文章目录
JavaWeb
1. 前言
- 静态web
- 技术栈:html,css
- 动态web
- 技术栈:Servlet/JSP,ASP,PHP
在java中,动态web资源开发的技术统称为JavaWeb
1.1 web应用程序
一个Web应用由多个部分组成(静态Web,动态Web)
- html,css,js
- jsp,servlet
- Java程序
- jar包
- 配置文件(Properties)
Web应用程序编写完毕后,若想提供给外界访问:需要一个服务器统一管理
1.2 静态web
- *.htm, *.html 这些都是网页的后缀,如果服务器上一直存在这些东西,我们就可以直接进行读取

- 静态web的缺点
- web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看的都是同一个页面
- 轮播图,点击特性:伪动态
- JavaScript
- VBScript
- 他无法和数据库交互(数据无法持久化,用户无法交互)
- web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看的都是同一个页面
1.3 动态web
Web的页面展示因人而异

缺点:
- 假如服务器的动态web资源出现了错误,我们需要重新编写我们的后台程序,重新发布;
- 停机维护
优点:
- 静态web的缺点
- web页面可以动态更新
- 他可以和数据库交互
2. web服务器
2.1 技术讲解
ASP:
- 微软:或内最早流行的
- 在 HTML 中嵌入了 VB 脚本, ASP + COM
- 在 ASP 开发中,基本一个页面有几千行业务代码,页面极其混乱
- 维护成本高
- C#
- IIS
PHP:
- PHP 开发速度很快,功能很强大,跨平台,代码很简单
- 无法承载大访问量的情况(局限性)
JSP/Servlet:
- sun公司主推的B/S架构,
- 基于Java语言
- 可以承载三高问题带来的影响
- 语法像ASP
…
2.2 web服务器
服务器是一种被动的操作,用来处理用户的一些请求和响应信息
IIS
- 微软的,ASP…,Windows中自带
Tomcat
-
Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目由于有了Sun 的参与和支持,最新的Servlet 和JSP 规范总是能在Tomcat 中得到体现。因为Tomcat 技术先进、性能稳定,而且免费,因而深受Java 爱好者的喜爱并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,成为比较流行的Web 应用服务器。
Tomcat 服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器,在中小型系统和并发访问用户不是很多的场合下被普遍使用,是开发和调试JSP 程序的首选。对于一个初学者来说,是最佳选择。
Tomcat 实际上运行JSP 页面和Servlet。
3. Tomcat

可以配置启动的端口号
- tomcat默认端口号:8080
- mysql:3306
- http:80
- https:443
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
可以配置主机名称
- 默认主机名:localhost
- 默认的网站应用存放位置为:webapps
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
高难度面试题
请你谈谈网站是如何进行访问的:
- 输入一个域名;回车
- 检查本机的 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 配置文件下有没有这个域名映射;
- 有:直接返回对应的 ip 地址,这个地址中,有我们需要访问的web程序,可以直接访问
- 没有:去DNS服务器找,找到的话就返回,找不到返回找不到(DNS:全世界的域名都在这里管理)
3.1 发布一个网站
模仿:将自己写的网站,放到服务器(Tomcat)中指定的 web 应用的文件夹(webapps)下,进行访问
网站应该有的结构:
-- webapps: Tomcat服务器的web目录
- ROOT
- study: 网站的目录名
- WEB-INF
- classes: Java程序
- lib: web应用所以来的jar包
- web.xml: 网站配置文件
- index.html 默认的首页
- static
- css
- style.css
- js
- img
- ...
4. Http
Http(超文本传输协议):是一个简单的请求-响应协议,通常运行在TCP之上
- 文本:html、字符串、…
- 超文本:图片、音乐、定位、地图…
- 默认端口:80
Https:安全的
- 默认端口:443
4.1 HTTP版本
-
http1.0
- HTTP/1.0:客户端可以与web服务器连接,只能获得一个web资源,断开连接
-
http2.0
- HTTP/1.1:客户端可以与web服务器连接,可以获得多个web资源
-
http3.0:参考https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/m0_46171043/article/details/115167824
-
减少了TCP三次握手及TLS握手时间

