卷积神经网络Convolution Neural Network
简答介绍
* CNN是一个模仿人类视觉原理的一个神经网络。
* 与全连接网络相比,CNN可以更大效率的降低参数的数量。
* 与全连接网络相比,CNN可以更好的提取图像的特征。
# 导入数据
import numpy as np
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.datasets import mnist
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
(train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理
train_data = train_data.reshape(60000, 28, 28, 1)
train_data = train_data.astype("float32") / 255.
test_data = test_data.reshape(10000, 28, 28, 1)
x_test = test_data.astype("float32") / 255.
train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels)
y_test = to_categorical(test_labels)
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(train_data, train_labels, random_state=42, test_size=0.25)Simple CNN
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense
from keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential()
# 第一层使用32个3*3的卷积核
# 要注意CNN的input层要注明通道数的
model.add(Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
# 使用2*2的Maxpooling池化层
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu'))
# Flatten层指的是将上面的卷积层的输出展平,以便后面可以作为全连接层的输入
model.add(Flatten())
# 先查看以上部分的网络的示意图
# 可得 7744=11*11*64是正确的,并且总共参数数量为18816
print(model.summary())
# 继续添加全连接层
model.add(Dense(units=64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(units=10, activation='softmax'))
print(model.summary())
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x=x_train, y=y_train, validation_data=(x_val, y_val), batch_size=128, epochs=20)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
# 经过了20个epoch,模型很快的达到了98.9%的准确率,如果更多点epoch或更深点的模型,达到100%也并非不可能
print(test_acc)卷积网络是如何提取图片特征的?
- CNN通过局部视野,提取局部特征
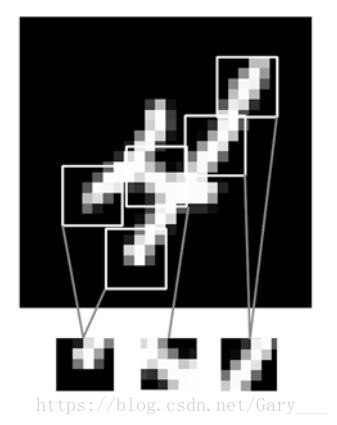
- CNN据具有平移不变性,是全连接网络不具备的,即当一个物体的位置或形状发送了变化,DNN可能就无法准确的检测出来。
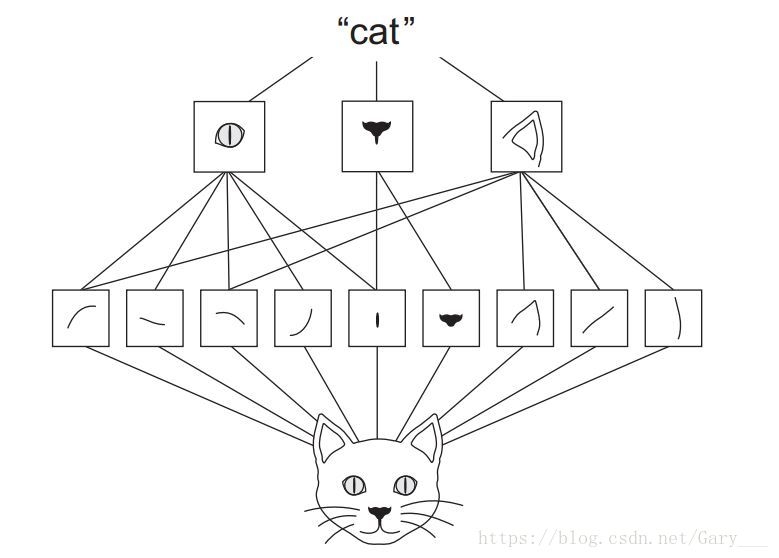
- CNN可以学习到空间层次的特征,可能在较浅的卷积层,学习到的是一些边缘线条,再之后更深的卷积层,学习到更多抽象的特征。
- 卷积是如何计算的,这个其实不难,可以看一下Andrew老师的CNN章节即可看懂。
# 我们来查看模型中间的卷积层学习的特征
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.models import Model
# 获取最后一个卷积层
conv2d_2_model = Model(inputs=model.input, outputs=model.get_layer("conv2d_2").output)
# 找一个样本
plt.imshow(x_train[0].reshape(28, 28))
plt.show()
pred_features = conv2d_2_model.predict(x_train[0].reshape(1, 28, 28, 1))
