一,纯虚函数:没有函数体的虚函数
abstract_base.h
/**
* C++中的纯虚函数(或抽象函数)是我们没有实现的虚函数!我们只需声明它!通过声明中赋值0来声明纯虚函数!
* 纯虚函数:没有函数体的虚函数
*/
/**
* 抽象类
*/
class AbstractBase {
public:
// 纯虚函数
virtual void show() = 0;
}
abstract.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
virtual void f() = 0; //纯虚函数
void g() { this-> f(); }
A() {}
};
class B: public A {
public:
// 实现父类A中的虚函数
void f() {
cout << "B:f()" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
B b;
b.g();
return 0;
}
编译运行

二,抽象类由派生类集成实现!
derived_full.cpp
/**
* 抽象类由派生类集成实现!
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
int x;
public:
virtual void fun() = 0;
int getX() {return x;}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void fun() {cout << "fun() called" << endl; } //实现fun()函数
};
int main(void) {
Derived d;
d.fun(); // 不是new出来的,用.
return 0;
}

三,抽象类可以有构造函数
interesting_facts1.cpp
/**
* 纯虚函数使一个类变成抽象类
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* 抽象类至少包含一个纯虚函数
*/
class Test {
int x;
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
int getX() {return x;}
};
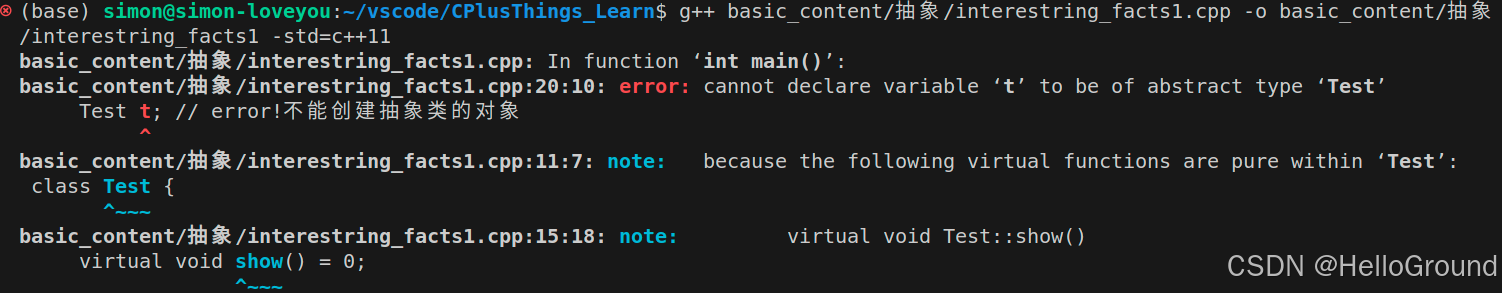
int main(void) {
Test t; // error!不能创建抽象类的对象
return 0;
}
四, 抽象类类型的指针和引用
interesting_facts2.cpp
/**
* 抽象类类型的指针和引用
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* 抽象类至少包含一个纯虚函数
*/
class Base {
int x;
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
int getX() { return x; }
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void show() { cout << "In derived \n"; }
Derived() {}
};
int main(void) {
// Base b; // error! 不能创建抽象类的对象
// Base *b = new Base(); error!
Base *bp = new Derived(); //抽象类的指针与引用 -> 由抽象类派生出来的类的对象
bp->show();
return 0;
}

五,如果我们不在派生类中覆盖纯虚函数,那么派生类也会变成抽象类
interesting_facts3.cpp
/**
* 如果我们不在派生类中覆盖纯虚函数,那么派生类也会变成抽象类
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
int x;
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
int getX() { return x; }
};
/**
* Derived 自动变为抽象类
*/
class Derived : public Base {
public:
// void show() {}
};
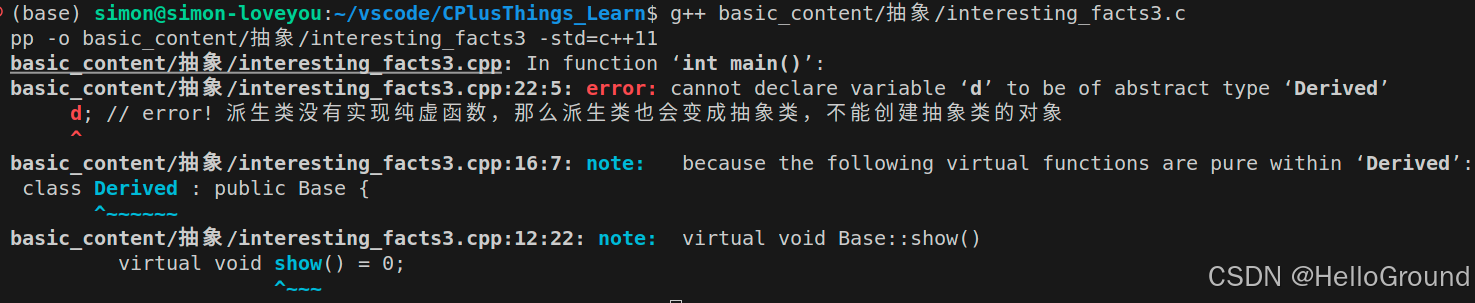
int main(void) {
Derived
d; // error! 派生类没有实现纯虚函数,那么派生类也会变成抽象类,不能创建抽象类的对象
return 0;
}
六,抽象类可以有构造函数
interesting_facts4.cpp
/**
* 抽象类可以有构造函数
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// An abstract class with constructor
class Base {
protected:
int x;
public:
virtual void fun() = 0;
// 抽象类的构造函数
Base(int i) { x = i; }
};
class Derived : public Base {
int y;
public:
// 调用父类构造函数
Derived(int i, int j) : Base(i) { y = j; }
// 实现父类抽象函数
void fun() { cout << "x = " << x << ", y = " << y; }
};
int main(void) {
Derived d(4, 5);
d.fun();
return 0;
}