-
…
-
4.2 HTTP请求
- 客户端 – 发请求(Request) – 服务器
百度
Request URL: https://www.baidu.com/ 请求地址
Request Method: GET get方法/post方法
Status Code: 200 OK 状态码
Remote(远程) Address: 14.215.177.39:443
Accept:text/html
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Connection: keep-alive
请求行:
- 请求行中的请求方式:GET
- 请求方式:Get,Post,HEAT,DELETE,PUT,TRACT…
- get:请求能够携带的参数比较小,大小有限制,会在浏览器的URL地址栏中显示数据内容,不安全,但高效
- post:请求能够携带的参数没有限制,大小没有限制,不会在浏览器的URL地址栏中显示数据内容,安全,但不高效
消息头:
Accept:告诉浏览器,他所支持的数据类型
Accept-Encoding:支持哪种编码格式
Accept-Language:语言环境
Cache-Control:缓存控制
Connection:告诉浏览器,请求完成是断开还是保持连接
HOST:主机
4.3 HTTP响应
-
服务器 – 响应 – 客户端
百度
Cache-Control: private 缓存控制
Connection: keep-alive 连接:保持连接
Content-Encoding: gzip 编码
Content-Type: text/html 类型
响应体
Accept:告诉浏览器,他所支持的数据类型
Accept-Encoding:支持哪种编码格式
Accept-Language:语言环境
Cache-Control:缓存控制
Connection:告诉浏览器,请求完成是断开还是保持连接
HOST:主机
Refrush:告诉客户端多久刷新一次
Location:让网页重新定位
响应状态码
- 200:请求响应成功
- 3**:请求重定向
- 4**:资源不存在
- 5**:服务器代码错误 500 502:网关错误
5. Maven
能够自动导入配置jar包
Maven项目架构管理工具
Maven核心思想:约定大于配置
- 有约束,不要去违反
Maven会规定好你该如何去编写我们的Java代码
5.1 下载安装Maven
官网:https://maven.apache.org/download.cgi

5.2 配置环境变量
在环境变量中进行如下配置:
- M2_HOME
- maven 目录下的bin目录
- MAVEN_HOME
- maven 的目录
- 在系统的 path 中配置 MAVEN_HOME
- %MAVEN_HOME%\bin
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-E12QT2Yu-1660027835505)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/02/EKvuMrFtGjgLTZ2.png)]

测试maven是否安装成功:

5.3 修改镜像
阿里云镜像:
<mirror>
<id>alimaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public/</url>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
</mirror>
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-UTkdhda1-1660027835508)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/02/DmcMK7X3AORrkLt.png)]
5.4 本地仓库
**建立一个本地仓库:**localRepository


5.5 在IDEA中使用maven
-
启动idea
-
创建mavenWeb项目(普通项目不用勾选,直接Next)
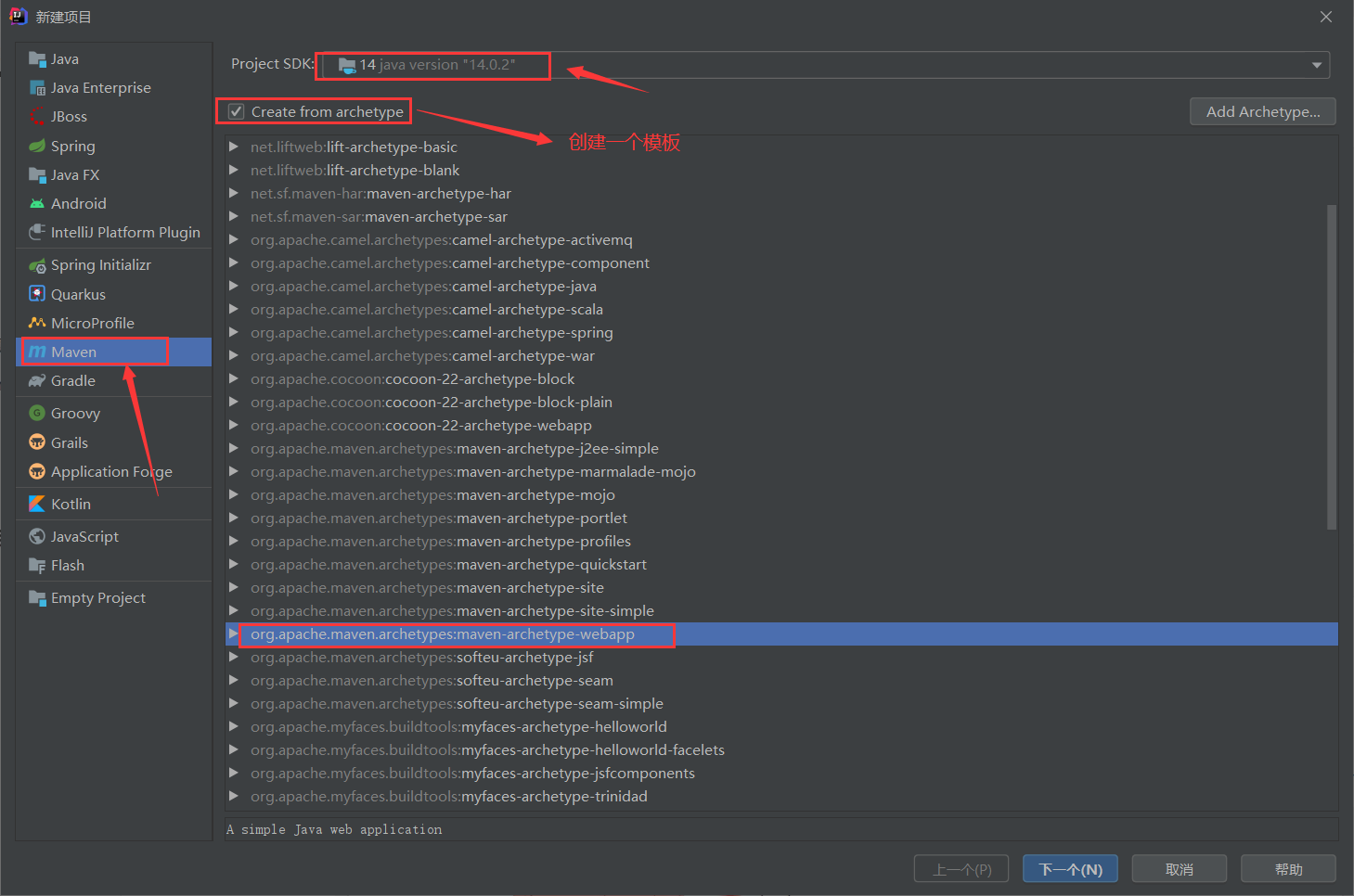

