一个api在线文档地址 http://tool.oschina.net/apidocs/apidoc?api=jdk-zh
简介
集合框架的由来:数据多了用对象进行存储,对象多了用集合来进行存储。而存储数据的方式(数据结构)各有不同,所以存储的容器也就有多种,从而形成了集合框架这一体系
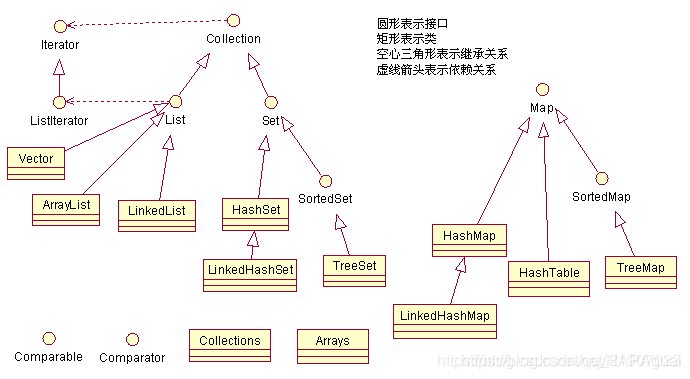
集合的的三种遍历方式(foreach,迭代器)
Collection c=new ArrayList<>();
c.add(23);
c.add(22);
c.add(25);
c.add(24);
c.add(35);
增强for循环:
for (Object object : c) {
System.out.println(object);
}
迭代器是集合所特有的遍历方式
Iterator it= c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
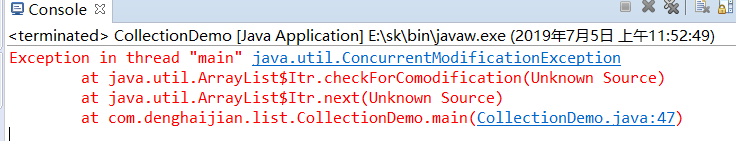
集合的remover方法和迭代器的remover方法的区别
集合的remover方法会出现一个并发问题
代码如下:
Iterator it= c.iterator();//创建迭代器
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
int num=(int) it.next();
if(num%2==0) {
System.out.println(it.next());
c.remove(num);
}
}
正确写法:
Iterator it= c.iterator();//创建迭代器
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
int num=(int) it.next();
if(num%2==0) {
System.out.println(it.next());
it.remove();
}
}
集合框架集合框架List(ArrayList特有方法、特有迭代器、具体对象特点、增长因子论证)
提供ArrayList的方法
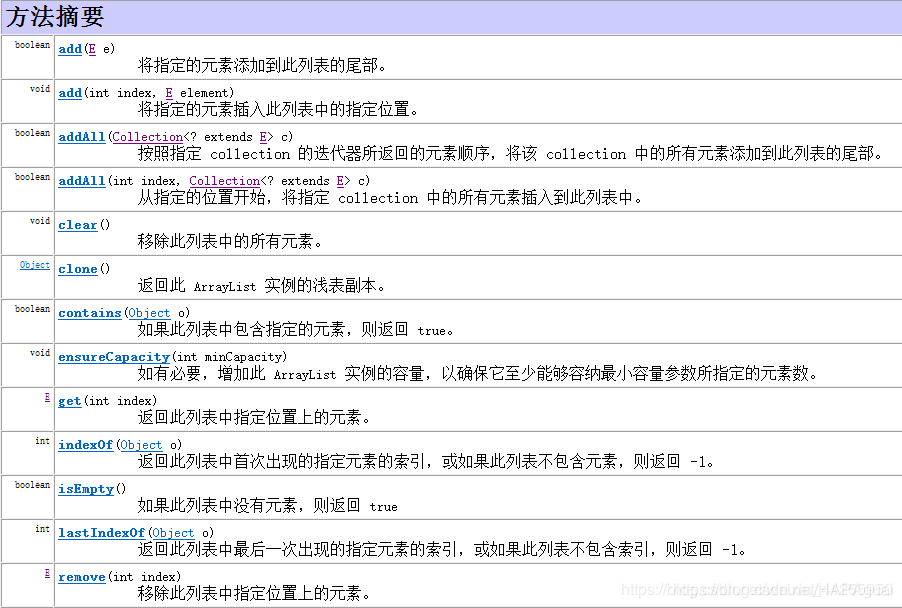
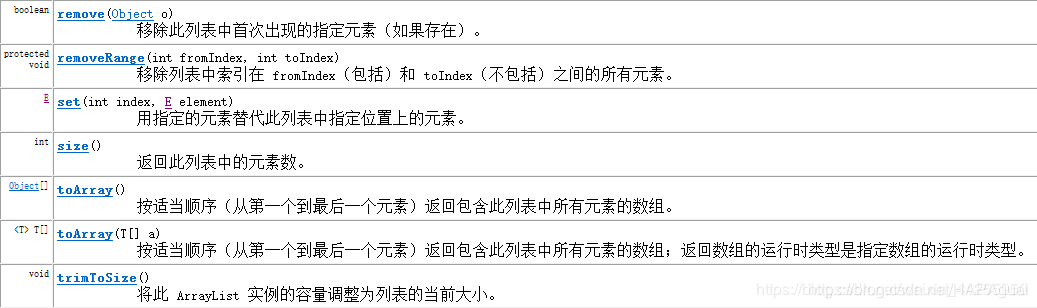
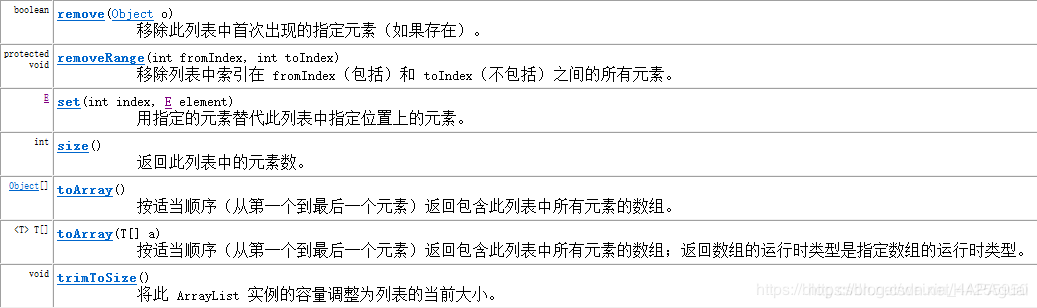
在其中可看到add(int index,E element) 和 remover(int index) 方法都是带有一个int类型的参数,可以看到这类的容器是有下标,可以按照下标去取、删除…等等的方式去操作容器的元素
特有迭代器
List l=new ArrayList<>();
l.add(18);
l.add(21);
l.add(26);
l.add(28);
l.add(33);
再来一个迭代器
Iterator it=l.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
运行结果ArrayList是由下标的
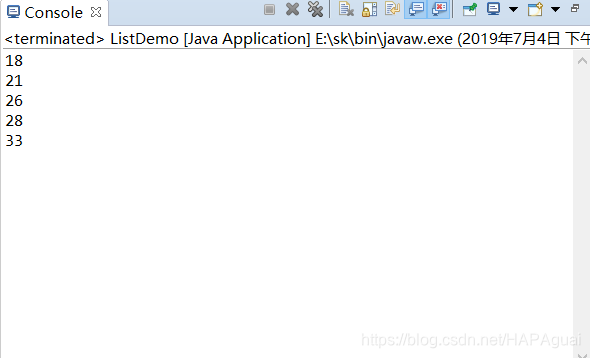
这个是从上往下便利和从下往上遍历:
ListIterator it=l.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()
) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("-------");
while(it.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.println(it.previous());
}
运行结果:
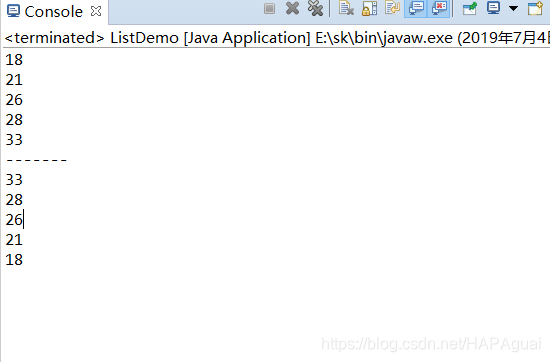
有个问题
必须要从上往下遍历了才能从下往上遍历,
否则运行会没有东西出来
具体对象特点,增长因子论证
3.1具体对象的特点
List的三个子类的特点:
①Arraylist:
数组结构 增删慢,查询快 有连续下标 线程不同步 增长因子为1.5 10
② Vector:
数组结构 增删改查都慢 有连续下标 线程同步 增长因子2 10
Vector相对ArrayList查询慢(线程安全的)
Vector相对LinkedList增删慢(数组结构)
③Linkedlist:
链表结构 增删快,查询慢 没有连续下标
3.2增长因子论证
在主方法中写入如下代码:
ArrayList al=new ArrayList<>(50);
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
al.add(i);
System.out.println(i+",");
getLen(al);
}
在主方法外面写一个方法:
public static void getLen(ArrayList al) {
try {
Field f=al.getClass().getDeclaredField("elementData");
f.setAccessible(true);
Object obj=f.get(al);
Object [] elementData=(Object[]) obj;
System.out.println("底层数组的长度:"+elementData.length);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
集合框架LinkedList
1.通过linkedList集合来制作一个堆栈结构的容器
2. 获取制作一个队列制作的结构的容器,
先理解LinkedList集合
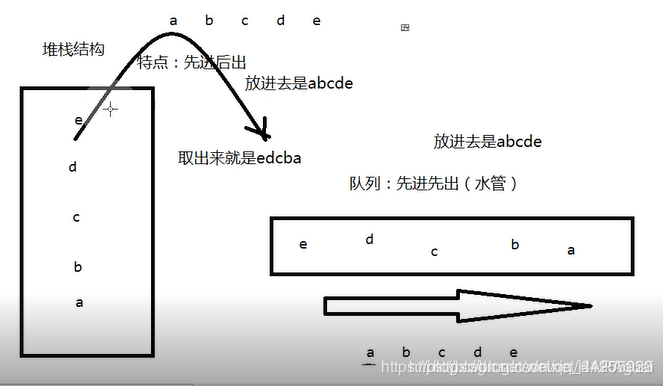
堆栈(先进后出)
代码如下:
class DuiZhan{ private LinkedList ll=new LinkedList<>();
public void push(Object obj) {
ll.addFirst(obj);
}
public Object pop() {
return ll.removeFirst();
}
public void bianli() {
Iterator it=ll.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
队列
代码如下:
Duilie dl=new Duilie();
dl.push(“a”);
dl.push(“b”);
dl.push(“c”);
dl.push(“d”);
dl.push(“e”);
dl.bianli();
再写一个方法:
class Duilie{
private LinkedList ll=new LinkedList<>();
