使用的Python 版本为3.10,IDE是Pycharm2024。
其中Pygame版本为2.6.1,numpy版本为2.1.3。
制作不易,感觉不赖的话可以点点赞,感谢!
一、结果展示
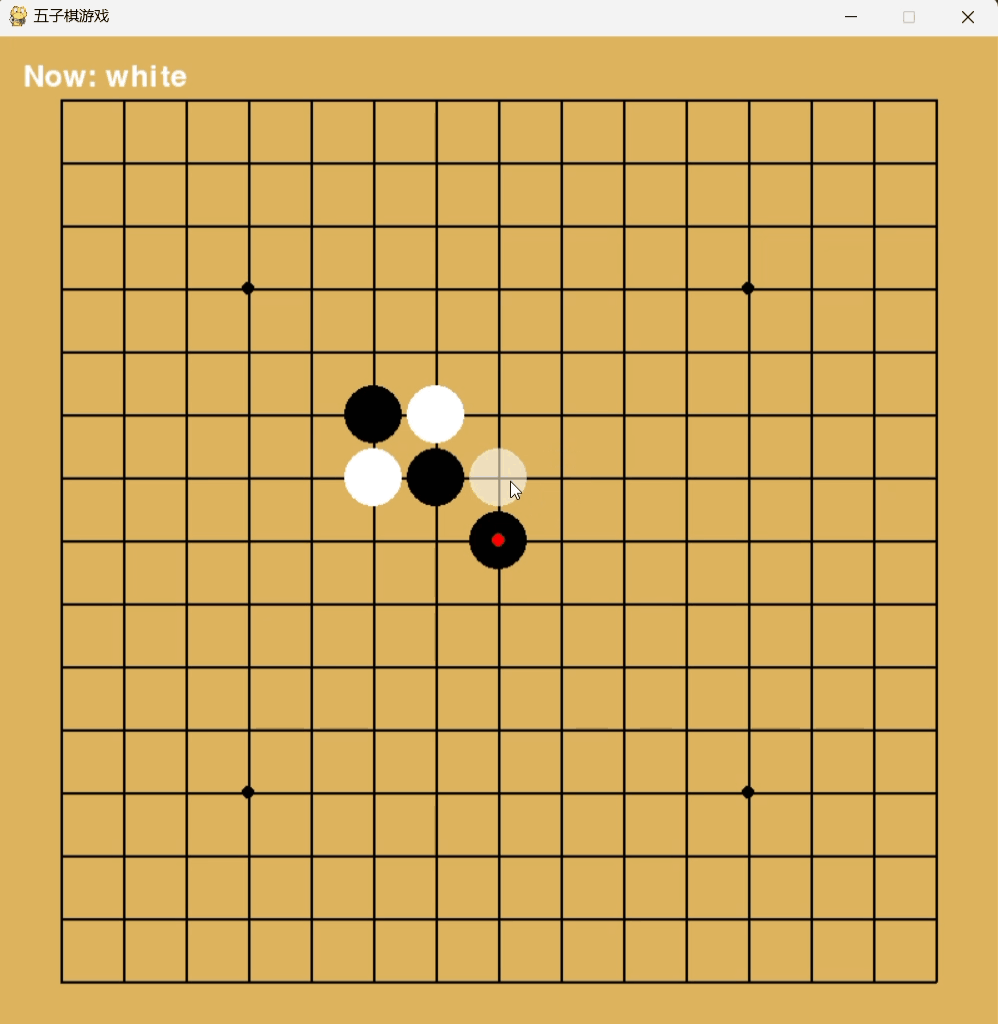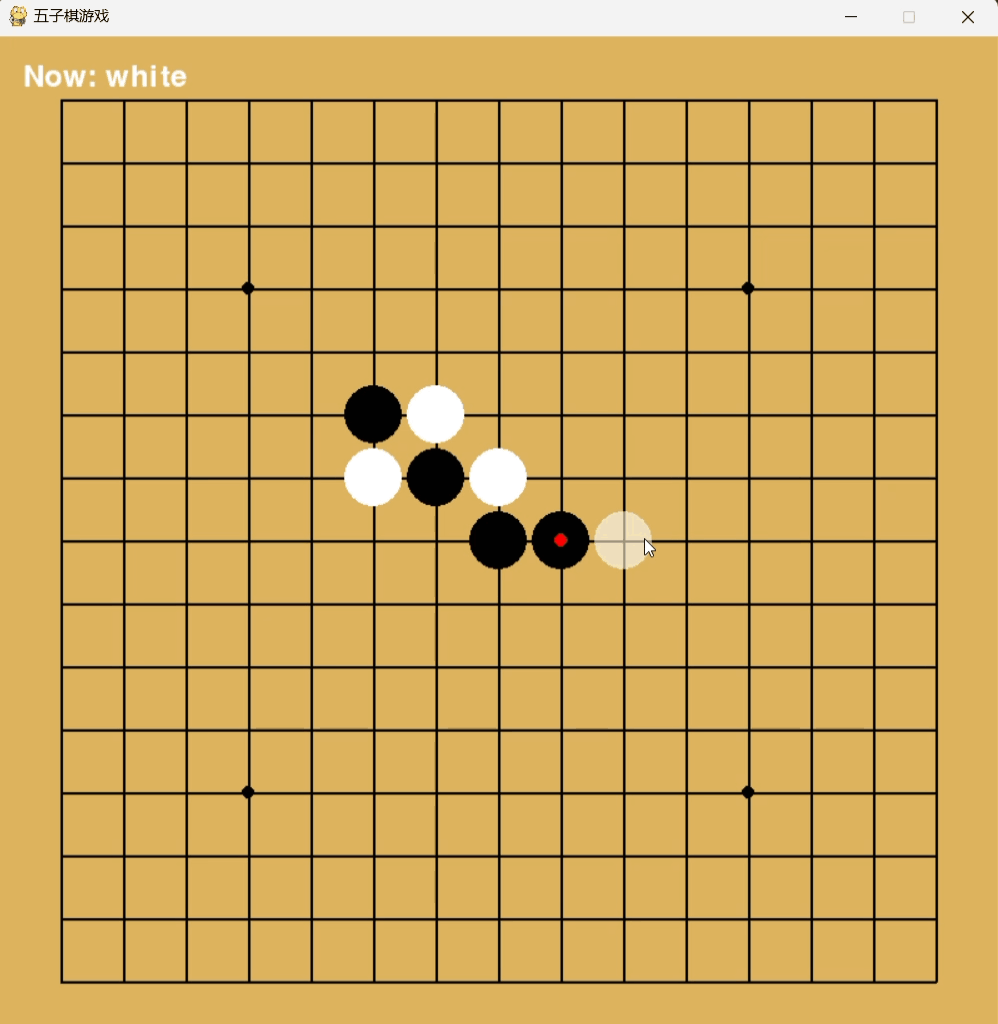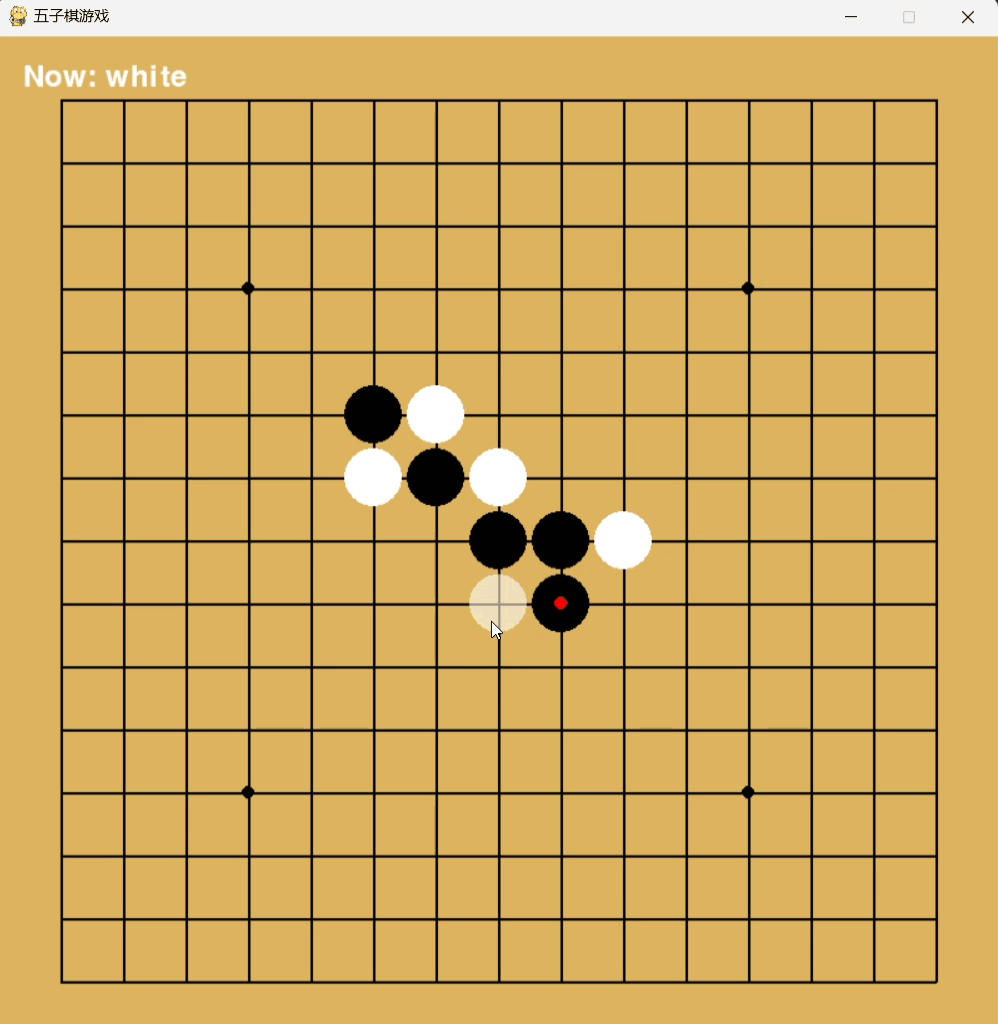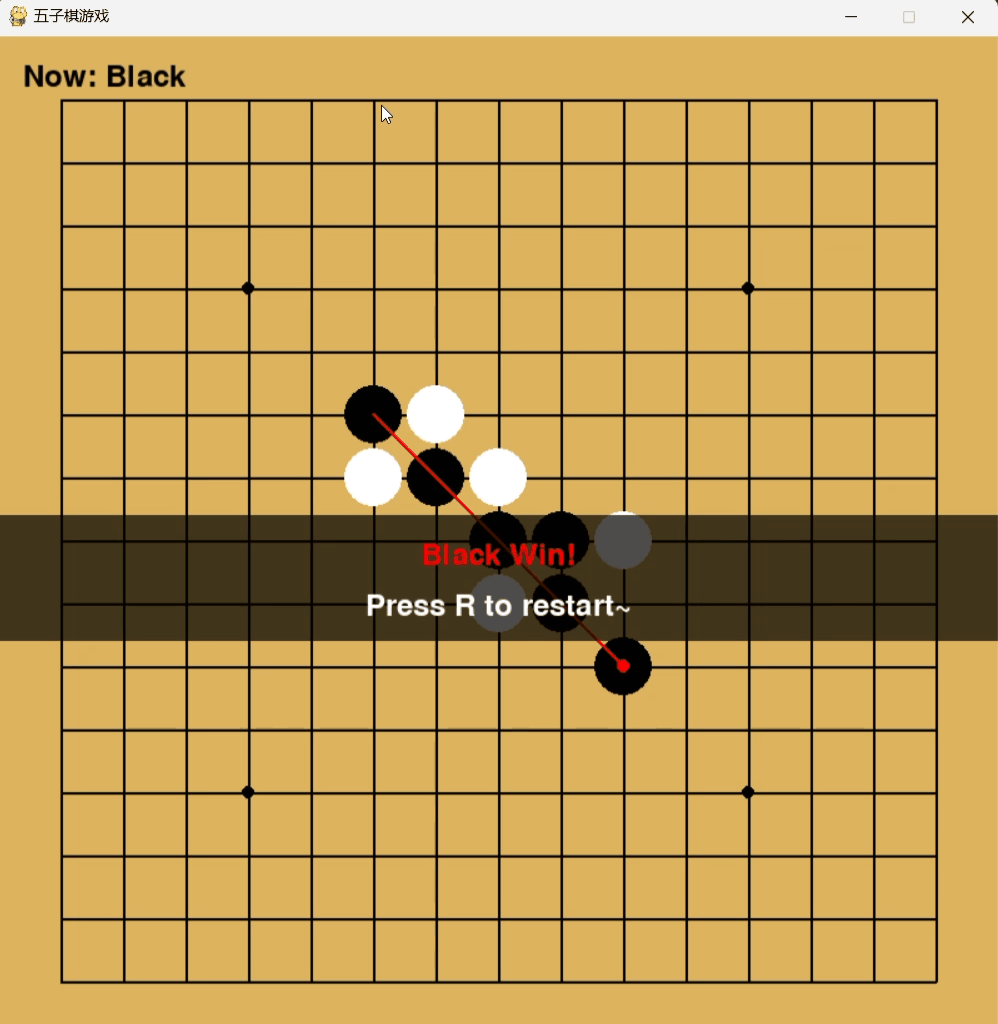
二、源码展示
import pygame
import numpy as np
# 初始化
pygame.init()
# 常量
WIDTH, HEIGHT = 800, 800
LINE_COUNT = 15
GRID_SIZE = WIDTH // (LINE_COUNT + 1)
BOARD_SIZE = GRID_SIZE * (LINE_COUNT - 1)
# 颜色表
BACKGROUND_COLOR = (220, 179, 92)
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
# 创建游戏窗口
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, HEIGHT))
pygame.display.set_caption("五子棋游戏")
font = pygame.font.SysFont(None, 36)
class GomokuGame:
def __init__(self):
self.reset_game()
self.offset = GRID_SIZE
def reset_game(self):
self.board = np.zeros((LINE_COUNT, LINE_COUNT), dtype=int)
self.current_player = 1
self.game_over = False
self.winner = None
self.last_move = None
self.winning_line = None
def draw_board(self):
screen.fill(BACKGROUND_COLOR)
for i in range(LINE_COUNT):
pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset, self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE),
(self.offset + BOARD_SIZE, self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE), 2)
pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE, self.offset),
(self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + BOARD_SIZE), 2)
# 绘制棋盘上的五个点
points = [(3, 3), (3, 11), (7, 7), (11, 3), (11, 11)]
for point in points:
x, y = point
pygame.draw.circle(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset + x * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + y * GRID_SIZE), 5)
def draw_pieces(self):
