目录
第十六章 异常机制和File类
16.1 异常机制(重点)
16.1.1 基本概念
- 异常就是"不正常"的含义,在Java语言中主要指程序执行中发生的不正常情况。
- java.lang.Throwable类是Java语言中错误(Error)和异常(Exception)的超类。
- 其中Error类主要用于描述Java虚拟机无法解决的严重错误,通常无法编码解决,如:JVM挂掉了 等。
- 其中Exception类主要用于描述因编程错误或偶然外在因素导致的轻微错误,通常可以编码解决, 如:0作为除数等。
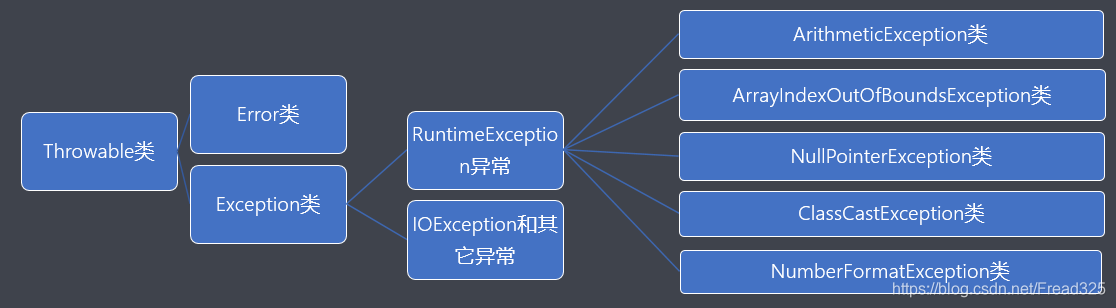
16.1.2 异常的分类
- java.lang.Exception类是所有异常的超类,主要分为以下两种:
RuntimeException - 运行时异常,也叫作非检测性异常
IOException和其它异常 - 其它异常,也叫作检测性异常,所谓检测性异常就是指在编译阶段都能 被编译器检测出来的异常。
- 其中RuntimeException类的主要子类:
ArithmeticException类 - 算术异常
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException类 - 数组下标越界异常
NullPointerException - 空指针异常
ClassCastException - 类型转换异常
NumberFormatException - 数字格式异常
- 注意:
当程序执行过程中发生异常但又没有手动处理时,则由Java虚拟机采用默认方式处理异常,而默认 处理方式就是:打印异常的名称、异常发生的原因、异常发生的位置以及终止程序。
代码: 异常的分类, 测试
package com.lagou.task16;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @date 2020/12/5 16:02
*/
public class ExcepetionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.见识下非检测性异常/运行时异常
// System.out.println(5 /0); // java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero 编译OK,运行阶段会发生算术异常,后续代码不会执行
//2.检测性异常
// Thread.sleep(1000); // java.lang.InterruptedException 编译错误,不处理就无法到运行阶段
System.out.println("程序正常结束!");
}
}16.1.3 异常的避免
- 在以后的开发中尽量使用if条件判断来避免异常的发生。
- 但是过多的if条件判断会导致程序的代码加长、臃肿,可读性差。
代码: 异常的避免 if 语句
package com.lagou.task16;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @date 2020/12/5 16:15
*/
public class ExceptionPreventTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 算术异常 ArithmeticException: / by zero
int ia = 10;
int ib = 0;
if (0 != ib) {
System.out.println(ia / ib);
}
// 数组下标越界异常 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
int[] arr = new int[5];
int pos = 5;
if (pos >= 0 && pos < 5) {
System.out.println(arr[pos]);
}
//空指针异常 NullPointerException
String str = null;
if (null != str) {
System.out.println(str.length());
}
//类型转换异常 ClassCastException: class java.lang.Exception cannot be cast to class java.io.IOException
Exception ex = new Exception();
if (ex instanceof IOException) {
IOException ie = (IOException)ex;
}
//数字格式异常 NumberFormatException: For input string: "123a"
String str2 = "123a";
if (str2.matches("\\d+")) {
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(str2));
}
System.out.println("程序正常结束。");
}
}
16.1.4 异常的捕获
- 语法格式
try {
编写可能发生异常的代码;
}
catch(异常类型 引用变量名) {
编写针对该类异常的处理代码;
}
...