public void push(Object obj) {
ll.addLast(obj);
}
public Object pop() {
return ll.removeFirst();
}
public void bianli() {
Iterator it=ll.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
集合框架ArrayList中的重复元素去重及其底层原理
元素是字符串
代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al=new ArrayList<>();
al.add("a");
al.add("b");
al.add("c");
al.add("d");
al.add("a");
ArrayList newAl=repeat(al);
System.out.println(newAl.size());
}
再定义一个方法:
public static ArrayList repeat(ArrayList al) {
ArrayList newAl = new ArrayList<>();
for (Object obj : al) {
if(!newAl.contains(obj)) {
newAl.add(obj);
}
}
return newAl;
}
}
元素是自定义对象
代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al=new ArrayList<>();
al.add(new Person("wanting", 18));
al.add(new Person("zhuangyaun", 20));
al.add(new Person("xiang", 30));
al.add(new Person("runchen", 19));
al.add(new Person("xiang", 30));
System.out.println(al.size());
}
在定义一个方法:
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
super();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Person p = (Person) obj;
// System.out.println(p.name+"---equals---"+this.name);
return p.name.equals(this.name)/* && p.age == this.age*/;
}
}







 本文深入解析了集合框架的起源、核心概念、遍历方式及不同集合类的特点,包括ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector的内部机制、增长策略及应用场合,同时探讨了集合去重方法及其实现原理。
本文深入解析了集合框架的起源、核心概念、遍历方式及不同集合类的特点,包括ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector的内部机制、增长策略及应用场合,同时探讨了集合去重方法及其实现原理。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