for row in range(LINE_COUNT):
for col in range(LINE_COUNT):
if self.board[row][col] == 1:
pygame.draw.circle(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE),
GRID_SIZE // 2 - 2)
elif self.board[row][col] == 2:
pygame.draw.circle(screen, WHITE,
(self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE),
GRID_SIZE // 2 - 2)
# 标记最后一步棋
if self.last_move:
row, col = self.last_move
pygame.draw.circle(screen, RED,
(self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE),
5)
# 绘制胜利线
if self.game_over and self.winning_line:
start_row, start_col, end_row, end_col = self.winning_line
start_x = self.offset + start_col * GRID_SIZE
start_y = self.offset + start_row * GRID_SIZE
end_x = self.offset + end_col * GRID_SIZE
end_y = self.offset + end_row * GRID_SIZE
pygame.draw.line(screen, RED, (start_x, start_y), (end_x, end_y), 3)
def place_piece(self, row, col):
if self.game_over:
return False
# 检查是否已有棋子
if self.board[row][col] != 0:
return False
# 放置棋子
self.board[row][col] = self.current_player
self.last_move = (row, col)
# 检查是否获胜
win_info = self.check_win(row, col)
if win_info[0]: # 如果获胜
self.game_over = True
self.winner = self.current_player
self.winning_line = win_info[1]
elif np.count_nonzero(self.board) == LINE_COUNT * LINE_COUNT:
self.game_over = True
self.winner = 0
else:
# 切换玩家
self.current_player = 3 - self.current_player
return True
def check_win(self, row, col):
player = self.board[row][col]
# 检查方向
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, -1)]
for dr, dc in directions:
count = 1 # 当前位置已经有一个棋子
start_row, start_col = row, col
end_row, end_col = row, col
r, c = row + dr, col + dc
