文章目录
1.小波变换
代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def Normalize(x):
ymax = 255
ymin = 0
xmax = x.max()
xmin = x.min()
return (ymax-ymin)*(x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin) + ymin
def dwt_init(x):
x01 = x[:, :, 0::2, :] / 2
x02 = x[:, :, 1::2, :] / 2
x1 = x01[:, :, :, 0::2]
x2 = x02[:, :, :, 0::2]
x3 = x01[:, :, :, 1::2]
x4 = x02[:, :, :, 1::2]
x_LL = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4
x_HL = -x1 - x2 + x3 + x4
x_LH = -x1 + x2 - x3 + x4
x_HH = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4
return torch.cat((x_LL, x_HL, x_LH, x_HH), 0)
# 使用哈尔 haar 小波变换来实现二维离散小波
def iwt_init(x):
r = 2
in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = x.size()
out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width = int(in_batch/(r**2)),in_channel, r * in_height, r * in_width
x1 = x[0:out_batch, :, :] / 2
x2 = x[out_batch:out_batch * 2, :, :, :] / 2
x3 = x[out_batch * 2:out_batch * 3, :, :, :] / 2
x4 = x[out_batch * 3:out_batch * 4, :, :, :] / 2
h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height,
out_width]).float().to(x.device)
h[:, :, 0::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4
h[:, :, 1::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 + x3 - x4
h[:, :, 0::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 - x3 - x4
h[:, :, 1::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4
return h
class DWT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DWT, self).__init__()
self.requires_grad = False # 信号处理,非卷积运算,不需要进行梯度求导
def forward(self, x):
return dwt_init(x)
class IWT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(IWT, self).__init__()
self.requires_grad = False
def forward(self, x):
return iwt_init(x)
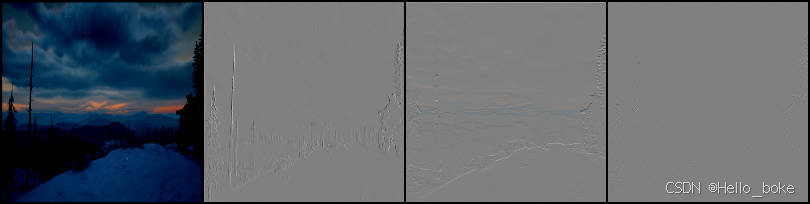
原始图像:
小波变换图像:
小波逆变换图像:
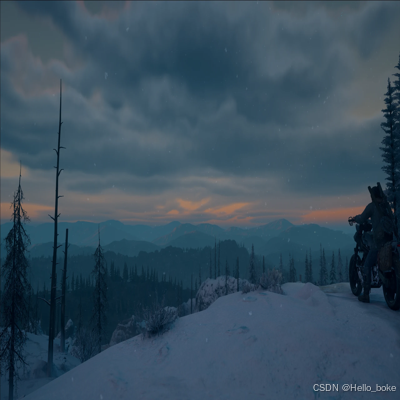
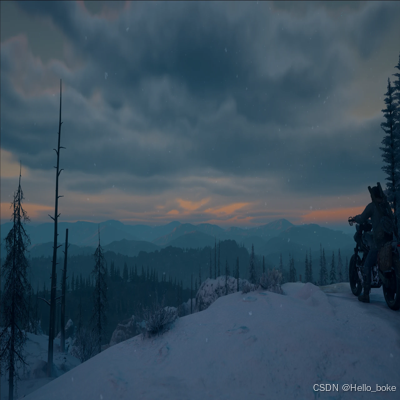






















 542
542

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








