文章目录
Java内置线程池-ExecutorService
方法

newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {}
- 每次执行任务的时候,如果之前的线程可用,则复用之前的线程,否则创建新线程
- 对线程的数量不做限制
- 线程默认空闲60s后会被销毁
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) {
es.submit(new MyRunnable(i));
}
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {}
- 支持自定义创建线程的类
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new ThreadFactory() {
// 自定义线程工厂创建线程
int n = 1;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "自定义线程" + n++);
}
});
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
es.submit(new MyRunnable2(i));
}
}
}
class MyRunnable2 implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable2(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
newFixedThreadPool
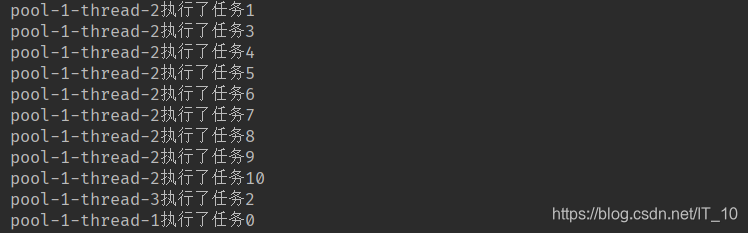
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {}
- 指定线程数量
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
es.submit(new MyRunnable3(i));
}
}
}
class MyRunnable3 implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable3(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
}
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {}
- 支持自定义线程创建类
- 线程数固定
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3, new ThreadFactory() {
// 自定义线程工厂创建线程
int n = 1;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "自定义线程" + n++);
}
});
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
es.submit(new MyRunnable4(i));
}
}
}
class MyRunnable4 implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable4(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
}
}

newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {}
- 只有一个线程执行任务,以无界队列方式运行线程
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
es.submit(new MyRunnable5(i));
}
}
}
class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable5(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
}
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {}
- 支持自定义线程创建类
Java内置线程池-ScheduledExecutorService
ScheduledExecutorService是ExecutorService的子接口,具备了延迟运行或者定期执行任务的能力
ScheduledExecutorService提供的方法

说明:第三个和第四个方法不同点在于第三个方法中,时间间隔是从上一次任务启动开始计时,每个时间间隔是固定的。而第四个方法是从上次任务执行完了,才计时间隔时间,所以两个任务开始的时间间隔不固定。
获取ScheduledExecutorService的方法

例子
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService ses = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
// 延迟2s执行任务
// 注意这里是延迟2s后开始执行所有任务,而不是每个任务都延迟2s后执行
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
ses.schedule(new MyRunnable1(i), 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
System.out.println("main");
}
}
class MyRunnable1 implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable1(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
}
}

public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService ses = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3, new ThreadFactory() {
int n = 0;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "自定义线程" + n++);
}
});
// 1s后,每隔2s执行一次任务
ses.scheduleAtFixedRate(new MyRunnable2(1), 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("main");
}
}
class MyRunnable2 implements Runnable {
private int id;
public MyRunnable2(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行了任务" + id);
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

Java内置线程池-异步计算结果Future
有些场景中,我们需要利用线程进行一些计算,然后获取计算结果,Future接口就是专门用于描述异步计算结果的,我们可以通过Future对象获取线程计算的结果。Future常用方法如下;

- boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)
取消任务的执行,如果成功取消,则返回true,如果取消失败(如任务已经执行完了), 则返回false。参数为true,表示如果当前任务正在执行,则中断任务,false则不中断任务。
例子
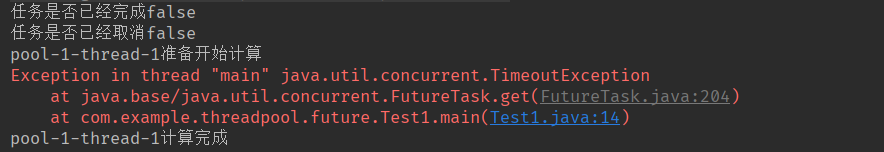
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<Integer> res = es.submit(new MyCallable(1, 2));
System.out.println("任务是否已经完成" + res.isDone());
System.out.println("任务是否已经取消" + res.isCancelled());
// 一直等到任务执行完成为止
//System.out.println("任务执行结果是" + res.get());
// 只等待1s,如果1s任务还没完成,就抛出TimeoutException
System.out.println("任务执行结果是" + res.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("任务是否已经完成" + res.isDone());
}
}
class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
private int a;
private int b;
public MyCallable(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public Integer call() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + "准备开始计算");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(name + "计算完成");
return a + b;
}
}
案例1

// 任务类:包含商品数量、客户名、送手机的行为
public class MyTask implements Runnable{
// 商品数量
private static int id = 10;
// 用户名
private String userName;
public MyTask(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(userName + "正在使用" + name + "参与秒杀");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (MyTask.class) {
if(id > 0) {
System.out.println(userName + "秒杀商品" + id-- + "成功");
}else{
System.out.println(userName + "秒杀商品" + id-- + "失败");
}
}
}
}
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(15));
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
pool.submit(new MyTask("客户" + i));
}
pool.shutdown();
}
}
案例2

public class MyTask implements Runnable{
// 用户名
private String username;
// 取款金额
private double money;
// 总金额
private static double total = 1000d;
public MyTask(String username, double money) {
this.username = username;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(username + "准备使用线程" + name + "取款" + money + "元");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (MyTask.class) {
if(total - money > 0) {
System.out.println(username + "取款" + money + "元成功");
}else{
System.out.println(username + "取款" + money + "元失败");
}
total -= money;
}
}
}
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2, new ThreadFactory() {
int id = 1;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "ATM" + id++);
}
});
for(int i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {
pool.submit(new MyTask("客户" + i, 800));
}
pool.shutdown();
}
}























 1585
1585

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