while 0 <= r < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= c < LINE_COUNT and self.board[r][c] == player:
count += 1
end_row, end_col = r, c
r += dr
c += dc
# 反向检查
r, c = row - dr, col - dc
while 0 <= r < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= c < LINE_COUNT and self.board[r][c] == player:
count += 1
start_row, start_col = r, c
r -= dr
c -= dc
if count >= 5:
return True, (start_row, start_col, end_row, end_col)
return False, None
def draw_game_info(self):
# 显示当前玩家
player_text = "Now: " + ("Black" if self.current_player == 1 else "White")
player_color = BLACK if self.current_player == 1 else WHITE
text_surface = font.render(player_text, True, player_color)
screen.blit(text_surface, (20, 20))
# 获胜信息
if self.game_over:
if self.winner == 0:
message = "Round Draw!"
else:
message = f"{'Black' if self.winner == 1 else 'White'} Win!"
# 半透明背景
s = pygame.Surface((WIDTH, 100), pygame.SRCALPHA)
s.fill((0, 0, 0, 180))
screen.blit(s, (0, HEIGHT - 420))
# 显示消息
text_surface = font.render(message, True, RED)
screen.blit(text_surface, (WIDTH // 2 - text_surface.get_width() // 2, HEIGHT - 400))
# 显示重新开始提示
restart_text = "Press R to restart~"
restart_surface = font.render(restart_text, True, WHITE)
screen.blit(restart_surface, (WIDTH // 2 - restart_surface.get_width() // 2, HEIGHT - 360))
def draw_mouse_hover(self, pos):
if self.game_over:
return
# 将鼠标位置转换为棋盘坐标
x, y = pos
col = round((x - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
row = round((y - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
# 检查坐标是否在棋盘范围内
if 0 <= row < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= col < LINE_COUNT:
# 如果该位置为空,绘制半透明的棋子预览
if self.board[row][col] == 0:
color = BLACK if self.current_player == 1 else WHITE