finally {
编写无论是否发生异常都要执行的代码;
}
- 注意事项
a. 当需要编写多个catch分支时,切记小类型应该放在大类型的前面;
b. 懒人的写法:
catch(Exception e) { }
c. finally通常用于进行善后处理,如:关闭已经打开的文件等。
- 执行流程
try {
a;
b; - 可能发生异常的语句
c;
}catch(Exception ex) {
d;
}finally {
e;
}
当没有发生异常时的执行流程:a b c e;
当发生异常时的执行流程:a b d e;
代码: 异常的捕获
package com.lagou.task16;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 15:14
*/
public class ExceptionFinallyTest {
public static int test() {
try {
int[] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println(arr[5]);
return 0 ;
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
}finally {
return 2; // 提前结束方法并返回数据
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int ia = 10;
int ib = 0;
System.out.println(ia / ib);
}catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
String str1 = null;
// str1.length();//NullPointerException
}finally {
System.out.println("无论是否发生异常,都执行。");
}
System.out.println("Over!");
int test = test();
System.out.println("test " + test); // 2
}
}
16.1.5 异常的抛出
- 基本概念
在某些特殊情况下有些异常不能处理或者不便于处理时,就可以将该异常转移给该方法的调用者,
这种方法就叫异常的抛出。当方法执行时出现异常,则底层生成一个异常类对象抛出,
此时异常代码后续的代码就不再执行。
- 语法格式
访问权限 返回值类型 方法名称(形参列表) throws 异常类型1,异常类型2,...{ 方法体; }
如:
public void show() throws IOException{}
- 方法重写的原则
a.要求方法名相同、参数列表相同以及返回值类型相同,从jdk1.5开始支持返回子类类型;
b.要求方法的访问权限不能变小,可以相同或者变大;
c.要求方法不能抛出更大的异常;
- 注意:
子类重写的方法不能抛出更大的异常、不能抛出平级不一样的异常,
但可以抛出一样的异常、更小 的异常以及不抛出异常。
- 经验分享
若父类中被重写的方法没有抛出异常时,则子类中重写的方法只能进行异常的捕获处理。
若一个方法内部又以递进方式分别调用了好几个其它方法,则建议这些方法内可以使用抛出 的方法处理到最后一层进行捕获方式处理。
代码: 异常的抛出, 重写规则,
package com.lagou.task16;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 15:31
*/
public class ExceptionThrowsTest {
public static void show() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/a.txt");
System.out.println("测试异常之后代码是否继续向下执行?"); // 抛出异常后没有执行这个语句
fis.close();
}
public static void test() throws IOException {
show();
}
public static void test1() throws IOException {
test();
}
public static void test2() throws IOException {
test1();
}
//不建议在main方法中抛出异常 JVM负担很重
public static void main(String[] args) /*throws IOException*/ {
try {
show();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//若一个方法内部又以递进方式分别调用了好几个其它方法,则建议这些方法内可以使用抛出 的方法处理到最后一层进行捕获方式处理。
try {
test2();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.lagou.task16;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 15:56
*/
public class ExceptionMethod {
public void show() throws IOException{}
}
package com.lagou.task16;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 15:59
*/
public class SubExceptionMethod extends ExceptionMethod{
// @Override
// public void show() throws IOException {} // 子类重写的方法可以抛出和父类方法中一样的异常
// public void show() throws FileNotFoundException {} // 子类重写的方法可以抛出更小的异常
// public void show() {} // 子类重写的方法可以不抛出异常
// public void show() throws ClassNotFoundException {} // 子类重写的方法不可以抛出平级不一样的异常
// public void show() throws Exception {} // 子类重写的方法不可以抛出更大的异常
}
16.1.6 自定义异常
- 基本概念
当需要在程序中表达年龄不合理的情况时,而Java官方又没有提供这种针对性的异常,
此时就需要 程序员自定义异常加以描述。
- 实现流程
a. 自定义xxxException异常类继承Exception类或者其子类。
b. 提供两个版本的构造方法,一个是无参构造方法,另外一个是字符串作为参数的构造方法。
- 异常的产生
throw new 异常类型(实参);
如:
throw new AgeException("年龄不合理!!!");
- Java采用的异常处理机制是将异常处理的程序代码集中在一起,与正常的程序代码分开,使得程序 简洁、优雅,并易于维护。
代码: 自定义异常
package com.lagou.task16;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 16:11
*/
public class AgeException extends Exception{
static final long serialVersionUID = -3387516993124229948L; // 序列化版本号 与序列化操作有关
public AgeException() {}
public AgeException(String message) {super(message);}
}
package com.lagou.task16;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 16:17
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) /*throws AgeException*/ {
setName(name);
setAge(age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) /*throws AgeException*/ {
