import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow. examples. tutorials. mnist import input_data
import time
"""
权重初始化
初始化为一个接近0的很小的正数
"""
def weight_variable ( shape) :
initial = tf. truncated_normal( shape, stddev = 0.1 )
return tf. Variable( initial)
def bias_variable ( shape) :
initial = tf. constant( 0.1 , shape = shape)
return tf. Variable( initial)
"""
卷积和池化,使用卷积步长为1(stride size),0边距(padding size)
池化用简单传统的2x2大小的模板做max pooling
"""
def conv2d ( x, W) :
return tf. nn. conv2d( x, W, strides= [ 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 ] , padding = 'SAME' )
def max_pool_2x2 ( x) :
return tf. nn. max_pool( x, ksize = [ 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 ] ,
strides = [ 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 ] , padding = 'SAME' )
start = time. clock( )
mnist = input_data. read_data_sets( r"./MNIST_data" , one_hot= True )
"""
第一层 卷积层
x_image(batch, 28, 28, 1) -> h_pool1(batch, 14, 14, 32)
"""
x = tf. placeholder( tf. float32, [ None , 784 ] )
x_image = tf. reshape( x, [ - 1 , 28 , 28 , 1 ] )
W_conv1 = weight_variable( [ 5 , 5 , 1 , 32 ] )
b_conv1 = bias_variable( [ 32 ] )
h_conv1 = tf. nn. relu( conv2d( x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2( h_conv1)
"""
第二层 卷积层
h_pool1(batch, 14, 14, 32) -> h_pool2(batch, 7, 7, 64)
"""
W_conv2 = weight_variable( [ 5 , 5 , 32 , 64 ] )
b_conv2 = bias_variable( [ 64 ] )
h_conv2 = tf. nn. relu( conv2d( h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2( h_conv2)
"""
第三层 全连接层
h_pool2(batch, 7, 7, 64) -> h_fc1(1, 1024)
"""
W_fc1 = weight_variable( [ 7 * 7 * 64 , 1024 ] )
b_fc1 = bias_variable( [ 1024 ] )
h_pool2_flat = tf. reshape( h_pool2, [ - 1 , 7 * 7 * 64 ] )
h_fc1 = tf. nn. relu( tf. matmul( h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
"""
Dropout
h_fc1 -> h_fc1_drop, 训练中启用,测试中关闭
"""
keep_prob = tf. placeholder( "float" )
h_fc1_drop = tf. nn. dropout( h_fc1, keep_prob)
"""
第四层 Softmax输出层
"""
W_fc2 = weight_variable( [ 1024 , 10 ] )
b_fc2 = bias_variable( [ 10 ] )
y_conv = tf. nn. softmax( tf. matmul( h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
"""
训练和评估模型
ADAM优化器来做梯度最速下降,feed_dict中加入参数keep_prob控制dropout比例
"""
y_ = tf. placeholder( "float" , [ None , 10 ] )
cross_entropy = - tf. reduce_sum( y_ * tf. log( y_conv) )
train_step = tf. train. AdamOptimizer( 1e - 4 ) . minimize( cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf. equal( tf. argmax( y_conv, 1 ) , tf. argmax( y_, 1 ) )
accuracy = tf. reduce_mean( tf. cast( correct_prediction, "float" ) )
sess = tf. Session( )
sess. run( tf. global_variables_initializer( ) )
for i in range ( 5000 ) :
batch = mnist. train. next_batch( 50 )
if i % 100 == 0 :
train_accuracy = accuracy. eval ( session = sess,
feed_dict = { x: batch[ 0 ] , y_: batch[ 1 ] , keep_prob: 1.0 } )
print ( "step %d, train_accuracy %g" % ( i, train_accuracy) )
train_step. run( session = sess, feed_dict = { x: batch[ 0 ] , y_: batch[ 1 ] ,
keep_prob: 0.5 } )
print ( "test accuracy %g" % accuracy. eval ( session = sess,
feed_dict = { x: mnist. test. images, y_: mnist. test. labels,
keep_prob: 1.0 } ) )
end = time. clock( )
print ( "running time is %g " ) % ( end- start)
"""
基于LeNet-5 的手写数字体MNIST识别
联系qq 605686962
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow. examples. tutorials. mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data. read_data_sets( r".\MNIST_data" , one_hot= True )
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.01
learning_rate_decay = 0.99
max_steps = 5000
def LeNet5 ( input_tensor, regularizer, avg_class, resuse) :
