Link:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1401
Problem:
Solitaire
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 3309 Accepted Submission(s): 1035
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
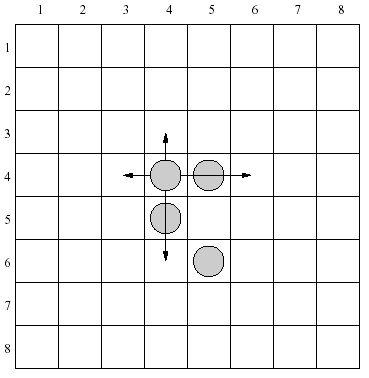
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).

There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5 2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
Source
题意就是有四颗棋子,能否在8步内走到目标状态
开个8维数组记录状态即可
单向BFS:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <queue>
- using namespace std;
- bool vis[8][8][8][8][8][8][8][8];
- bool map[10][10];
- int to[4][2] = {1,0,-1,0,0,1,0,-1};
- struct point
- {
- int x[4],y[4],step;
- } s,e;
- int check(point a)//判断是否为最终态
- {
- for(int i = 0; i<4; i++)
- {
- if(!map[a.x[i]][a.y[i]])
- return 0;
- }
- return 1;
- }
- int empty(point a,int k)//看要将要到达的那格是否为空
- {
- for(int i = 0; i<4; i++)
- {
- if(i!=k && a.x[i] == a.x[k] && a.y[i] == a.y[k])
- return 0;
- }
- return 1;
- }
- int judge(point next)//判断是否符合要求
- {
- int i;
- for(i = 0; i<4; i++)
- {
- if(next.x[i]<0 || next.x[i]>=8 || next.y[i]<0 || next.y[i]>=8)
- return 1;
- }
- if(vis[next.x[0]][next.y[0]][next.x[1]][next.y[1]][next.x[2]][next.y[2]][next.x[3]][next.y[3]])
- return 1;
- return 0;
- }
- int bfs()
- {
- memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
- int i,j;
- queue<point> Q;
- point a,next;
- a.step = 0;
- for(i = 0; i<4; i++)
- {
- a.x[i] = s.x[i];
- a.y[i] = s.y[i];
- }
- Q.push(a);
- vis[a.x[0]][a.y[0]][a.x[1]][a.y[1]][a.x[2]][a.y[2]][a.x[3]][a.y[3]] = true;
- while(!Q.empty())
- {
- a = Q.front();
- Q.pop();
- if(a.step>=8)//因为后面循环有判断减枝,所以这里要包括8步
- return 0;
- if(check(a))
- return 1;
- for(i = 0; i<4; i++)
- {
- for(j = 0; j<4; j++)
- {
- next = a;
- next.x[i]+=to[j][0];
- next.y[i]+=to[j][1];
- next.step++;
- if(judge(next))
- continue;
- if(empty(next,i))//要去的那一格是空
- {
- if(check(next))
- return 1;
- vis[next.x[0]][next.y[0]][next.x[1]][next.y[1]][next.x[2]][next.y[2]][next.x[3]][next.y[3]] = true;
- Q.push(next);
- }
- else//非空则继续往前
- {
- next.x[i]+=to[j][0];
- next.y[i]+=to[j][1];
- if(judge(next) || !empty(next,i))//继续往前也要满足要求且是空格
- continue;
- if(check(next))
- return 1;
- vis[next.x[0]][next.y[0]][next.x[1]][next.y[1]][next.x[2]][next.y[2]][next.x[3]][next.y[3]] = true;
- Q.push(next);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int i;
- while(~scanf("%d%d",&s.x[0],&s.y[0]))
- {
- s.x[0]--;
- s.y[0]--;
- for(i = 1; i<4; i++)
- {
- scanf("%d%d",&s.x[i],&s.y[i]);
- s.x[i]--;
- s.y[i]--;
- }
- memset(map,false,sizeof(map));
- for(i = 0; i<4; i++)
- {
- scanf("%d%d",&e.x[i],&e.y[i]);
- e.x[i]--;
- e.y[i]--;
- map[e.x[i]][e.y[i]] = true;
- }
- int flag = bfs();
- if(flag)
- printf("YES\n");
- else
- printf("NO\n");
- }
- return 0;
- }








 本文深入探讨了游戏开发领域的核心技术,包括Unity3D、Cocos2d-X等游戏引擎的使用,以及OpenGL ES、OpenCV等图像处理技术在游戏中的应用。同时,也涉及到了游戏程序设计、游戏美术、游戏策划等多方面的内容。
本文深入探讨了游戏开发领域的核心技术,包括Unity3D、Cocos2d-X等游戏引擎的使用,以及OpenGL ES、OpenCV等图像处理技术在游戏中的应用。同时,也涉及到了游戏程序设计、游戏美术、游戏策划等多方面的内容。
















 805
805

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








