1、概述
std::future和std::promise是C++11标准库引入的用于处理异步编程模板类,适合线程之间只有1次交互数据的场景。
2、使用方法
1、主线程:创建promise对象
2、主线程:从promise对象获取future对象
3、启动新线程,并把promise对象传给新线程
4、新线程中给promise赋值
5、主线程:调用future的get方法获取结果
备注:
1、对照下面代码一起看,会理解更深刻
2、新线程中给promise赋值,无论成功失败都要给promise设置值,否则future的get方法会抛异常
3、代码
void do_something(std::promise<int> && prom) {
try {
// Simulate some work being done.
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));
// Set the value of the promise, which will be available to the future.
prom.set_value(42);
}
catch (...) {
// If something goes wrong, set an exception.
prom.set_exception(std::current_exception());
}
}
int main()
{
// Create a promise and get its associated future.
std::promise<int> prom;
std::future<int> fut = prom.get_future();
// Launch a thread that will set the value of the promise.
std::thread t(do_something, std::move(prom));
// Wait for the result from the future.
try {
int result = fut.get(); // This will block until the result is available.
std::cout << "Got result: " << result << '\n';
}
catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << '\n';
}
// Join the thread before exiting.
if (t.joinable()) {
t.join();
}
return 0;
}4、future、promise常用方法
promise方法
set_value(T value): 设置 promise 的值。一旦设置,与之关联的 future 就可以获取这个值。
set_exception(std::exception_ptr p): 设置一个异常,如果调用 future 的 get() 方法时,该异常会被重新抛出。
get_future(): 获取一个与该 promise 关联的 future 对象。每个 promise 只能调用一次此方法。
future方法
get():阻塞等待future的结果
wait(): 阻塞当前线程直到 future 的结果变得可用。
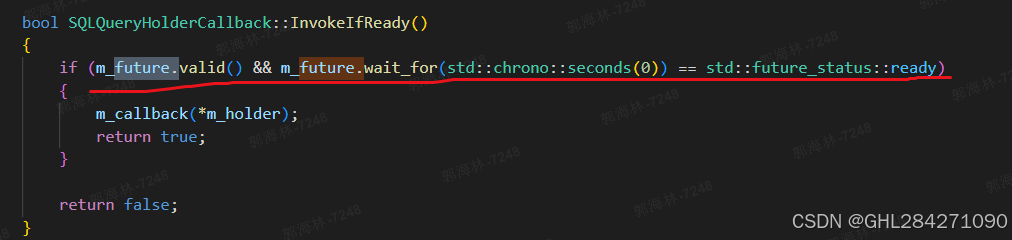
wait_for(const std::chrono::duration& rel_time): 阻塞当前线程,最多等待给定的时间段。返回 std::future_status 枚举值,表示是否超时、就绪或延迟。
wait_until(const std::chrono::time_point& abs_time): 类似于 wait_for,但是它等待直到指定的时间点。
valid(): 检查 future 是否与一个共享状态相关联。只有当 future 是由 std::async、std::promise 或 std::packaged_task 创建时才为真。
学习链接:https://github.com/0voice
























 535
535

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