s = pygame.Surface((GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE), pygame.SRCALPHA)
pygame.draw.circle(s, (*color, 150), (GRID_SIZE // 2, GRID_SIZE // 2), GRID_SIZE // 2 - 2)
screen.blit(s, (self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE - GRID_SIZE // 2,
self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE - GRID_SIZE // 2))
def run(self):
# 游戏主循环
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
# 鼠标点击事件
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN and not self.game_over:
if event.button == 1:
x, y = event.pos
col = round((x - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
row = round((y - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
if 0 <= row < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= col < LINE_COUNT:
self.place_piece(row, col)
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
if event.key == pygame.K_r:
self.reset_game()
self.draw_board()
self.draw_pieces()
self.draw_mouse_hover(pygame.mouse.get_pos())
self.draw_game_info()
pygame.display.flip()
if __name__ == "__main__":
game = GomokuGame()
game.run()
三、代码解释
想要制作一个五子棋游戏,那我们首先就得了解五子棋的规则:(内容来自百度)
-
棋盘布局:五子棋棋盘为15×15的方形格子。
-
棋子标记:通常用黑白两种颜色的棋子,黑棋先手。
-
落子顺序:黑方先下,轮流落子,每次只能下一个棋子。
-
落子位置:棋子放在棋盘的任意交叉点上。
-
胜利条件:先在棋盘上形成五个相同颜色的棋子连成一条线(横、竖、斜线皆可)的一方获胜。
了解完五子棋游戏以后,初步思路是利用pygame的可视化界面以及对鼠标键盘的事件响应来实现棋盘展现、棋子的放置等等。然后通过numpy库的矩阵计算来实现五子棋的胜利逻辑。
1.全局变量
初始设置一些需要用到的常量,例如窗口的长宽,棋盘的宽度以及颜色表,方便后续编写时调用。
# 常量
WIDTH, HEIGHT = 800, 800 # 窗口尺寸
LINE_COUNT = 15 # 棋盘的宽度,一般为15*15
GRID_SIZE = WIDTH // (LINE_COUNT + 1) # 棋盘的网格尺寸
BOARD_SIZE = GRID_SIZE * (LINE_COUNT - 1) # 棋盘大小
# 颜色表
BACKGROUND_COLOR = (220, 179, 92) # 棋盘配色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
