03-树3 Tree Traversals Again(25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
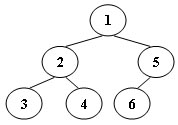
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1解题过程:
通过Push操作,我们可以得到先序遍历的结果,通过Pop操作可以得到中续遍历的结果。这一题,可以通过不构造树,单纯用数组实现(本文参考自MOOC)。
核心算法采用的分治递归的方式。由于根节点在后续遍历中是最后访问的,先序遍历最先访问,中序遍历中间时候访问,因此可以通过根节点来分成左右两颗子树,继续调用上面的方法,即可,详细步骤在程序中已经给出注释。
可以边读程序边对本文这个例子分析,帮助理解
Pre 1 2 3 4 5 6
In 3 2 4 1 6 5
Post 3 4 2 6 5 1程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int pre[31], in[31], post[31], tempPre[31]; // 建立前序、中续、后续、存放前序遍历结果的数组
void solve(int preL, int inL, int postL, int n) // 前序、中序、后序数组下标和结点个数
{
if (n == 0) // 如果没有结点,这种情况在在左右子树缺少时出现
return;
if (n == 1) // 如果只剩一个结点
{
post[postL] = pre[preL];
return;
}
int root = pre[preL], i;
post[postL + n - 1] = root; // 把根节点放入后续数组的尾巴上
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (in[inL + i] == root)
break;
}
int L = i; // 左分支的结点数
int R = n - L - 1; // 右分支的结点数,这里还要再减1是把中序遍历的根结点去掉
solve(preL+1, inL, postL, L); // 递归调用左分支
solve(preL+L+1, inL+L+1, postL+L, R); // 递归调用右分支
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int N, x, idxPop = 0, idxPre = 0, tempIdxPre = 0;
string operation; // 表示操作
cin >> N;
while (idxPop < N) // 当Pop操作达到N次说明以结束
{
cin >> operation;
if (operation == "Push")
{
cin >> x;
pre[idxPre++] = x;
tempPre[tempIdxPre++] = x;
}
else{
in[idxPop++] = tempPre[--tempIdxPre]; // 把tempPre数组的"栈顶"弹出放入in
}
}
solve(0, 0, 0, N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) // 输出格式
{
if (i != 0)
cout << " ";
cout << post[i];
}
return 0;
}




 本文介绍了一种通过栈操作实现二叉树中序非递归遍历的方法,并利用给定的栈操作序列生成唯一的二叉树。文章提供了一个具体的样例分析及对应的程序代码,展示了如何从栈操作中获取前序、中序遍历序列,并进一步得到后序遍历序列。
本文介绍了一种通过栈操作实现二叉树中序非递归遍历的方法,并利用给定的栈操作序列生成唯一的二叉树。文章提供了一个具体的样例分析及对应的程序代码,展示了如何从栈操作中获取前序、中序遍历序列,并进一步得到后序遍历序列。
















 477
477

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








