题目描述:
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
输入样例其实为两个字符串,如:[2,4,3] [5,6,4],输出为:[7,0,8]
解题思路:
- 将ListNode链先逆序一下再转换成数字类型,根据两个数字相加之后的结果转换成ListNode链即为输出。
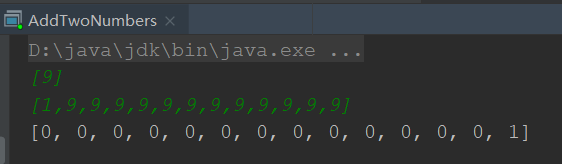
但是输入有可能很长,超出了int的范围,例如:[1] [9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9]。所以这种方法不可取 - 通过仔细观察输入输出样例,发现它和正常的加法很类似。两个数正常相加,从最低位开始相加,如果低位相加之后的数值大于等于10,则向高位进一位。而题目给出的加法是从最高为开始相加,如果高位相加之后的数值大于等于10,则向低位进一位。
在计算的过程中,两个ListNode链从最高位(即ListNode链头部)对应相加,直到某一条链到头为止,然后再依次添加上最长链的每一位。
java代码如下:
/* -----------------------------------
* WARNING:
* -----------------------------------
* Your code may fail to compile
* because it contains public class
* declarations.
* To fix this, please remove the
* "public" keyword from your class
* declarations.
*/
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode list = new ListNode(0);
ListNode r = list;//标记指针,指list头部
list.val = l1.val + l2.val;
if(list.val >= 10) {
list.next = new ListNode(1);
list.val -= 10;
}
while(l1.next != null){
if(l2.next != null){
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
if(list.next != null){
list.next.val += l1.val + l2.val;
}else {
list.next = new ListNode(l1.val + l2.val);
}
} else {//l1比l2长
l1 = l1.next;
if(list.next != null){
list.next.val += l1.val;
} else {
list.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
}
}
list = list.next;
if(list.val >= 10) {
list.next = new ListNode(1);
list.val -= 10;
}
}
while(l2.next != null){//l2比l1长
l2 = l2.next;
if(list.next != null){
list.next.val += l2.val;
} else {
list.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
}
list = list.next;
if(list.val >= 10) {
list.next = new ListNode(1);
list.val -= 10;
}
}
return r;
}
}
public class AddTwoNumbers {
public static int[] stringToIntegerArray(String input) {
input = input.trim();
input = input.substring(1, input.length() - 1);
if (input.length() == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
String[] parts = input.split(",");
int[] output = new int[parts.length];
for (int index = 0; index < parts.length; index++) {
String part = parts[index].trim();
output[index] = Integer.parseInt(part);
}
return output;
}
public static ListNode stringToListNode(String input) {
// Generate array from the input
int[] nodeValues = stringToIntegerArray(input);
// Now convert that list into linked list
ListNode dummyRoot = new ListNode(0);
ListNode ptr = dummyRoot;
for (int item : nodeValues) {
ptr.next = new ListNode(item);
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return dummyRoot.next;
}
public static String listNodeToString(ListNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return "[]";
}
String result = "";
while (node != null) {
result += Integer.toString(node.val) + ", ";
node = node.next;
}
return "[" + result.substring(0, result.length() - 2) + "]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
ListNode l1 = stringToListNode(line);
line = in.readLine();
ListNode l2 = stringToListNode(line);
ListNode ret = new Solution().addTwoNumbers(l1, l2);
String out = listNodeToString(ret);
System.out.print(out);
}
}
}
测试结果





 本文介绍了一种解决链表加法问题的方法,通过遍历两个链表并逐位相加,处理进位,最终生成新的链表作为结果。讨论了如何避免整数溢出,并提供了详细的Java代码实现。
本文介绍了一种解决链表加法问题的方法,通过遍历两个链表并逐位相加,处理进位,最终生成新的链表作为结果。讨论了如何避免整数溢出,并提供了详细的Java代码实现。
















 486
486

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








