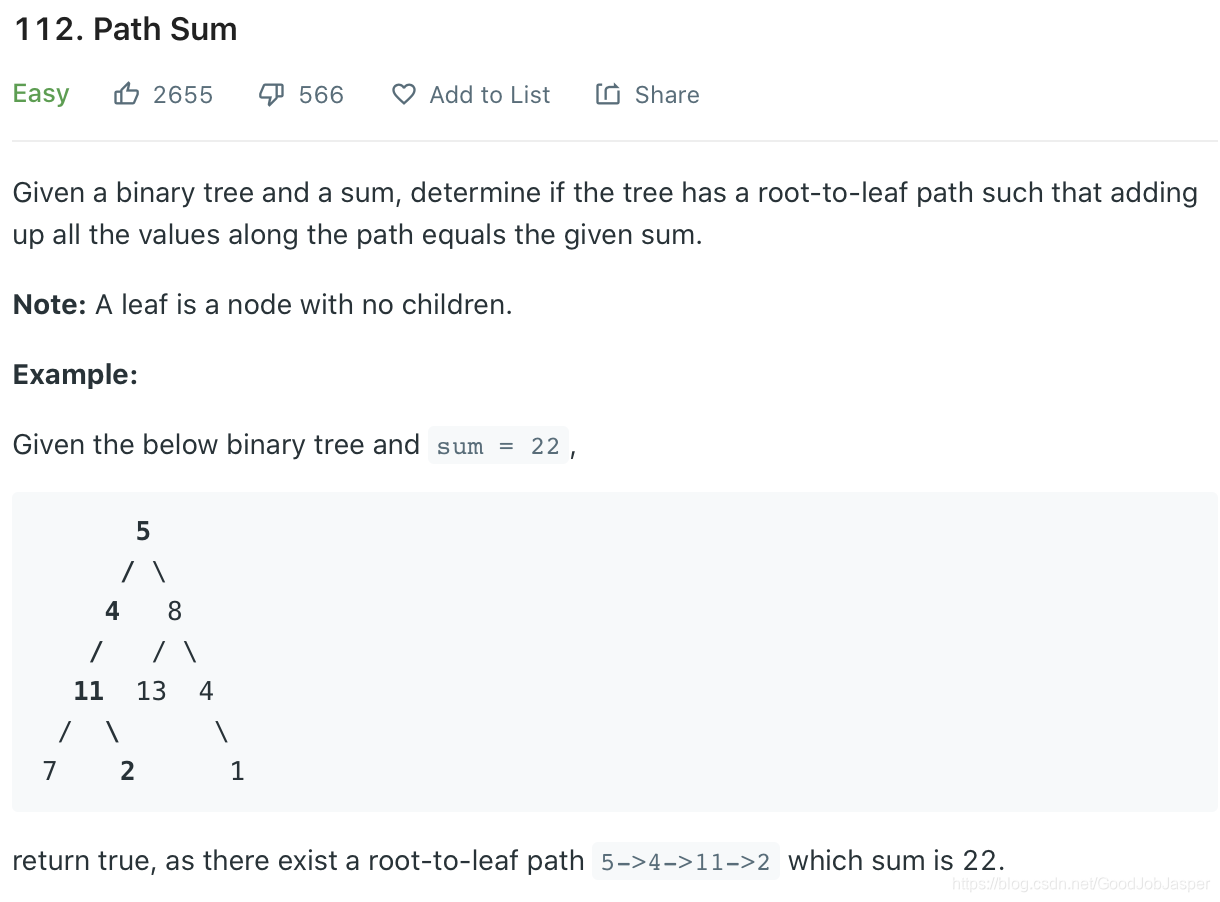
方法1: recursion,其实也是dfs。时间复杂n,空间复杂logn。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root == null) return false;
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
if(left == null && right == null && root.val == sum) return true;
return hasPathSum(left, sum-root.val) || hasPathSum(right, sum-root.val);
}
}
方法2: dfs using stack/iteration。这边依旧是用了两个stack,一个用来装treenode,另一个用来存储curr_sum。时间复杂n,空间复杂logn。
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<Integer> sums = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(root);
sums.push(sum);
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&(root!=null)){
int value = sums.pop();
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
if(top.left==null&&top.right==null&&top.val==value){
return true;
}
if(top.right!=null){
stack.push(top.right);
sums.push(value-top.val);
}
if(top.left!=null){
stack.push(top.left);
sums.push(value-top.val);
}
}
return false;
}
总结:
- 这题dfs其实是preorder traversal。root->left->right。





 本文介绍了两种DFS方法解决二叉树路径和问题,包括递归和迭代版本。通过栈实现的DFS展示了预序遍历过程。时间复杂度均为O(n),空间复杂度为O(logn)。
本文介绍了两种DFS方法解决二叉树路径和问题,包括递归和迭代版本。通过栈实现的DFS展示了预序遍历过程。时间复杂度均为O(n),空间复杂度为O(logn)。
















 577
577

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