注意:在IDEA项目自动创建完成后,Mavenhome有时会使用IDEA默认,如果发现这个问题,手动改为本地
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-cO1IR5Dr-1660027835513)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/03/Nt1JwoK4f9XuU8P.png)]
-
等待项目初始化完毕
-
IDEA中的maven设置
注意:IDEA项目创建完成后,在setting中看一眼Maven配置是否正确
IDEA中标记文件夹内容:

5.6 在IDEA中配置Tomcat
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5iF6wrg1-1660027835516)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/04/NbTidoCf4MOLW6X.gif)]
配置后应用完成

启动成功

5.7 pom文件
pom.xml 是 Maven 的核心配置文件


maven 由于其约定大于配置,可能会遇到我们写的配置文件,无法被导出或生效
解决方案:
<!-- 在bulid中配置resources,防止我们倒出资源失败 -->
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
6.Servlet
- Servlet 就是sun公司开发动态Web的一门技术
- sun公司在这些API中提供了一个接口叫做:Servlet,想开发一个Servlet程序,只需完成两个步骤
- 编写一个类,实现Severlet接口
- 把开发好的Java类部署到web服务器中
把实现类Serverlet接口的Java程序叫做Servlet
6.1 HelloServlet
Servlet 接口sun公司有两个默认的实现类:HttpServlet,GenericServlet
-
构建一个普通的Maven项目,删掉里面的src目录,之后的学习就在这个项目里建立Moudel;这个空的工程就是Maven的主工程
-
关于Maven 父子工程的理解:
父项目中会有
<modules> <module>servlet01</module> </modules>子项目中会有
<parent> <artifactId>javaweb-02-servlet</artifactId> <groupId>com.swust</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent>父项目中的jar包子项目可以直接使用
-
Maven 环境优化
- 修改web.xml为最新
- 将Maven的结构搭建完整
-
编写一个servlet
-
编写一个普通类
-
实现Servlet接口,这里我们直接继承HttpServlet
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { // 由于get或者post只是实现请求的不同的方式,可以相互调用,业务逻辑都一样 @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream(); PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();//响应流 writer.print("Hello Servlet"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req, resp); } }
-
-
编写Servlet的映射
为什么需要映射:我们写的是Java程序,但是需要通过浏览器访问,而浏览器需要连接web服务器,所以我们需要在web服务中注册我们写的Servlet,还需给他一个浏览器能够访问的路径
<!-- 注册Servlet --> <servlet> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <!-- Servlet的请求路径 --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> -
配置Tomcat
-
启动测试
6.2 Servlet原理
Servlet 是由web服务器调用,web服务器在收到浏览器请求后会:

6.3 mapping问题
-
一个servlet可以指定一个映射路径
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> -
一个servlet可以指定多个映射路径
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello1</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello3</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello4</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> -
一个servlet可以指定通用映射路径
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
-
默认请求路径
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> -
指定一些后缀或者前缀等…
注意:* 前不能加项目映射路径
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
-
优先级问题
指定了固有的映射路径优先级最高,如果找不到就会走默认的处理请求;
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet> <servlet-name>error</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.ErrorServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>error</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
6.4 ServletContext
web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,他代表了当前的web应用;
1.共享数据
我在这个Servlet中保存的数据,可以在另外一个Servlet中拿到;
创建属性
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Hello");
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String name = "张三";
context.setAttribute("name",name);
}
}
从ServletContext得到属性
public class GetServlet extends HelloServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String name = (String) context.getAttribute("name");
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.getWriter().print("名字"+name);
}
}
配置Servlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>get</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.GetServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>get</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/get</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
测试结果:**
-
先get后hello
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-30WV56CN-1660027835528)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/05/xGenl4zJfYVL2M6.png)]
-
先hello后get

