,有 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建的 核心作用:创建SqlSession
SqlSession 指的是会话,定义一些操作数据库的方法,线程不安全
6.mybatis.xml的相关配置
6.1属性配置 引用外部资源配置
<properties resource="db.properties"></properties>
6.2别名
<!-- 重命名 -->
<typeAliases>
<!--type:给谁起别名 alias:别名 -->
<!-- <typeAlias type="cn.pojo.User" alias="user"/> -->
<!-- 批量起别名 别名的名字的对象就是User user或User -->
<package name="cn.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
7.传统dao开发方式
声明一个dao接口
声明dao的实现类
配置userMapper.xml
8.mapper动态代理实现要求
1).mappper.xml的名字要与接口的名字一样
2).namespace 接口的全路径
3).mappper.xml的sql的id要和接口方法中的名字一致
4).输入参数类型要一致
5).输出结果类型要一致
9.mapper.xml 的详解
9.1 parameterType的类型:java简单类型,pojo自定义对象,hashmap
传递map #{map的key} #{}里是map的key 取出来的是map的value
传递多个参数 sql语句中用来代替参数 #{0} #{1}
9.2 输出结果类型:java简单类型,pojo自定义对象,hashmap
resultType: 表示的是返回结果的单条记录的类型,pojo对象和表的字段必须一一对应
resultMap: 可以解决pojo对象和表字段不对应的问题
单个表
<resultMap type="cn.pojo.Car" id="CarMap">
<!--
id:唯一标识
result 普通字段
column 表中的字段
property pojo对象的属性名称
column和property放在一起表示对应关系,将sql查询的结果映射到pojo对应的属性名称
单个表中可以只写名字对应不匹配的一项(最好全写上)
-->
<!-- <id column="carId" property="carId"/> -->
<result column="name" property="carName"/>
<!-- <result column="userId" property="userId"/> -->
</resultMap>
<!--查询所有汽车 -->
<select id="selectCar" resultMap="CarMap">
select * from car
</select>
多个表
<resultMap type="cn.pojo.UserVo" id="UserVoMap">
<!--
id:唯一标识
result 普通字段
column 表中的字段
property pojo对象的属性名称
column和property放在一起表示对应关系,将sql查询的结果映射到pojo对应的属性名称
属性必须全写
-->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
<!-- 集合的封装 -->
<collection property="cars" ofType="cn.pojo.Car">
<id column="carId" property="carId"/>
<result column="name" property="carName"/>
<result column="userId" property="userId"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- 查询用户和汽车 -->
<select id="selectUser" resultMap="UserVoMap">
select * from user u , car c where u.id=c.userId
</select>
Map:不会报错
10.动态sql
10.1 判断 <if test="username!=null and username!=''">
10.2 条件查询: 可以去除多余的and 或者or
<!-- 条件查询用户列表 -->
<!-- <where>可以去除多余的and 或者or -->
<select id="selectUserByParams" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="id!=null and id!=0">
and id=#{id}
</if>
</where>
</select>
10.3 遍历 批量标签
<!-- collection:指定传递的参数类型 list map
item:当前循环中的对象
open:开始
close:结束
separator:分隔符
-->
<select id="selectUserByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="user">
select * from user where id in
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
10.4 去除多余的’,’
<!-- 修改用户信息
需求:每次修改的时候 不确定要修改哪个字段
-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update user
<!-- set 去除多余的',' -->
<set>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="address!=null and address!=''">
address=#{address},
</if>
<if test="birthday!=null and birthday!=''">
birthday=#{birthday},
</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
sex=#{sex},
</if>
</set>
where id#{id}
</update>




 本文详细介绍MyBatis框架的基本概念、安装配置步骤及常见应用场景,包括如何搭建环境、配置核心文件、创建映射文件,并提供了增删改查的具体示例。
本文详细介绍MyBatis框架的基本概念、安装配置步骤及常见应用场景,包括如何搭建环境、配置核心文件、创建映射文件,并提供了增删改查的具体示例。
















 448
448

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








