本文介绍Spring框架的几个日常开发重要扩展接口,方便日常项目中按需扩展使用。
一、Processor 系列接口
用途: Processor 系列接口包括 BeanPostProcessor 和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,它们的设计目的是在 Spring 容器启动过程中对 Bean 和 BeanFactory 进行自定义处理,实现一些额外的逻辑。加深理解SpringBean的生命周期理解,以及扩展更多自定义实现。

BeanPostProcessor该接口目前有两个方法:
-
postProcessBeforeInitialization 该在初始化方法之前调用。
-
postProcessAfterInitialization 该方法再初始化方法之后调用。
源码如下:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor <i>before the target bean gets instantiated</i>.
* The returned bean object may be a proxy to use instead of the target bean,
* effectively suppressing default instantiation of the target bean.
* <p>If a non-null object is returned by this method, the bean creation process
* will be short-circuited. The only further processing applied is the
* {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization} callback from the configured
* {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors}.
* <p>This callback will be applied to bean definitions with their bean class,
* as well as to factory-method definitions in which case the returned bean type
* will be passed in here.
* <p>Post-processors may implement the extended
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor} interface in order
* to predict the type of the bean object that they are going to return here.
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code null}.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to expose instead of a default instance of the target bean,
* or {@code null} to proceed with default instantiation
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessAfterInstantiation
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#getBeanClass()
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#getFactoryMethodName()
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Perform operations after the bean has been instantiated, via a constructor or factory method,
* but before Spring property population (from explicit properties or autowiring) occurs.
* <p>This is the ideal callback for performing custom field injection on the given bean
* instance, right before Spring's autowiring kicks in.
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}.
* @param bean the bean instance created, with properties not having been set yet
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return {@code true} if properties should be set on the bean; {@code false}
* if property population should be skipped. Normal implementations should return {@code true}.
* Returning {@code false} will also prevent any subsequent InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* instances being invoked on this bean instance.
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean, without any need for property descriptors.
* <p>Implementations should return {@code null} (the default) if they provide a custom
* {@link #postProcessPropertyValues} implementation, and {@code pvs} otherwise.
* In a future version of this interface (with {@link #postProcessPropertyValues} removed),
* the default implementation will return the given {@code pvs} as-is directly.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} which proceeds with the existing properties
* but specifically continues with a call to {@link #postProcessPropertyValues}
* (requiring initialized {@code PropertyDescriptor}s for the current bean class)
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @since 5.1
* @see #postProcessPropertyValues
*/
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean. Allows for checking whether all dependencies have been
* satisfied, for example based on a "Required" annotation on bean property setters.
* <p>Also allows for replacing the property values to apply, typically through
* creating a new MutablePropertyValues instance based on the original PropertyValues,
* adding or removing specific values.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code pvs} as-is.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param pds the relevant property descriptors for the target bean (with ignored
* dependency types - which the factory handles specifically - already filtered out)
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} to skip property population
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessProperties
* @see org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues
* @deprecated as of 5.1, in favor of {@link #postProcessProperties(PropertyValues, Object, String)}
*/
@Deprecated
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
}
案例一:获取当前项目启动过程中所有的实现扩展实现类。
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SkywalkApplication.class, args);
String[] beanNames = context.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for(String bean:beanNames){
System.out.println("实现后置处理器:"+bean);
}
运行如下:


案例二:监控Bean的初始化信息例如最耗时的Bean。
package com.boot.skywalk.processor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* 通用的Bean的后置处理器统计最耗时的Bean
*/
@Component
public class CommonBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 初始化前的Map,Bean->时间点
*/
private static final Map<String,Long> BEGIN_INIT_MAP=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 初始化后的Map,Bean->时间点
*/
private static final Map<String,Long> INIT_COST_MAP=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 最耗时的Bean
*/
private static final int TOP_COST_INIT_BEAN=3;
/**
* Bean初始化之前
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
BEGIN_INIT_MAP.putIfAbsent(beanName, System.currentTimeMillis());
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Long initPoint = BEGIN_INIT_MAP.get(beanName);
INIT_COST_MAP.put(beanName, System.currentTimeMillis()-initPoint);
return bean;
}
/**
* 流式获取3,List返回Map.collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue())
* @return
*/
public Map<String,Long> getTopCostInitBean(){
Map<String, Long> result = INIT_COST_MAP.entrySet()
// 降序排列
.stream().sorted((a,b)-> (int) (b.getValue()-a.getValue()))
// 转换Map或者是List<Object[]>
.limit(TOP_COST_INIT_BEAN).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
return result;
}
CommonBeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor= context.getBean(CommonBeanPostProcessor.class);
Map<String, Long> topCostInitBean = beanPostProcessor.getTopCostInitBean();
topCostInitBean.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key+":"+value+"ms");
});

