//有我这么写的嘛 居然过了。。
Treasure Hunt
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 5637 | Accepted: 2343 |
Description
Archeologists from the Antiquities and Curios Museum (ACM) have flown to Egypt to examine the great pyramid of Key-Ops. Using state-of-the-art technology they are able to determine that the lower floor of the pyramid is constructed from a series of straightline
walls, which intersect to form numerous enclosed chambers. Currently, no doors exist to allow access to any chamber. This state-of-the-art technology has also pinpointed the location of the treasure room. What these dedicated (and greedy) archeologists want
to do is blast doors through the walls to get to the treasure room. However, to minimize the damage to the artwork in the intervening chambers (and stay under their government grant for dynamite) they want to blast through the minimum number of doors. For
structural integrity purposes, doors should only be blasted at the midpoint of the wall of the room being entered. You are to write a program which determines this minimum number of doors.
An example is shown below:
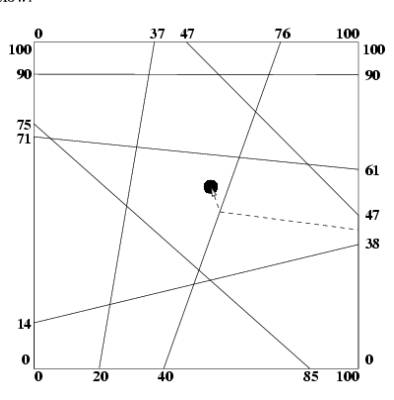
An example is shown below:

Input
The input will consist of one case. The first line will be an integer n (0 <= n <= 30) specifying number of interior walls, followed by n lines containing integer endpoints of each wall x1 y1 x2 y2 . The 4 enclosing walls of the pyramid have fixed endpoints
at (0,0); (0,100); (100,100) and (100,0) and are not included in the list of walls. The interior walls always span from one exterior wall to another exterior wall and are arranged such that no more than two walls intersect at any point. You may assume that
no two given walls coincide. After the listing of the interior walls there will be one final line containing the floating point coordinates of the treasure in the treasure room (guaranteed not to lie on a wall).
Output
Print a single line listing the minimum number of doors which need to be created, in the format shown below.
Sample Input
7 20 0 37 100 40 0 76 100 85 0 0 75 100 90 0 90 0 71 100 61 0 14 100 38 100 47 47 100 54.5 55.4
Sample Output
Number of doors = 2
//Code
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
#include <time.h>
//#include<Windows.h>
//#include <xfunctional>
#define inf 0xfffffff
#define eps 1e-9
#define pi 3.14159265
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL maxn = 37;
//ifstream fin("input.txt");
//ofstream fout("output.txt");
#define Time_counter(){ printf("%d ms.\n", clock()); }
typedef struct Point{
double x, y;
Point(){}
Point(double x, double y){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
}Point;
typedef struct Vec{
double x, y;
Vec(){}
Vec(Point s, Point e){
this->x = e.x - s.x;
this->y = e.y - s.y;
}
}Vec;
bool operator == (Point a, Point b){
return(fabs(a.x - b.x) <= eps && fabs(a.y - b.y) <= eps);
}
Point operator + (Point a, Point b){
return Point(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
Point operator - (Point a, Point b){
return Point(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
double operator * (Vec a, Vec b){
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
double Distance(Point a, Point b){
return sqrtl(powl(a.x - b.x, 2) + powl(a.y - b.y, 2));
}
typedef struct Radial{
Point s;
Vec direc;
Radial(){}
Radial(Point s, Vec v){
this->s = s;
this->direc = v;
}
}Radial;
typedef struct Segment{
Point p[2];
double length;
Segment(){}
Segment(Point a, Point b){
this->p[0] = a;
this->p[1] = b;
this->length = Distance(a, b);
}
Segment(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2){
this->p[0].x = x1;
this->p[0].y = y1;
this->p[1].x = x2;
this->p[1].y = y2;
this->length = Distance(this->p[0], this->p[1]);
}
}Segment;
typedef struct Line{
double a, b, c;
Line(){}
Line(double a, double b, double c){
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
this->c = c;
}
Line(Point p1, Point p2){
this->a = p2.y - p1.y;
this->b = p1.x - p2.x;
this->c = p1.y*(p2.x - p1.x) - p1.x*(p2.y - p1.y);
}
}Line;
double Angle(Vec v1, Vec v2){
return acos(v1*v2 / (sqrt(v1.x*v1.x + v1.y*v1.y)*sqrt(v2.x*v2.x + v2.y*v2.y)));
}
double CrossMulti(Vec a, Vec b){
return a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x;
}
bool isPointOnLine(Point p, Line L){
return fabs(p.x*L.a + p.y*L.b + L.c) <= eps;
}
bool isPointOnSegment(Point p, Segment s){
double length = Distance(s.p[0], s.p[1]);
double len1 = Distance(p, s.p[0]); double len2 = Distance(p, s.p[1]);
return fabs(len1 + len2 - length) <= eps;
}
int isPointInPloygon(Point p0, Point p[], int n){
//p0在多边形上返回1 在外返回2 在内返回0
int cnt = 0; double x_trans;
Point p1 = p[0], p2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
p2 = p[i%n];
Segment s(p1, p2);
if (isPointOnSegment(p0, s))
return 1;
if (p0.y > min(p1.y, p2.y)){
if (p0.y <= max(p1.y, p2.y)){
if (p0.x <= max(p1.x, p2.x)){
if (p1.y != p2.y){
x_trans = p1.x + (p0.y - p1.y)*(p2.x - p1.x) / (p2.y - p1.y);
if (p1.x == p2.x || p0.x <= x_trans)
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
p1 = p2;
}
if (cnt % 2 == 0)
return 2;
return 0;
}
int isLineInter(Line L1, Line L2){
//相交返回1 平行返回-1 重合返回0
double a1 = L1.a, b1 = L1.b, c1 = L1.c;
double a2 = L2.a, b2 = L2.b, c2 = L2.c;
if (fabs(a1*b2 - a2*b1) <= eps){
if (fabs(a1*c2 - a2*c1) <= eps&&fabs(b1*c2 - b2*c1) <= eps)
return 0;
else
return -1;
}
else
return 1;
}
Point LineInter(Line L1, Line L2){
//最好在相交于一点时使用
//如果重合或平行 返回p(inf,inf)即无穷远
double a1 = L1.a, b1 = L1.b, c1 = L1.c;
double a2 = L2.a, b2 = L2.b, c2 = L2.c;
if (isLineInter(L1, L2) == 1){
double x;
if (fabs(b1) <= eps){
x = -c1 / a1;
return Point(x, (-c2 - a2*x) / b2);
}
else{
x = (c1 * b2 - b1 * c2) / (b1 * a2 - b2 * a1);
return Point(x, (-c1 - a1 * x) / b1);
}
}
else
return Point(inf, inf);
}
bool isSegmentInter(Segment s1, Segment s2){
Line L1(s1.p[0], s1.p[1]), L2(s2.p[0], s2.p[1]);
if (isLineInter(L1, L2) == -1)
return 0;
else if (isLineInter(L1, L2) == 0){
return !(!isPointOnSegment(s1.p[0], s2) && !isPointOnSegment(s1.p[1], s2) && !isPointOnSegment(s2.p[0], s1) && !isPointOnSegment(s2.p[1], s1));
}
else{
Point p_Inter = LineInter(L1, L2);
return isPointOnSegment(p_Inter, s1) && isPointOnSegment(p_Inter, s2);
}
}
typedef struct Circle{
Point p_center;
double radius;
Circle(){}
Circle(Point p, double r){
this->p_center = p;
this->radius = r;
}
Circle(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3){
Point p_m1(1.0*(p1.x + p2.x) / 2, 1.0*(p1.y + p2.y) / 2), p_m2(1.0*(p1.x + p3.x) / 2, 1.0*(p1.y + p3.y) / 2);
double k1 = 1.0*(p2.y - p1.y) / (p2.x - p1.x), k2 = 1.0*(p3.y - p1.y) / (p3.x - p1.x);
double k11 = -1.0 / k1, k22 = -1.0 / k2;
Line L1(k11, -1.0, p_m1.y - k11*p_m1.x), L2(k22, -1.0, p_m2.y - k22*p_m2.x);
this->p_center = LineInter(L1, L2);
this->radius = Distance(LineInter(L1, L2), p1);
}
}Circle;
int main(){
int n; cin >> n; int x1, y1, x2, y2; Segment s[maxn];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
s[i] = Segment(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
s[n + 1] = Segment(0, 0, 0, 100); s[n + 2] = Segment(0, 100, 100, 100);
s[n + 3] = Segment(100, 100, 100, 0); s[n + 4] = Segment(100, 0, 0, 0);
double p_cx, p_cy; cin >> p_cx >> p_cy;
Point p_c(p_cx, p_cy); Point p[4] = { Point(0, 0), Point(0, 100), Point(100, 100), Point(100, 0) };
double radius = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
radius = max(radius, Distance(p_c, p[i]));
radius = radius + 1.0;
int ans = inf;
for (int i = 0; i <= 360; i++){
int cnt = 0;
double x = p_cx + radius*cos(1.0*pi*i / 180);
double y = p_cy + radius*sin(1.0*pi*i / 180);
Point p_e(x, y); Segment ra(p_c, p_e);
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 4; j++){
if (isSegmentInter(ra, s[j]))
cnt++;
}
if (ans > cnt)
ans = cnt;
}
cout << "Number of doors = " << ans << endl;
//Time_counter();
return 0;
}






















 334
334

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