2.获取初始化参数
创建一个初始化参数:
<context-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis</param-value>
</context-param>
从ServletContext中获取初始化参数:
public class GetServlet extends HelloServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String name = (String) context.getAttribute("name");
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.getWriter().print("名字"+name);
}
}
配置Servlet:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>demo</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.ServletDemo03</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>demo</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/demo</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
测试:

3.请求转发
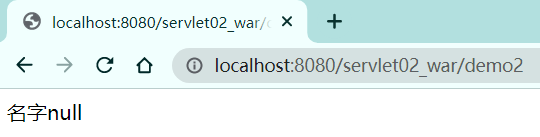
public class ServletDemo04 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
// RequestDispatcher dispatcher = context.getRequestDispatcher("/get");//请求转发路径
// dispatcher.forward(req,resp);//调用forward实现请求转发
context.getRequestDispatcher("/get").forward(req,resp);
}
}
<servlet>
<servlet-name>demo2</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.ServletDemo04</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>demo2</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/demo2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
测试结果:
4.读取资源文件
Properties:
username=root
password=123456
- 在Java目录下新建Properties
- 在resources目录下新建Properties
发现:在target中都被打包到同一个路径下:classes,我们称这个路径为classpath
创建文件流
public class ServletDemo05 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
InputStream stream = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("WEB-INF/classes/db.properties");
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(stream);
String name = prop.getProperty("username");
String pwd = prop.getProperty("password");
resp.getWriter().print(name+":"+pwd);
}
}
配置Servlet:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>demo3</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.ServletDemo05</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>demo3</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/demo3</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
测试结果:

6.5 HttpServletResponse
Web服务器接收到客户端的http请求,针对这个请求,分别创建:
- 代表请求的
HttpServletRequest对象 - 代表响应的
HttpServletResponse对象
如果要获取我们客户端请求过来的参数:找 HttpServletRequest
如果给客户端相应一些信息:找 HttpServletResponse
1.简单分类
负责向浏览器发送数据的方法
public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException;
public PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException;
负责向浏览器发送响应头的方法
public void setCharacterEncoding(String charset);
public void setContentLength(int len);
public void setContentLengthLong(long len);
public void setContentType(String type);
public void setDateHeader(String name, long date);
public void addDateHeader(String name, long date);
public void setHeader(String name, String value);
public void addHeader(String name, String value);
public void setIntHeader(String name, int value);
public void addIntHeader(String name, int value);
响应的状态码:
public static final int SC_CONTINUE = 100;
/**
* Status code (101) indicating the server is switching protocols
* according to Upgrade header.
*/
public static final int SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
/**
* Status code (200) indicating the request succeeded normally.
*/
public static final int SC_OK = 200;
/**
* Status code (201) indicating the request succeeded and created
* a new resource on the server.
*/
public static final int SC_CREATED = 201;
/**
* Status code (202) indicating that a request was accepted for
* processing, but was not completed.
*/
public static final int SC_ACCEPTED = 202;
/**
* Status code (203) indicating that the meta information presented
* by the client did not originate from the server.
*/
public static final int SC_NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
/**
* Status code (204) indicating that the request succeeded but that
* there was no new information to return.
*/
public static final int SC_NO_CONTENT = 204;
/**
* Status code (205) indicating that the agent <em>SHOULD</em> reset
* the document view which caused the request to be sent.
*/
public static final int SC_RESET_CONTENT = 205;
/**
* Status code (206) indicating that the server has fulfilled
* the partial GET request for the resource.
*/
public static final int SC_PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
/**
* Status code (300) indicating that the requested resource
* corresponds to any one of a set of representations, each with
* its own specific location.
*/
public static final int SC_MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
/**
* Status code (301) indicating that the resource has permanently
* moved to a new location, and that future references should use a
* new URI with their requests.
*/
public static final int SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
/**
* Status code (302) indicating that the resource has temporarily
* moved to another location, but that future references should
* still use the original URI to access the resource.
*
* This definition is being retained for backwards compatibility.
* SC_FOUND is now the preferred definition.
*/
public static final int SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
/**
* Status code (302) indicating that the resource reside
* temporarily under a different URI. Since the redirection might
* be altered on occasion, the client should continue to use the
* Request-URI for future requests.(HTTP/1.1) To represent the
* status code (302), it is recommended to use this variable.
*/
public static final int SC_FOUND = 302;
/**
* Status code (303) indicating that the response to the request
* can be found under a different URI.
*/
public static final int SC_SEE_OTHER = 303;
/**
* Status code (304) indicating that a conditional GET operation
* found that the resource was available and not modified.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
/**
* Status code (305) indicating that the requested resource
* <em>MUST</em> be accessed through the proxy given by the
* <code><em>Location</em></code> field.
*/
public static final int SC_USE_PROXY = 305;
/**
* Status code (307) indicating that the requested resource
* resides temporarily under a different URI. The temporary URI
* <em>SHOULD</em> be given by the <code><em>Location</em></code>
* field in the response.
*/
public static final int SC_TEMPORARY_REDIRECT = 307;
/**
* Status code (400) indicating the request sent by the client was
* syntactically incorrect.
*/
public static final int SC_BAD_REQUEST = 400;
/**
* Status code (401) indicating that the request requires HTTP
* authentication.
*/
public static final int SC_UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
/**
* Status code (402) reserved for future use.
*/
public static final int SC_PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
/**
* Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request
* but refused to fulfill it.
*/
public static final int SC_FORBIDDEN = 403;
/**
* Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not
* available.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_FOUND = 404;
/**
* Status code (405) indicating that the method specified in the
* <code><em>Request-Line</em></code> is not allowed for the resource
* identified by the <code><em>Request-URI</em></code>.
*/
public static final int SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
/**
* Status code (406) indicating that the resource identified by the
* request is only capable of generating response entities which have
* content characteristics not acceptable according to the accept
* headers sent in the request.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
/**
* Status code (407) indicating that the client <em>MUST</em> first
* authenticate itself with the proxy.
*/
public static final int SC_PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
/**
* Status code (408) indicating that the client did not produce a
* request within the time that the server was prepared to wait.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
/**
* Status code (409) indicating that the request could not be
* completed due to a conflict with the current state of the
* resource.
*/
public static final int SC_CONFLICT = 409;
/**
* Status code (410) indicating that the resource is no longer
* available at the server and no forwarding address is known.
* This condition <em>SHOULD</em> be considered permanent.
*/
public static final int SC_GONE = 410;
/**
* Status code (411) indicating that the request cannot be handled
* without a defined <code><em>Content-Length</em></code>.
*/
public static final int SC_LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
/**
* Status code (412) indicating that the precondition given in one
* or more of the request-header fields evaluated to false when it
* was tested on the server.
*/
public static final int SC_PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
/**
* Status code (413) indicating that the server is refusing to process
* the request because the request entity is larger than the server is
* willing or able to process.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
/**
* Status code (414) indicating that the server is refusing to service
* the request because the <code><em>Request-URI</em></code> is longer
* than the server is willing to interpret.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG = 414;
/**
* Status code (415) indicating that the server is refusing to service
* the request because the entity of the request is in a format not
* supported by the requested resource for the requested method.
*/
public static final int SC_UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
/**
* Status code (416) indicating that the server cannot serve the
* requested byte range.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
/**
* Status code (417) indicating that the server could not meet the
* expectation given in the Expect request header.
*/
public static final int SC_EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
/**
* Status code (500) indicating an error inside the HTTP server
* which prevented it from fulfilling the request.
*/
public static final int SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
/**
* Status code (501) indicating the HTTP server does not support
* the functionality needed to fulfill the request.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
/**
* Status code (502) indicating that the HTTP server received an
* invalid response from a server it consulted when acting as a
* proxy or gateway.
*/
public static final int SC_BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
/**
* Status code (503) indicating that the HTTP server is
* temporarily overloaded, and unable to handle the request.
*/
public static final int SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
/**
* Status code (504) indicating that the server did not receive
* a timely response from the upstream server while acting as
* a gateway or proxy.
*/
public static final int SC_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
/**
* Status code (505) indicating that the server does not support
* or refuses to support the HTTP protocol version that was used
* in the request message.
*/
public static final int SC_HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
2.常见应用
- 向浏览器输出消息(上一节有)
- 下载文件
- 获取下载文件的路径
- 下载的文件名
- 让浏览器支持下载我们需要的东西
- 获取下载文件的输入流
- 创建缓冲区
- 获取OutputStream对象
- 将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区
- 使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端
代码:
package com.swust.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
public class FileServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
// 1. 获取下载文件的路径
String path = "D:\\工作文件\\学习笔记\\JavaWeb\\javaweb-02-servlet\\response01\\target\\response01\\WEB-INF\\classes\\猫猫.jpg";
System.out.println("下载文件的路径" + path);
// 2. 下载的文件名
String fileName = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1);
// 3. 让浏览器支持下载我们需要的东西,中文文件名URLEncoder.encode编码,否则有可能乱码
resp.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName,"UTF-8"));
// 4. 获取下载文件的输入流
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);
// 5. 创建缓冲区
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
// 6. 获取OutputStream对象
ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream();
// 7. 将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区,使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端
while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
配置Servlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>down</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.FileServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>down</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/down</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
测试结果:
3.验证码实现
验证怎么来的?
- 前端实现
- 后端实现,需要用到Java图片类,产生一个图片
代码
package com.swust.servlet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
public class ImageServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
// 浏览器3秒自动刷新一次
resp.setHeader("refresh","3");
// 在内存中创建一个图片
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(80,20,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// 得到图片
Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D) image.getGraphics();//笔
// 设置图片的背景颜色
g.setColor(Color.white);
g.fillRect(0,0,80,20);
// 给图片写数据
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.setFont(new Font(null,Font.BOLD,20));
g.drawString(makeNum(),0,20);
// 告诉浏览器,这个请求用图片的方式打开
resp.setContentType("image/jpeg");
// 网站存在缓存,不让浏览器缓存
resp.setDateHeader("expires",-1);
resp.setHeader("Cache-Control","no-cache");// 缓存策略,不缓存
resp.setHeader("Pragma","no-cache");
// 把图片写给浏览器
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",resp.getOutputStream());
}
// 生成随机数
private String makeNum() {
Random random = new Random();
String num = random.nextInt(9999999) + ""; // 加""变为字符串
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 7-num.length(); i++) {
sb.append("0");
}
return sb + num;
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
配置Servlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>img</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.ImageServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>img</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/img</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
测试结果