# 创建游戏窗口
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, HEIGHT)) # 创建800*800的窗口
pygame.display.set_caption("五子棋游戏") # 设置窗口标题
font = pygame.font.SysFont(None, 36) # 字体设置,None表示默认字体
2.类的编写
__init__()和reset_game()
此处部分较多且为代码的核心部分,所以下方我逐个函数进行分析:
以下代码我创建一个GomokuGame类来实现五子棋的功能和性质。作为五子棋,每次调用为实例时应该呈现的是一个15*15的空棋盘。所以在初始化方法__init__()中写入重置棋盘的函数,并且设置棋盘的距离窗口的边距,让棋盘有一个居中的视觉效果。
在reset_game函数中:
- 利用np中的零矩阵来模拟空的棋盘。
- 设定黑为1,白为2。根据规则,黑棋先行,current_player = 1
- 其余的就是将游戏结束信号、赢家、最后一步棋的位置以及胜利连线全部初始化为空。
这样就算是完全重新开了一局新的游戏。
# 五子棋类
class GomokuGame:
def __init__(self):
self.reset_game() # 重置游戏
self.offset = GRID_SIZE # 棋盘的边距
def reset_game(self):
self.board = np.zeros((LINE_COUNT, LINE_COUNT), dtype=int) # 空棋盘
self.current_player = 1 # 黑棋为1,先行
self.game_over = False # 游戏结束信号
self.winner = None # 赢家
self.last_move = None # 最后一步棋位置记录
self.winning_line = None # 胜利连线
draw_board()和draw_pieces()
此处为绘制图像,也就是最终呈现的棋盘部分,其中我通过for循环 + pygame中的draw模块的line函数来绘制棋盘,循环次数为之前的常量LINE_COUNT。其中以绘制横线那部分为例来详细解释一下各个参数表示的意思:
- screen:绘制的目标,即我之前创建的窗口
- BLACK:线条颜色
- (self.offset, self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE): 起点坐标(x = 边距, y = 边距 + 循环每格)
- (self.offset + BOARD_SIZE, self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE): 终点坐标(x = 边距 + 棋盘总长, y = 边距 + 循环每格)
- 最后一个2表示线条的宽度。
然后是绘制棋子的部分,绘制棋子的部分比较简单,通过两个for循环嵌套来遍历整个棋盘board,也就是初始化时设置的零矩阵。如果该处为1,那么表示此处为黑子,此时绘制黑棋。如果为2,此时绘制白棋。绘制利用circle()函数,其参数与上述的差不多。
除了绘制棋子之外,还用红点标记最后一步棋子的位置,以便玩家做出相应的对策。同时,当胜利的时候,还要记录胜利的五子位置,所以还应记录胜利五子的首尾棋子的位置,便于绘制连接线。
def draw_board(self):
screen.fill(BACKGROUND_COLOR) # 背景颜色填充
# 绘制网格线
for i in range(LINE_COUNT):
# 横线
pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset, self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE),