运行截图,可以据此数据来分析项目中哪些Bean可以设置为延迟加载,提高项目启动速度。

BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
Spring 在容器启动时,会检测容器中是否存在实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 Bean,并在 BeanFactory 实例化之后、Bean 实例化之前调用其相应的方法。通过实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,我们可以在容器启动时对 BeanFactory 进行配置,如修改 Bean 的定义、添加 Bean 的属性值等。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
二、Aware 接口
Aware 接口的设计目的是增强 Bean 对容器的感知能力,使 Bean 能够更方便地与容器进行交互,获取容器中的特定资源或实例。
Spring提供了大量以 Aware 命名的接口,如BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware等。
这些接口定义了回调方法,通过这些回调方法,Spring容器可以将容器中的一些资源、状态、环境信息注入到Bean中。
例如:ApplicationContextAware
org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor#invokeAwareInterfaces
首先会判断对象是否属于 Aware接口类型,接着根据不同的Aware接口实现类,调用不同的实现类的逻辑。
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware) {
((ApplicationStartupAware) bean).setApplicationStartup(this.applicationContext.getApplicationStartup());
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
案例一:通过Aware接口获取ApplicationContext和BeanFactory访问容器中其他Bean。
先看相关接口源码,比较简单。
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
public interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware {
/**
* Callback that supplies the owning factory to a bean instance.
* <p>Invoked after the population of normal bean properties
* but before an initialization callback such as
* {@link InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()} or a custom init-method.
* @param beanFactory owning BeanFactory (never {@code null}).
* The bean can immediately call methods on the factory.
* @throws BeansException in case of initialization errors
* @see BeanInitializationException
*/
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
@Service
public class HomeApplicationContextAwareService implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
}
public void getBean(){
Home home = (Home)applicationContext.getBean("home");
home.test();
}
}
@Service
public class HomeBeanFactoryAwareService implements BeanFactoryAware {
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory=beanFactory;
}
public void getBean(){
Home bean = (Home) beanFactory.getBean("home");
bean.test();
}
}
三、ImportSelector 接口
用途: ImportSelector 接口的设计目的是允许在配置类中根据条件动态选择需要导入的其他配置类,以实现模块化和条件化配置。
常见应用场景:
- 根据不同的环境条件选择性地导入不同的配置类。
- 实现特定模块的自动配置功能,根据用户的配置情况动态加载相应的配置类。
源码如下:
public interface ImportSelector {
/**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
* @return the class names, or an empty array if none
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata);
/**
* Return a predicate for excluding classes from the import candidates, to be
* transitively applied to all classes found through this selector's imports.
* <p>If this predicate returns {@code true} for a given fully-qualified
* class name, said class will not be considered as an imported configuration
* class, bypassing class file loading as well as metadata introspection.
* @return the filter predicate for fully-qualified candidate class names
* of transitively imported configuration classes, or {@code null} if none
* @since 5.2.4
*/
@Nullable
default Predicate<String> getExclusionFilter() {
return null;
}
}
案例一:注入指定的Bean
public class ConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{EmailService.class.getName(),MessageService.class.getName(),PhoneService.class.getName()};
}
}
@Import(ConfigurationImportSelector.class)
@Configuration
public class ServiceConfiguration {
}
public interface ConfigurationService {
void doService();
}
public class EmailService implements ConfigurationService{
@Override
public void doService() {
System.out.println("Email Service");
}
}
public class MessageService implements ConfigurationService{
@Override
public void doService() {
System.out.println("Message Service");
}
}
public class EmailService implements ConfigurationService{
@Override
public void doService() {
System.out.println("Email Service");
}
}