# 查看特征的shape, 是一个width=11, height=11, channel=64的feature map
pred_features.shape
# 查看前10个特征, 由图中可以看到,每一个feature map所学习的特征大概都不相同,符合了局部特征的提取,最后进行空间层次的组合
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(2, 5, i+1)
plt.imshow(pred_features[0][:,:,i])
plt.show()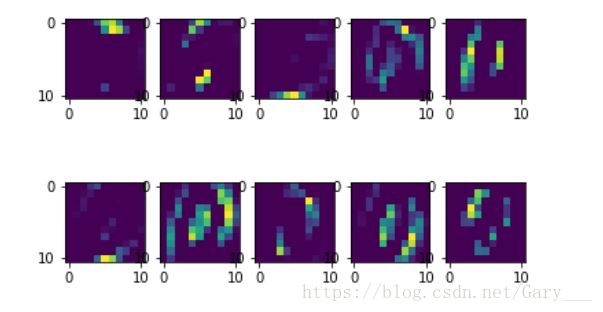
LeNet-5
LeNet-5模型是Yann LeCun教授(卷积神经网络之父)在1998年提出的第一个成功应用在数字识别问题的卷积神经网络。
LeNet-5总共有7层网络,如下图:
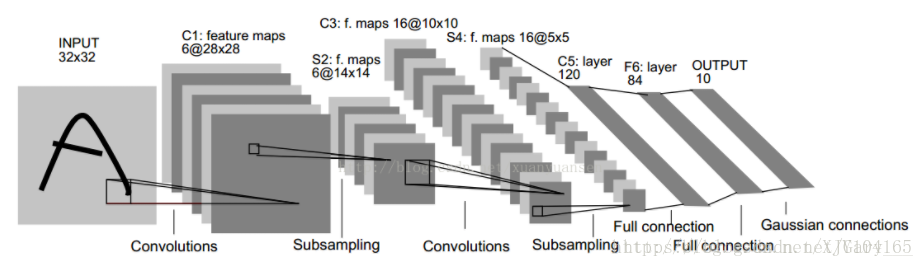
* conv1: kernel_size: 5*5, filters=6, strides=1
* pool1: averagePooling, pool_size:2*2, strides=2
* conv2: kernel_size: 5*5, filters=16, strides=1
* pool2: averagePooling, pool_size=2*2, strides=2
* dense1: units:120
* dense2: units: 84
* dense3: units: 10
# 下面我们使用keras构建一个LeNet模型
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, AveragePooling2D, Flatten
def LeNet():
'''
这个LeNet-5版本可能与LeCun教授的论文不那么一致,如activation等,但都是遵从了大概的结构模型
'''
LeNet_5 = Sequential()
LeNet_5.add(Conv2D(filters=6, kernel_size=(5, 5), activation='relu', strides=1, input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
LeNet_5.add(AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=2))
LeNet_5.add(Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=(5, 5), activation='relu', strides=1))
LeNet_5.add(AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=2))
LeNet_5.add(Flatten())
LeNet_5.add(Dense(units=120, activation='relu'))
LeNet_5.add(Dense(units=84, activation='relu'))
LeNet_5.add(Dense(units=10, activation='softmax'))
return LeNet_5
LeNet = LeNet()
LeNet.summary()
LeNet.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练
LeNet.fit(x=x_train, y=y_train, validation_data=(x_val, y_val), batch_size=128, epochs=10)
test_loss, test_acc = LeNet.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
# 同样地,LeNet在10个epoch后在测试集上达到了98.78%的准确率,并且参数型对于上面的模型更少,且更深。
print(test_acc)






 本文介绍了卷积神经网络(CNN),它模仿人类视觉原理,相比全连接网络能更高效降低参数数量、更好提取图像特征。阐述了CNN提取图片特征的方式,具有平移不变性。还介绍了首个成功用于数字识别的LeNet - 5模型,包含其网络层数及各层参数。
本文介绍了卷积神经网络(CNN),它模仿人类视觉原理,相比全连接网络能更高效降低参数数量、更好提取图像特征。阐述了CNN提取图片特征的方式,具有平移不变性。还介绍了首个成功用于数字识别的LeNet - 5模型,包含其网络层数及各层参数。

















 1146
1146

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