with tf. variable_scope( "C1-conv" , reuse= resuse) :
conv1_weights = tf. get_variable( "weight" , [ 5 , 5 , 1 , 32 ] ,
initializer= tf. truncated_normal_initializer( stddev= 0.1 ) )
conv1_biases = tf. get_variable( "bias" , [ 32 ] , initializer= tf. constant_initializer( 0.0 ) )
conv1 = tf. nn. conv2d( input_tensor, conv1_weights, strides= [ 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 ] , padding= "SAME" )
relu1 = tf. nn. relu( tf. nn. bias_add( conv1, conv1_biases) )
with tf. name_scope( "S2-max_pool" , ) :
pool1 = tf. nn. max_pool( relu1, ksize= [ 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 ] , strides= [ 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 ] , padding= "SAME" )
with tf. variable_scope( "C3-conv" , reuse= resuse) :
conv2_weights = tf. get_variable( "weight" , [ 5 , 5 , 32 , 64 ] ,
initializer= tf. truncated_normal_initializer( stddev= 0.1 ) )
conv2_biases = tf. get_variable( "bias" , [ 64 ] , initializer= tf. constant_initializer( 0.0 ) )
conv2 = tf. nn. conv2d( pool1, conv2_weights, strides= [ 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 ] , padding= "SAME" )
relu2 = tf. nn. relu( tf. nn. bias_add( conv2, conv2_biases) )
with tf. name_scope( "S4-max_pool" , ) :
pool2 = tf. nn. max_pool( relu2, ksize= [ 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 ] , strides= [ 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 ] , padding= "SAME" )
shape = pool2. get_shape( ) . as_list( )
nodes = shape[ 1 ] * shape[ 2 ] * shape[ 3 ]
reshaped = tf. reshape( pool2, [ - 1 , nodes] )
with tf. variable_scope( "layer5-full1" , reuse= resuse) :
Full_connection1_weights = tf. get_variable( "weight" , [ nodes, 512 ] ,
initializer= tf. truncated_normal_initializer( stddev= 0.1 ) )
tf. add_to_collection( "losses" , regularizer( Full_connection1_weights) )
Full_connection1_biases = tf. get_variable( "bias" , [ 512 ] ,
initializer= tf. constant_initializer( 0.1 ) )
if avg_class == None :
Full_1 = tf. nn. relu( tf. matmul( reshaped, Full_connection1_weights) + \
Full_connection1_biases)
else :
Full_1 = tf. nn. relu( tf. matmul( reshaped, avg_class. average( Full_connection1_weights) )
+ avg_class. average( Full_connection1_biases) )
with tf. variable_scope( "layer6-full2" , reuse= resuse) :
Full_connection2_weights = tf. get_variable( "weight" , [ 512 , 10 ] ,
initializer= tf. truncated_normal_initializer( stddev= 0.1 ) )
tf. add_to_collection( "losses" , regularizer( Full_connection2_weights) )
Full_connection2_biases = tf. get_variable( "bias" , [ 10 ] ,
initializer= tf. constant_initializer( 0.1 ) )
if avg_class == None :
result = tf. matmul( Full_1, Full_connection2_weights) + Full_connection2_biases
else :
result = tf. matmul( Full_1, avg_class. average( Full_connection2_weights) ) + \
avg_class. average( Full_connection2_biases)
return result
x = tf. placeholder( tf. float32, [ None , 28 , 28 , 1 ] , name= "x-input" )
y_ = tf. placeholder( tf. float32, [ None , 10 ] , name= "y-input" )
regularizer = tf. contrib. layers. l2_regularizer( 0.0001 )
y = LeNet5( x, regularizer, avg_class= None , resuse= False )
cross_entropy = tf. nn. sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( logits= y, labels= tf. argmax( y_, 1 ) )
cross_entropy_mean = tf. reduce_mean( cross_entropy)
loss = cross_entropy_mean + tf. add_n( tf. get_collection( 'losses' ) )
training_step = tf. Variable( 0 , trainable= False )
learning_rate = tf. train. exponential_decay( learning_rate,
training_step, mnist. train. num_examples / batch_size ,
learning_rate_decay, staircase= True )
