Python OpenCV通过灰度平均值进行二值化处理以减少像素误差
前言
前提条件
相关介绍
- Python是一种跨平台的计算机程序设计语言。是一个高层次的结合了解释性、编译性、互动性和面向对象的脚本语言。最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。
实验环境
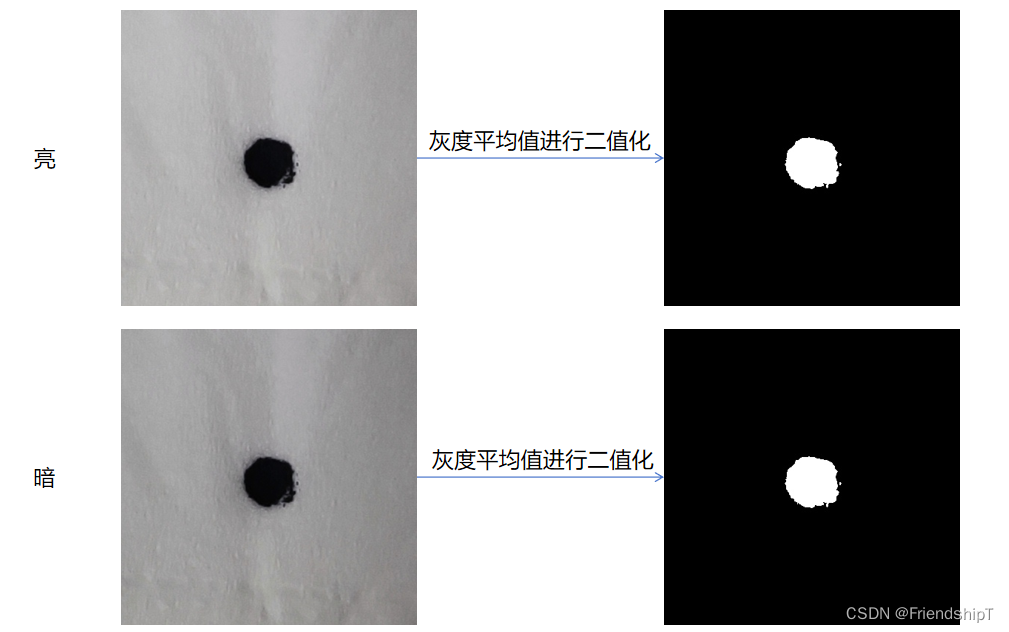
通过灰度平均值进行二值化处理以减少像素误差
- 背景:同一物体(黑色异物)但不同亮度大小的图片,单纯地使用固定阈值的二值化处理,所得到的物体(黑色异物)的像素个数误差较大,实验表明,通过灰度平均值进行二值化处理,可以有效地减少像素个数的误差。
- 亮

- 暗

固定阈值二值化
代码实现
import cv2
import numpy as np
def show(name, img):
cv2.namedWindow(name, 0)
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def count_pix_nums(img_path):
img=cv2.imread(img_path,0)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img,60,255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
pix_nums = np.count_nonzero(thresh)
return pix_nums
if __name__=="__main__":
light_pix_nums = count_pix_nums('imgs/light.jpg')
dark_pix_nums = count_pix_nums('imgs/dark.jpg')
print("亮度较大的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为:",light_pix_nums)
print("亮度较小的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为:",dark_pix_nums)
亮度较大的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为: 3558
亮度较小的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为: 3693
灰度平均值二值化
代码实现
import cv2
import numpy as np
def show(name, img):
cv2.namedWindow(name, 0)
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def count_pix_nums(img_path):
img=cv2.imread(img_path,0)
mean_gray_value = np.mean(img)
threshold_value_bias = 60
threshold_value = mean_gray_value - threshold_value_bias
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img,threshold_value,255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
pix_nums = np.count_nonzero(thresh)
return pix_nums
if __name__=="__main__":
light_pix_nums = count_pix_nums('imgs/light.jpg')
dark_pix_nums = count_pix_nums('imgs/dark.jpg')
print("亮度较大的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为:",light_pix_nums)
print("亮度较小的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为:",dark_pix_nums)
亮度较大的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为: 3950
亮度较小的图,物体(黑色异物)像素个数为: 3948











 该博客围绕Python和OpenCV展开,介绍通过灰度平均值进行二值化处理以减少像素误差。指出同一物体不同亮度大小图片,固定阈值二值化处理像素个数误差大,而灰度平均值二值化可有效减少误差,还给出了固定阈值和灰度平均值二值化的代码实现。
该博客围绕Python和OpenCV展开,介绍通过灰度平均值进行二值化处理以减少像素误差。指出同一物体不同亮度大小图片,固定阈值二值化处理像素个数误差大,而灰度平均值二值化可有效减少误差,还给出了固定阈值和灰度平均值二值化的代码实现。




















 694
694

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