4.实现重定向
一个web资源B收到客户端A的请求后,B会通知客户端A去访问另外一个web资源C,这个过程叫做重定向
常见场景:用户登录
所用方法:
public void sendRedirect(String location) throws IOException;
代码:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
/*
resp.setHeader("Location",getServletContext().getContextPath()+"/img");
resp.setStatus(302);
*/
resp.sendRedirect(getServletContext().getContextPath()+"/img"); // 重定向
}
面试题:重定向与转发的区别
相同点:
- 页面都会实现跳转
不同点:
- 请求转发的时候,url不会产生变化:307
- 重定向的时候,url地址栏会发生变化:302
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xO9BuZmY-1660027835536)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/06/dz4GFy5gNSm9a7x.png)]
6.6 HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest代表客户端的请求,用户通过HTTP协议访问服务器,HTTP请求中的所有信息会封装到HttpServletRequest,通过HttpServletRequest的方法,获得客户端的多有信息;
1.获取前端传递的参数
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QoQC6jWo-1660027835536)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/12/S8wXzEYHjsKJem2.png)]
2.请求转发
请求转发不用写当前web应用的路径getContextPath(),重定向需要写
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 后台接收乱码问题
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
String[] hobbies = req.getParameterValues("hobbies");
System.out.println("===================================");
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbies));
System.out.println("===================================");
// 通过请求转发
// 请求转发不用写当前web应用的路径getContextPath(),重定向需要写
req.getRequestDispatcher("/success.jsp").forward(req,resp);
}
7.Cookie、Session
7.1 会话
**会话:**用户打开一个浏览器,点击了很多超链接,访问了多个web资源,关闭浏览器,这个过程可以称之为会话
**有状态会话:**一个同学来过教室,下次再来教室,我们会知道这个同学曾经来过
一个网站,怎么证明你来过?
客户端 服务端
- 服务端给客户端一个信件,客户端下次访问服务器带上信件就可以了; cookie
- 服务器等级你来过了,下次来的时候匹配你; session
7.2 保存会话的两种技术
cookie
- 客户端技术(响应,请求)
session
- 服务器技术,利用这个技术,可以保存用户的会话信息。我们可以把信息或数据放在session中
常见场景:网站登陆之后,下次不用再登录
7.3 Cookie
- 从请求中拿到cookie信息
- 服务器响应到客户端cookie
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();//获得Cookie
cookie.getName();//获得Cookie中得到key
cookie.getValue();//获得Cookie中的value
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("LastLoginTime", System.currentTimeMillis()+"");//新建一个Cookie
cookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60);//设置Cookie的有效期
resp.addCookie(cookie);//响应给客户端一个Cookie

cookies:一般会保存在本地目录的 用户目录 下 Appdata;
一个网站 cookie 是否存在上限!聊聊细节
- 一个cookie只能保存一个信息;
- 一个web站点可以给浏览器发送多个cookie,最多存放20个cookie;
- cookie大小有限制:4kb;
- 300个(浏览器上限)
删除Cookie:
- 不设置有效期:关闭浏览器,自动失效;
- 设置有效期时间为0;
编码解码
URLEncoder.encode("张三", "utf-8");
URLDecoder.decode("张三","utf-8");
示例:
public class CookieDemo01 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
// 服务器告诉你,你来的时间,把这个时间封装成一个信件,下次带来,服务器就知道了
// 解决中文乱码
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
//Cookie,服务器端从客户端获取
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();// 这里返回数组,说明Cookie可能存在多个
//判断Cookie是否存在
if (cookies != null) {
//如果存在
out.write("你上一次访问的时间是:");
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
//获取cookie的名字
if (cookie.getName().equals("LastLoginTime")) {
//获取cookie中的值
long LastLoginTime = Long.parseLong(cookie.getValue());
Date date = new Date(LastLoginTime);
out.write(date.toLocaleString());
}
}
} else {
out.write("这是您第一次访问本站");
}
//服务器给客户端响应一个cookie
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("LastLoginTime", System.currentTimeMillis()+"");
//cookie有效期为一天
cookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60);
resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}