七,构造函数不能是虚函数,而析构函数可以是虚析构函数。
interesting_facts5.cpp
/**
* 构造函数不能是虚函数,而析构函数可以是虚析构函数。
* 例如:当基类指针指向派生类对象并删除对象时,我们可能希望
* 调用适当的析构函数。如果析构函数不是虚拟的,则只能调用基类的析构构函数。
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
Base() { cout << "Constructor: Base" << endl; }
virtual ~Base() { cout << "Destructor: Base" << endl; }
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
Derived() { cout << "Constructor: Derived" << endl; }
~Derived() { cout << "Destructor: Derived" << endl; }
};
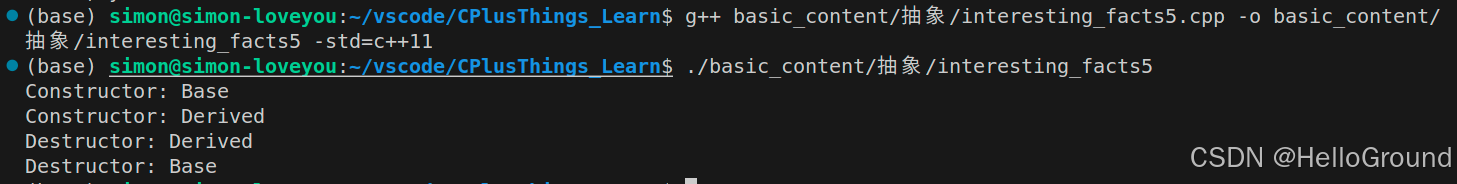
int main() {
Base *Var = new Derived();
delete Var;
return 0;
}
八, 纯虚函数:没有函数体的虚函数。抽象类:包含纯虚函数的类
pure_virtual.cpp
/**
* 纯虚函数:没有函数体的虚函数
* 抽象类:包含纯虚函数的类
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
private:
int a;
public:
virtual void show() = 0; // 纯虚函数
};
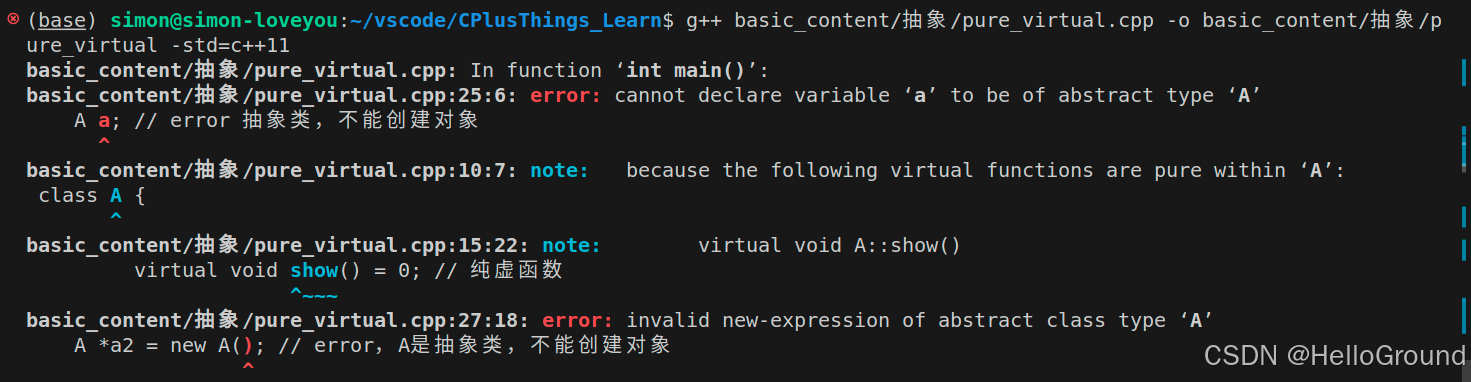
int main() {
/**
* 1. 抽象类只能作为基类来派生新类使用
* 2. 抽象类的指针和引用->由抽象类派生出来的类的对象!
*/
A a; // error 抽象类,不能创建对象
A *a1; // ok 可以定义抽象类的指针
A *a2 = new A(); // error,A是抽象类,不能创建对象
}




















 2054
2054

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