train_step = tf. train. GradientDescentOptimizer( learning_rate) . \
minimize( loss, global_step= training_step)
variable_averages = tf. train. ExponentialMovingAverage( 0.99 , training_step)
variables_averages_op = variable_averages. apply ( tf. trainable_variables( ) )
average_y = LeNet5( x, regularizer, variable_averages, resuse= True )
with tf. control_dependencies( [ train_step, variables_averages_op] ) :
train_op = tf. no_op( name= 'train' )
crorent_predicition = tf. equal( tf. arg_max( average_y, 1 ) , tf. argmax( y_, 1 ) )
accuracy = tf. reduce_mean( tf. cast( crorent_predicition, tf. float32) )
with tf. Session( ) as sess:
sess. run( tf. global_variables_initializer( ) )
for i in range ( max_steps) :
if i % 100 == 0 :
x_val, y_val = mnist. validation. next_batch( batch_size)
reshaped_x2 = np. reshape( x_val, ( batch_size, 28 , 28 , 1 ) )
validate_feed = { x: reshaped_x2, y_: y_val}
validate_accuracy = sess. run( accuracy, feed_dict= validate_feed)
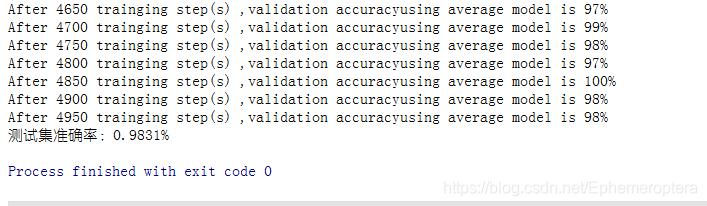
print ( "After %d trainging step(s) ,validation accuracy"
"using average model is %g%%" % ( i, validate_accuracy * 100 ) )
x_train, y_train = mnist. train. next_batch( batch_size)
reshaped_xs = np. reshape( x_train, ( batch_size , 28 , 28 , 1 ) )
sess. run( train_op, feed_dict= { x: reshaped_xs, y_: y_train} )
xtest = mnist. test. images
ytest = mnist. test. labels
XT = np. reshape( xtest, ( - 1 , 28 , 28 , 1 ) )
test_accuracy = sess. run( accuracy, feed_dict= { x: XT, y_: ytest} )
print ( "测试集准确率:%g%%" % ( test_accuracy* 100 ) )
from keras. datasets import mnist
from keras. layers import Input, Conv2D, BatchNormalization, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape
from keras. models import Model, load_model
from keras. utils. np_utils import to_categorical
from keras import backend as K
import numpy as np
import os
os. environ[ "CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES" ] = "0"
def LeNet5 ( x, n_classes= 10 ) :
x = Conv2D( 32 , ( 3 , 3 ) , strides= ( 1 , 1 ) , activation= 'relu' , padding= 'same' ) ( x)
x = BatchNormalization( axis= 3 ) ( x)
x = MaxPooling2D( pool_size= ( 2 , 2 ) ) ( x)
x = Conv2D( 64 , ( 3 , 3 ) , strides= ( 1 , 1 ) , activation= 'relu' , padding= 'same' ) ( x)
x = BatchNormalization( axis= 3 ) ( x)
x = MaxPooling2D( pool_size= ( 2 , 2 ) ) ( x)
x = Flatten( ) ( x)
x = Dropout( 0.2 ) ( x)
x = Dense( 512 , activation= 'relu' ) ( x)
x = Dropout( 0.2 ) ( x)
x = Dense( 512 , activation= 'relu' ) ( x)
x = Dropout( 0.2 ) ( x)
x = Dense( n_classes, activation= 'softmax' ) ( x)
return x
def get_model ( ) :
input = Input( shape= ( 28 , 28 , 1 ) )
model = Model( inputs= input , outputs= LeNet5( input , N_CLASSES) )
model. summary( )
return model
def train ( ) :
model = get_model( )
model. compile ( optimizer= 'adam' , loss= "categorical_crossentropy" , metrics= [ 'accuracy' ] )
model. fit( x_train, y_train, batch_size= BATCH_SIZE, epochs= EPOCHS)
model. save( MODEL_FILE)
def test ( ) :
model = load_model( MODEL_FILE)
score = model. evaluate( x_test, y_test, batch_size= BATCH_SIZE)
print ( 'test score:' , score)
if __name__ == "__main__" :
EPOCHS = 20
BATCH_SIZE = 128
N_CLASSES = 10
MODEL_FILE = "./LeNet5_minist.h5"
( x_train, y_train) , ( x_test, y_test) = mnist. load_data( )
x_train = np. expand_dims( x_train, axis= 3 )
x_test = np. expand_dims( x_test, axis= 3 )
y_train = to_categorical( y_train, N_CLASSES)
y_test = to_categorical( y_test, N_CLASSES)
train( )
test( )























 1052
1052

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