7.4 Session(重点)
什么是session:
- 服务器会给每一个用户(浏览器)创建一个Session对象;
- 一个Session独占一个浏览器,只要浏览器没有关闭,这个Session就存在;
- 用户登录后,整个网站他都可以访问

Session 和 Cookie 的区别:
- Cookie是吧用户的数据写给用户的浏览器,浏览器保存(可以保存多个);
- Session把用户的数据写到用户独占的Session中,服务器端保存(保存重要的信息,减少服务器资源的浪费);
- Session对象由服务器创建
Session使用场景:
- 保存一个登录用户的信息;
- 购物车信息;
- 在整个网站中经常会使用的数据,我们将它保存的Session中;
示例:
public class SessionDemo01 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 解决乱码问题
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//得到session
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
//给session中存东西
session.setAttribute("name", new Person("张三",3));
//获取session的id
String sessionid = session.getId();
//判断是不是新创建的session
if (session.isNew()) {
resp.getWriter().write("session创建成功,ID:" + sessionid);
} else {
resp.getWriter().write("session已经存在,ID:" + sessionid);
}
//session在创建的时候做了什么事情
//Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID",sessionid);
//resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
得到属性:
-
Person:
package com.swust.pojo; public class Person { private String name; private int age; public Person() { } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } } -
Session
public class SessionDemo02 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 解决乱码问题 resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //得到session HttpSession session = req.getSession(); Person person = (Person) session.getAttribute("name"); System.out.println(person.toString()); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req, resp); } }
手动注销Session:
public class SessionDemo03 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.removeAttribute("name");
//手动注销session
session.invalidate();
}
}
xml设置Session时效:
<!-- 设置session默认的失效时间 -->
<session-config>
<!-- 15分钟后session自动失效 -->
<session-timeout>15</session-timeout>
</session-config>
8. JSP
8.1 什么是JSP
Java Server Pages:Java服务器端页面,也和Servlet一样,用于开发动态web技术!
最大的特点:
- 写JSP就像在写HTML
- 区别:
- HTML只给用户提供静态的数据
- JSP页面中可以嵌入Java代码,为用户提供动态数据
8.2 JSP原理
浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet!
JSP最终也会被转换为一个Java类
JSP本质上就是一个Servlet
//初始化
public void _jspInit() {
}
//销毁
public void jspDestroy() {
}
//JspService
public abstract void _jspService(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2){
}
-
判断请求
-
内置一些对象
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; //页面上下文 final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; //applicationContext final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; //config javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; //out final java.lang.Object page = this; //page:当前页 HttpServletRequest request //请求 HttpServletResponse response //响应 -
输出页面前增加的代码
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8"); pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, false, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out; -
以上的这些个对象,我们可以在JSP页面直接使用

在JSP页面中,只要是Java代码,就会原封不动的输出;
如果是HTML代码,就会转换为:
out.write("<html>\r\n");
这样的格式输出到前端
8.3 JSP基础语法
JSP表达式
<%--JSP表达式
作用:用来将程序的输出,输出到客户端
<%=变量或表达式%>
--%>
<%=new java.util.Date().toLocaleString()%>

JSP脚本片段
<%--JSP脚本片段
--%>
<%
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
out.println("<h1>sum=" + sum + "</h>");
%>

脚本片段再实现
<%
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
%>
Hello,World<%=i%>
<hr>
<%
}
%>

JSP声明
<%!
static {
System.out.println("Loading Servlet");
}
private final int globalVar = 0;
public void abc() {
System.out.println("进入了方法abc");
}
%>
JSP声明:会被编译到JSP生成的Java类中!其他的就会被生成到jspService方法!
在JSP,嵌入Java代码即可
8.4 JSP指令
<%@page args... %>
<%@include file=""%>
<%-- JSP 标签:
jsp:include:拼接页面,本质还是三个--%>
<jsp:include page="/commo/header.jsp"/>
<h1>
网页主体
</h1>
<jsp:include page="/commo/footer.jsp"/>
...
8.5 9大内置对象
- PageContext 存东西
- Request 存东西
- Response
- Session 存东西
- Application【ServletContext】存东西
- config【ServletConfig】
- out
- page 不用了解
- exception
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("name1","张1");//保存的数据只在一个页面中有效
request.setAttribute("name2","张2");//保存的数据只在一次请求中有效,请求转发会携带这个数据
session.setAttribute("name3","张3");//保存的数据只在一次会话中有效,从打开浏览器到关闭浏览器
application.setAttribute("name4","张4");//保存的数据在服务器中有效,从打开服务器到关闭服务器
%>
request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如:新闻
session:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完一会还有用,比如:购物车
application:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户看完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如:聊天数据
8.6 JSP标签、JSTL标签、EL表达式
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet.jsp.jstl/jstl-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/taglibs/standard -->
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
EL表达式:${}
- 获取数据
- 执行运算
- 获取web开发的常用对象
- 调用Java方法
JSP标签:
<%--jsp:include--%>
<%--
http://localhost:8080/jsptag.jsp?name=zhangsan&age=2
--%>
<jsp:forward page="/jsptag2.jsp">
<jsp:param name="name" value="zhangsan"></jsp:param>
<jsp:param name="age" value="12"></jsp:param>
</jsp:forward>
JSTL表达式:
JSTL标签库的使用就是为了弥补HTML标签的不足;他自定义了许多标签,标签的功能和Java代码一样
JSTL标签库使用步骤:
-
引入对应的taglib
引用核心标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> -
使用其中的方法
核心标签

