💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
💥1 概述
摘要:
传统的汽车电池系统由大量电池单元组成,在安全性、可靠性、寿命和能源效率方面存在各种挑战。可重构电池系统(RBS)是解决传统电池系统问题的一个有前景的解决方案。然而,RBS中大量的组件也增加了故障概率。为了应对故障容忍方面的挑战,本文讨论了RBS中的故障隔离问题,该系统每个电池单元包括两个开关。基于电热模型进行结构分析,并找到具有最佳故障隔离性能的传感器集。由于系统由许多方程组成,引入了一种新算法,用于有效计算故障诊断的最小结构过定义(MSO)子系统。对于每个故障,该算法允许确定具有最少方程数量的MSO集合。算法的复杂性分析表明,与计算所有MSO集的现有算法相比,所提出的算法在具有高冗余度的系统(如RBS)中的计算成本显著较低。由于该算法考虑了开关状态,因此适用于通过开关进行主动故障隔离。对RBS的应用表明,由于模型的不确定性,电气方程优先于热方程。
为了实现全球气候目标,混合动力和电动汽车被广泛认为是可持续交通的一部分,具有环境影响意义[1]。由于其长寿命、高功率和能量密度,锂离子(Li-ion)电池被认为是此类应用的理想选择[2]。为了满足里程和性能要求,大量的Li-ion电池被并联和串联连接以形成电池组。大多数关于汽车电池组的文献都涉及电池管理系统[3],[4]以及相关的信号处理[5],[6],快速充电[7],电池均衡策略[8],[9]和电池安全[10],[11]。特别是,电池系统的安全性至关重要,因为Li-ion电池的故障操作可能导致电池的热失控。在电池组中,热失控也可能会传播[12],[13]。
作为传统电池系统问题的一个有前景的解决方案,可重构电池系统(RBSs)在文献中受到越来越多的关注。使用直流-直流转换器或开关,RBSs可以动态重新配置并适应当前条件[14],[15]。根据使用的拓扑结构,RBSs允许修改单元级拓扑结构并主动适应电池以适应单元特性。这使得可以根据电池的充电状态[16]和健康状态[17]进行连续的均衡,并实现高效能的运行[18]。在发生故障时,RBSs可以绕过故障单元以实现容错性(坏块管理)[19]。此外,RBSs适用于通过高频开关实现混合存储的应用[14]。RBSs还可以通过将单元从活动状态切换到旁路状态来生成正弦波电压。因此,另一个应用是采用模块化多电平变换器形式的交流电池[20]–[23],它可以与坏块管理有利地结合在一起。详细文章见第4部分。
📚2 运行结果
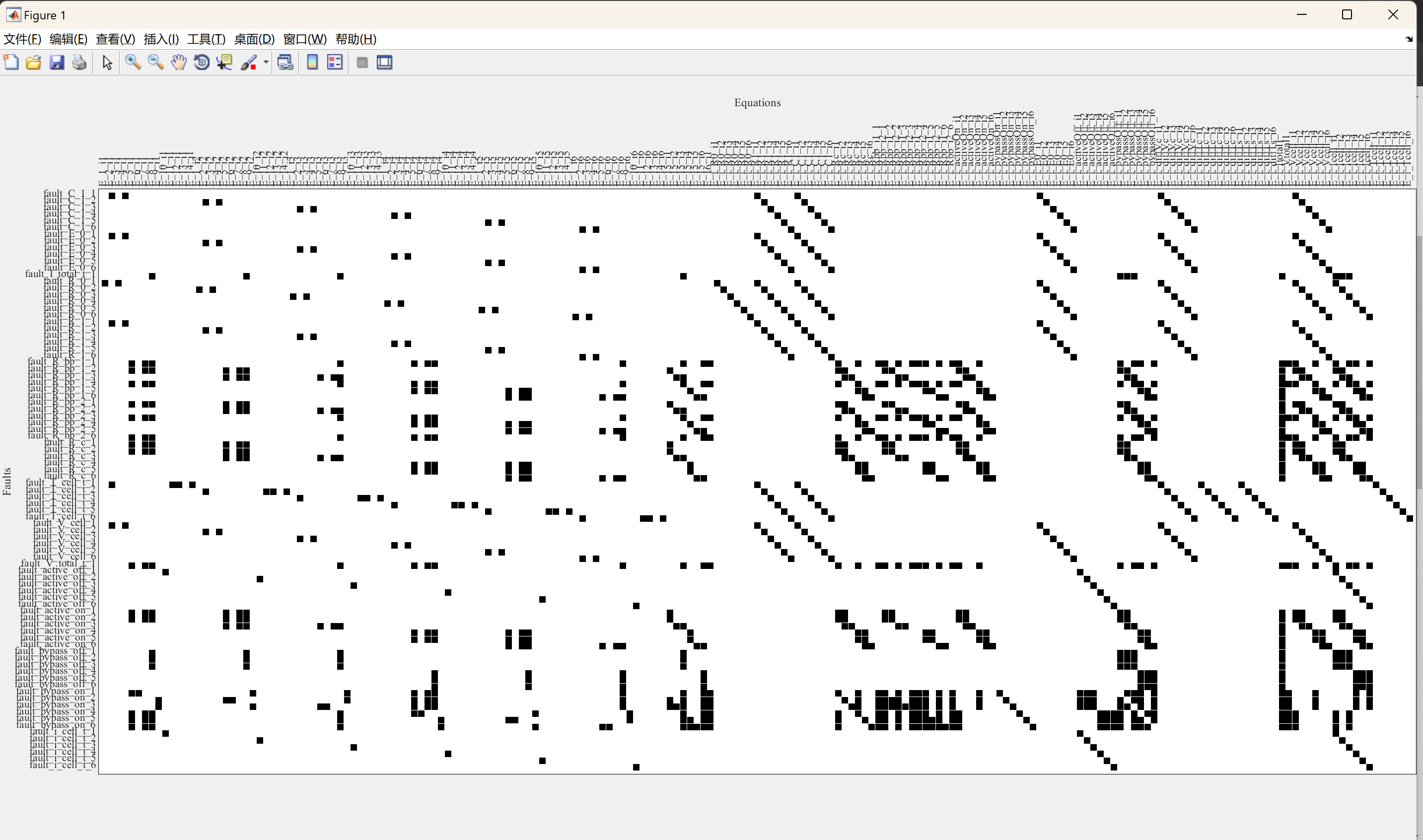
部分代码:
%create symbolic variables for the time dependent symbolic variables
I_total_t = sym('I_ges_t'); % total current
V_total_t = sym('V_ges_t'); % total voltage
V_c_t = sym('V_c_t', [numCells 1]); % voltage over RC-element in cell
V_c_t_dot = sym('V_c_t_dot', [numCells 1]); % derivative of the voltage over RC-element in cell
V_byp_t = sym('V_byp_t', [numCells 1]); % voltage over the bypass transistor
V_cell_t = sym('V_cell_t', [numCells 1]); % cell voltage