if (age >0 && age< 150) {
this.age = age;
} else {
// System.out.println("年龄不合理哦。");
try {
throw new AgeException("年龄不合理哦。");
} catch (AgeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
package com.lagou.task16;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 16:20
*/
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Person p1 = null;
try {
p1 = new Person("zhangfei",-30);
} catch (AgeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("p1 = " + p1); // p1 = null*/
Person p1 = new Person("zhangfei",-30);
System.out.println("p1 = " + p1); // p1 = Person{name='zhangfei', age=0}
}
}
16.2 File类(重点)
16.2.1 基本概念
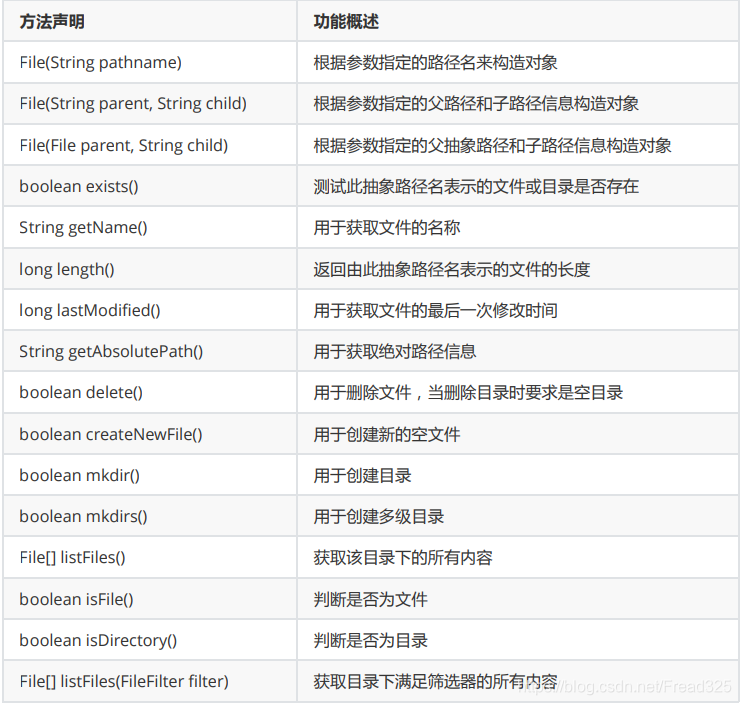
- java.io.File类主要用于描述文件或目录路径的抽象表示信息,可以获取文件或目录的特征信息, 如:大小等。
16.2.2 常用的方法
- 案例题目
遍历指定目录以及子目录中的所有内容并打印出来。
代码: File 类的测试
package com.lagou.task16;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author Lemon.Wong
* @description
* @date 2020/12/6 17:06
*/
public class FileTest {
//自定义成员方法实现指定目录以及子目录的所有内容并打印
public static void show(File file) {
// 获取目录f3下的所有内容并记录到一维数组中
File[] filesArray = file.listFiles();
// 遍历数组
for (File tf: filesArray) {
String name = tf.getName();
if (tf.isFile()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
if (tf.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("[" + name + "]");
show(tf);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.构造File类型的对象与d:/a.txt文件关联
File f1 = new File("d:/a.txt");
// 2.若文件存在则获取文件的相关特性信息并打印后删除文件
if (f1.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件的名称是:" + f1.getName());
System.out.println("文件的大小是:" + f1.length());
Date ldt = new Date(f1.lastModified());
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:SS");
System.out.println("文件的最后一次修改时间是:" + sdf.format(ldt));
//绝对路径: 主要指以根目录开始的路径信息,如:c:/ d:/ /..
//相对路径: 主要指以当前目录所在位置开始的路径信息,如:./ ../
System.out.println("文件的绝对路径信息是:" + f1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(f1.delete()?"文件删除成功":"文件呢删除失败");
} else {
// 3.若文件不存在则创建新的空文件
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile()?"文件创建成功":"文件创建失败");
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------");
// 4.实现目录的删除与创建
File f2 = new File("d:/捣乱");
// File f2 = new File("d:/捣乱/捣乱/捣乱");
if (f2.exists()) {
System.out.println("目录名称是:" + f2.getName());
// System.out.println(f2.delete()?"目录删除成功":"目录删除失败");
} else {
System.out.println(f2.mkdir()?"目录创建成功":"目录创建失败"); // 创建单层目录
// System.out.println(f2.mkdirs()?"目录创建成功":"目录创建失败"); // 创建多层目录
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------");
// 5.实现将指定目录中的所有内容打印出来
File f3 = new File("d:/捣乱");
// 获取目录f3下的所有内容并记录到一维数组中
File[] filesArray = f3.listFiles();
// 遍历数组
for (File tf: filesArray) {
String name = tf.getName();
if (tf.isFile()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
if (tf.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("[" + name + "]");
}
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
// 6.实现目录中所有内容的获取的同时进行过滤
// 匿名内部类的语法格式:接口/父类类型 引用变量名 = new 接口/父类类型() {方法的重写}
/* FileFilter fileFilter = new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
//若文件名是以.avi为结尾的,则返回true表示保留 否则返回false表示丢弃
return pathname.getName().endsWith(".avi");
}
};*/
// Lambda表达式的格式:(参数列表) -> {方法体};
FileFilter fileFilter = (File pathname) -> {return pathname.getName().endsWith(".avi");};
File[] filesArray2 = f3.listFiles(fileFilter);
for (File tf : filesArray2) {
System.out.println(tf);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");
// 7.使用递归思想获取目录及子目录中的所有内容
show(new File("d:/捣乱"));
}
}





 本文详细介绍了Java中的异常处理机制,包括异常的基本概念、分类、避免、捕获、抛出以及自定义异常等内容,并深入讲解了File类的使用方法。
本文详细介绍了Java中的异常处理机制,包括异常的基本概念、分类、避免、捕获、抛出以及自定义异常等内容,并深入讲解了File类的使用方法。
















 5290
5290

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