- 格式化标签
- SQL标签
9. JavaBean
实体类
JavaBean有特定的写法
- 必须要有一个无参构造
- 属性必须私有化
- 必须有对应的get/set方法
一般用来和数据库的字段做映射 ORM;
ORM:对象关系映射
- 表 --> 类
- 字段 --> 属性
- 行记录 --> 对象
举例:我们创建一个实体类People:
public class People {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String address;
public People() {
}
public People(int id, String name, int age, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
在数据库中也创建同样的表:

则在jsp中,下述两种方法是等效的:
-
<% People people = new People(); people.setAddress("西安"); people.setId(1); people.setAge(3); people.setName("张三"); %> <%=people.getAddress()%> <%=people.getId()%> <%=people.getAge()%> <%=people.getName()%> -
<jsp:useBean id="people" class="com.swust.pojo.People" scope="page"/> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="address" value="西安"/> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="id" value="1"/> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="age" value="3"/> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="name" value="张三"/> 姓名:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="name"/> Id:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="id"/> 年龄:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="age"/> 地址:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="address"/>
10. MVC三层架构
什么是MVC:Model,view,Controller 模型,视图,控制器
早期开发:

用户直接访问控制层,控制层就可以直接操作数据:
servlet – CRUD – 数据库
弊端:程序十分臃肿,不利于维护
servlet的代码中:处理请求、响应、维护、视图跳转、处理JDBC、处理业务代码、处理逻辑代码架构:没有什么事加一层解决不了的!
MVC三层架构:

Model
- 业务处理:业务逻辑(Service)
- 数据持久层:CRUD(Dao)
View
- 展示数据
- 提供链接发起的Servlet请求(a,form,img…)
Controller
- 接收用户的请求:(req:请求参数、Session信息…)
- 交给业务层处理对应的代码
- 控制视图的跳转
登录—>接收用户的登录请求—>处理用户的请求(获取用户登录的参数,username,password)—>交给业务层处理登录业务(判断用户密码是否正确:事务)—>Dao层查询用户名和密码是否正确—>数据库
11. Filter
Filter:过滤器,用来过滤网站的数据;
- 处理中文乱码
- 登录验证

Filter开发步骤:
-
导包
-
编写过滤器
- 导包不要错(一定要选择javax.servlet)

-
代码
Java(过滤器)
public class CharacterEncodingFilter implements Filter { //初始化:web服务器启动,就已经初始化了,随时等待过滤对象出现! @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter初始化"); } //Chain :链 /* 1.过滤器中的所有代码,在过滤特定请求的时候都会执行 2.必须要让过滤器继续通行 filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse); */ @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { servletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); servletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); servletResponse.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter执行前......"); filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//让我们的请求继续走,如果不写,程序到这里就拦截停止 System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter执行后......"); } //销毁:web服务器关闭的时候,过滤器会销毁 @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter销毁"); } }Java(Servlet)
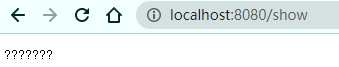
public class ShowServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-16"); resp.getWriter().write("你好呀,世界!"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req, resp); } }
-
在web.xml配置Fileter
<servlet> <servlet-name>ShowServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.swust.servlet.ShowServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ShowServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/servlet/show</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ShowServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/show</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.swust.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <!--只要是/Servlet的任何请求,都会经过这个过滤器--> <url-pattern>/servlet/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> -
测试结果

12. 过滤器、监听器常见应用
用户登录之后才能进入主页!用户注销后就不能进入主页:
-
用户登录之后,向Session中放入用户的数据
-
进入主页的时候要判断用户是否已经登录,在过滤器中实现
@Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse; if(request.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION")==null){ response.sendRedirect("/error.jsp"); } filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse); }





















 791
791

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