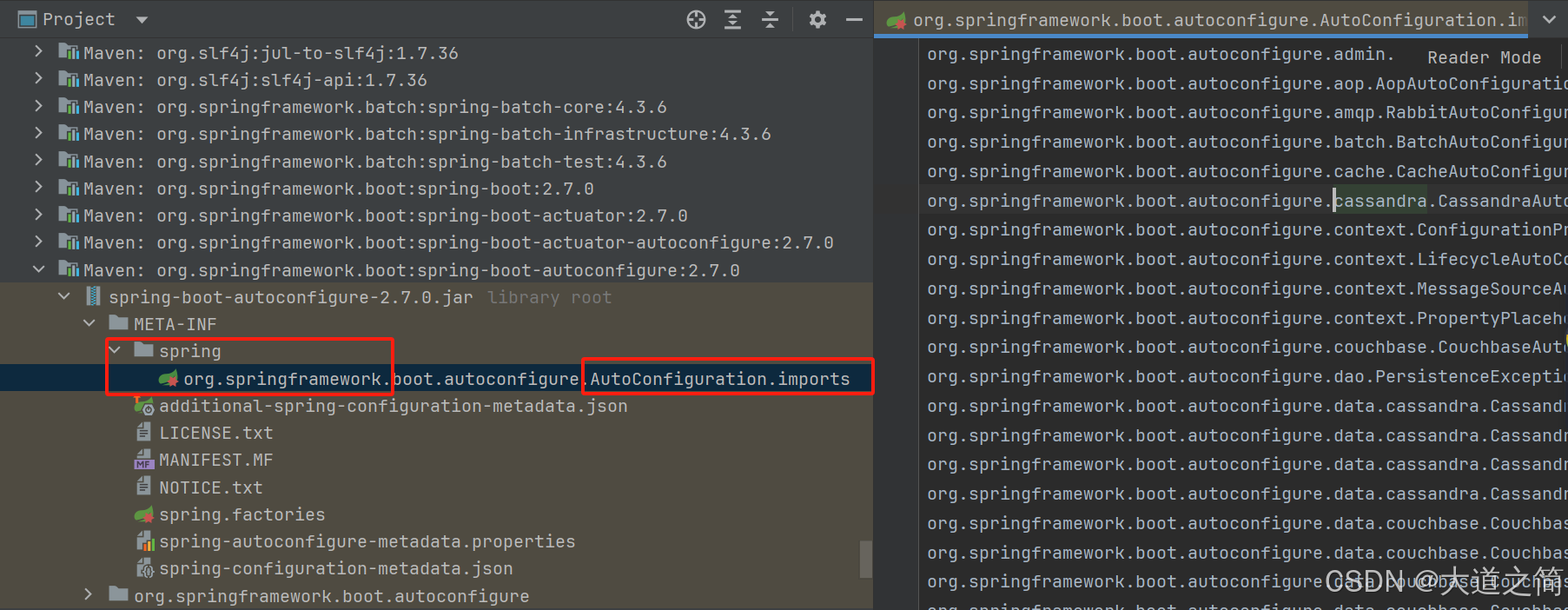
案例二:SpringBoot的底层Import注解实现的自动配置扫描实现

跟进入。





点进去,这些自动配置的类都要注入到Spring容器中。
【附录】
Spring Boot 项目启动时如何排除一个 Bean
1、使用
@Conditional注解
@Conditional 注解是 Spring 框架提供的一个核心注解,它可以根据指定的条件来决定是否注册 Bean。我们可以自定义一个条件类,实现Condition 接口,并在该类的matches 方法中编写判断逻辑。如果条件不满足,则返回false,表示不注册 Bean。
假设我们有一个名为MyBean 的类,我们希望只有在某个配置属性my.feature.enabled 为true 时才注册它。我们可以创建一个条件类MyFeatureCondition:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
public class MyFeatureCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 获取配置属性的值
boolean enabled = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("my.feature.enabled", Boolean.class);
// 如果配置属性为 true,则注册 Bean
return enabled;
}
}
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
@Conditional(MyFeatureCondition.class)
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
}
这样,只有当my.feature.enabled 为true 时,MyBean 才会被注册到 Spring 容器中。
2、使用
@Profile注解
@Profile 注解可以用来指定 Bean 只在特定的环境配置下注册。我们可以为不同的环境(如开发环境、测试环境、生产环境)定义不同的配置文件,并在配置文件中指定激活的环境。
假设我们有一个名为DevBean 的类,我们希望它只在开发环境中注册。我们可以在application-dev.properties 配置文件中定义开发环境的配置,并在DevBean 类上使用@Profile 注解:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
@Profile("dev")
public DevBean devBean() {
return new DevBean();
}
}
然后,在启动应用程序时,通过指定spring.profiles.active=dev 来激活开发环境,DevBean 就会被注册到 Spring 容器中。如果激活其他环境,则DevBean 不会被注册。
3、使用
@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解
@ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解可以用来指定只有在容器中不存在某个 Bean 时,才注册当前 Bean。这在我们想要提供一个默认的 Bean 实现,但又允许用户自定义实现时非常有用。
假设我们有一个名为MyService 的接口,我们提供了一个默认的实现DefaultMyService,但用户可以自定义实现CustomMyService。我们可以在DefaultMyService 上使用@ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MyService defaultMyService() {
return new DefaultMyService();
}
}
这样,如果用户没有自定义MyService 的实现,DefaultMyService 就会被注册到 Spring 容器中。如果用户定义了CustomMyService,则DefaultMyService 不会被注册。
4、使用
@ComponentScan注解的excludeFilters属性
@ComponentScan 注解的excludeFilters 属性可以用来指定扫描时需要排除的类或类名。我们可以使用@ComponentScan 注解来配置组件扫描,并通过excludeFilters 属性排除特定的 Bean。
假设我们有一个名为MyComponent 的类,我们希望在组件扫描时排除它。我们可以在配置类上使用@ComponentScan 注解,并设置excludeFilters 属性:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(
basePackages = "com.example",
excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = MyComponent.class)
)
public class MyConfig {
// 其他配置...
}
这样,在扫描com.example 包下的类时,MyComponent 就会被排除,不会被注册到 Spring 容器中。
























 756
756

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










