SSD基本原理
SSD code:https://github.com/balancap/SSD-Tensorflow/issues
SSD paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.02325
建议先看论文再阅读源码
SSD,全称Single Shot MultiBox Dector,是ECCV 2016刘伟提出的一种目标检测算法,类似于YOLO将目标检测转化为回归的思想。基于Faster RCNN中的anchor,提出相似的prior box。SSD同样加入了基于特征金字塔(Pyramidal Feature Hierachy)的检测方式,即在多个feature map上同时进行softmax分类和位置回归。
SSD网络结构图

SSD于VGG的基础上加了8个额外的特征图。这里着重讲下SSD论文中feature map cell和default box的差别。
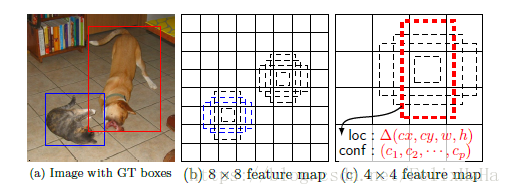
- feature map cell就是将feature map切分成之后的一个个格子。
- default box是每一个格子上一系列固定大小的默认框,SSD中也叫prior box。
SSD-Tensorflow源码分析
SSD训练
SSD训练时与RCNN系列目标检测算法的主要区别是:SSD训练图像的groundtruth需要赋予固定输出的boxes上。看论文可以知道,SSD的输出是一系列固定大小的bouding boxes。如上图狗的groundtruth是红色的bouding boxes,但在label标注的时候需将红色的groundtruthbox赋予上图(c)中一系列固定输出boxes中的一个,即图(c)中的红色虚线框。当将图像中的GT与固定输出的default boxes对应之后就可以根据损失函数进行端对端进行损失函数计算及反向传播更新参数。
SSD anchor生成代码解析
源码中在每一feature layer中都执行如下函数,为每一feature layer生成anchor,该函数返回该feature layer的所有anchor中心点坐标及anchor的h和w,代码如下:
def ssd_anchor_one_layer(img_shape,
feat_shape,
sizes,
ratios,
step,
offset=0.5,
dtype=np.float32):
#配置文件中的feature layer anchor_size和anchor_ratio
'''
anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),#这个size是 21 45 99 153 207 261 315写成turple为了好计算论文中sqrt(SkSk+1)
(45., 99.),
(99., 153.),
(153., 207.),
(207., 261.),
(261., 315.)],
anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]],
anchor_steps=[8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300],
'''
"""Computer SSD default anchor boxes for one feature layer.
#为每一feature layer计算anchor boxes
Determine the relative position grid of the centers, and the relative
width and height.
#参数:
img_shape: 输入的图片大小
feat_shape: 特征图大小
size: 框的size
ratio: 框的长宽比
offset: 网格偏移
Arguments:
feat_shape: Feature shape, used for computing relative position grids;
size: Absolute reference sizes;
ratios: Ratios to use on these features;
img_shape: Image shape, used for computing height, width relatively to the
former;
offset: Grid offset.
Return:
y, x, h, w: Relative x and y grids, and height and width.
"""
# Compute the position grid: simple way.
# y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]]
# y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) / feat_shape[0]
# x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) / feat_shape[1]
# Weird SSD-Caffe computation using steps values...
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]] #y,x为特征图上每个点的坐标,y范围[0,feat_shape[0]),x范围[0,feat_shape[1])
y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) * step / img_shape[0] #*step/img_shape[0]是特征图坐标于原图中归一化
x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) * step / img_shape[1] #+0.5是因为每个框相当于间隔是1,所以中点加0.5
#经过上面计算得到y,x是默认框的中心,于特征图每两个点中间,并规一化
# Expand dims to support easy broadcasting.
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1) #扩展维度 axis = -1是最后一个维度
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)
# Compute relative height and width.
# Tries to follow the original implementation of SSD for the order.
num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios) #计算anchors数量
h = np.zeros((num_anchors, ), dtype=dtype) #最后计算的anchor的h和w存于数组中
w = np.zeros((num_anchors, ), dtype=dtype)
# Add first anchor boxes with ratio=1.
h[0] = sizes[0] / img_shape[0] 







 SSD(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)是一种目标检测算法,它在多个特征图上进行分类和位置回归。文章详细分析了SSD的基本原理、网络结构、训练过程、anchor生成、匹配策略和损失函数,提供了SSD-Tensorflow源码的解读,并引用了相关博客进行深入探讨。
SSD(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)是一种目标检测算法,它在多个特征图上进行分类和位置回归。文章详细分析了SSD的基本原理、网络结构、训练过程、anchor生成、匹配策略和损失函数,提供了SSD-Tensorflow源码的解读,并引用了相关博客进行深入探讨。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 2213
2213

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