V_contact_t = sym('V_contact_t', [numCells 1]); % voltage at the contact resistance of each cell
i_contact_t = sym('i_contact_t', [numCells 1]); % total going into the smart cell
i_cell_t = sym('i_cell_t', [numCells 1]); % cell current
Q_cell_t = sym('Q_cell_t', [numCells 1]); % cell temperature
%Termperature
T_c_t = sym('T_c_t', [numCells 1]); % cell temperature
T_c_t_dot = sym('T_c_t_dot', [numCells 1]); % derivative of cell temperature
T_s_t = sym('T_s_t', [numCells 1]); % cell surface temperature
T_s_t_dot = sym('T_s_t_dot', [numCells 1]); % derivative of cell surface temperature
R_tc_normal = sym('R_tc_normal_', [numCells 6]); % surface-ambient temperature resistance in temperature model
R_ts_normal = sym('R_ts_normal_', [numCells 6]); % cell-surface temperature resistance in temperature model
C_tc_normal = sym('C_tc_normal_', [numCells 6]); % cell temperature capacity in temperature model
C_ts_normal = sym('C_ts_normal_', [numCells 6]); % surface temperature capacity in temperature model
T_amb_normal = sym('T_amb_normal'); % ambient room temperature
E_0_t = sym('E_0_t_', [1 numCells]); % Open circuit voltage of each cell
faultyTActiveOff = sym('faultyTActiveOff_', [1, numCells]); % faults in the closed transistors are modelled as currents
% --> cell current in case of a fault in the closed active transistor
faultyTBypassOff = sym('faultyTBypassOff_', [1, numCells]); % current over the bypass in case of a fault in the closed bypass transistor
%%% Name of the equations (see paper)
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