(self.offset + BOARD_SIZE, self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE), 2)
# 竖线
pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE, self.offset),
(self.offset + i * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + BOARD_SIZE), 2)
# 绘制棋盘上的天元和星(棋盘都有的五个点,严谨加上)
points = [(3, 3), (3, 11), (7, 7), (11, 3), (11, 11)]
for point in points:
x, y = point
pygame.draw.circle(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset + x * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + y * GRID_SIZE), 5)
def draw_pieces(self):
for row in range(LINE_COUNT):
for col in range(LINE_COUNT):
if self.board[row][col] == 1: # 绘制黑棋
pygame.draw.circle(screen, BLACK,
(self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE),
GRID_SIZE // 2 - 2)
elif self.board[row][col] == 2: # 绘制白棋
pygame.draw.circle(screen, WHITE,
(self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE),
GRID_SIZE // 2 - 2)
# 标记最后一步棋
if self.last_move:
row, col = self.last_move
pygame.draw.circle(screen, RED,
(self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE, self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE),
5)
# 绘制胜利线
if self.game_over and self.winning_line:
start_row, start_col, end_row, end_col = self.winning_line
start_x = self.offset + start_col * GRID_SIZE
start_y = self.offset + start_row * GRID_SIZE
end_x = self.offset + end_col * GRID_SIZE
end_y = self.offset + end_row * GRID_SIZE
pygame.draw.line(screen, RED, (start_x, start_y), (end_x, end_y), 3)
place_piece()和 check_win()
此处为放置棋子和判断胜利的逻辑,后续会跟鼠标的点击事件联系。也是整个程序中最重要的部分,五子相连的逻辑判断。主要时对于check_win()程序进行讲解:
check_win函数需要的参数是当前棋子的位置,即行和列(row,col)。player表示当前是白棋还是黑棋。设置directions列表,里面包括四个方向向量:水平、垂直、主对角线方向、副对角线方向。
其中使用for循环对每个方向进行检查,dr、dc分别表示行方向的变化量和列方向上的变化量。初始化count = 1,start和end。因为当前已经有了一个棋子,所以数量记为1,其中起点和终点都是该棋子。
以水平方向检查为例,r和c为当前方向的延伸,同时在while循环中来确保棋子仍在棋盘内而且属于该player的棋子。在该棋子正方向上延伸,如果有棋子count就加1,并且更新终点位置end,同时继续向正方向延伸直到没有同类棋子。当正向检查结束之后,开始反向检查,基本同理,就是r和c向左方延伸,然后逐个查找是否为同类棋子,直至不满足条件。
如果水平方向上没有满足胜利条件,那么就会继续垂直、主对角线、副对角线这三个方向上进行查找。如果有满足count>=5的,那么即为胜利,返回胜利五子的起点坐标和终点坐标。
place_piece()函数主要是检查落子的合法性以及执行落子操作,接收的是当前要落子的行坐标和列坐标。在self.board上更新为当前的棋子,黑棋就是1,白棋就是2。并且更新last_move为当前的棋子位置。
通过调用check_win()来检查是否达成胜利,胜利了就更新game_over信号、并且将当前棋子定为赢家,同时将起点终点的坐标载入到winning_line。如果棋盘被填满(非零元素为零个)且无人获胜,则视为平局。否则就通过数学简便写法 3 - current_player 来切换黑子和白子。
def place_piece(self, row, col):
if self.game_over: # 游戏结束时不能下棋
return False
# 检查是否已有棋子
if self.board[row][col] != 0:
return False
# 放置棋子
self.board[row][col] = self.current_player
self.last_move = (row, col)
# 检查是否获胜
win_info = self.check_win(row, col)
if win_info[0]: # 如果获胜
self.game_over = True
self.winner = self.current_player
self.winning_line = win_info[1]
elif np.count_nonzero(self.board) == LINE_COUNT * LINE_COUNT: # 平局
self.game_over = True
self.winner = 0
else:
# 切换玩家
self.current_player = 3 - self.current_player
return True
def check_win(self, row, col):
player = self.board[row][col]
# 检查方向
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, -1)]
for dr, dc in directions:
count = 1 # 当前位置已经有一个棋子
start_row, start_col = row, col # 五子首
end_row, end_col = row, col # 五子尾
# 正向检查
r, c = row + dr, col + dc
while 0 <= r < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= c < LINE_COUNT and self.board[r][c] == player:
count += 1
end_row, end_col = r, c
r += dr
c += dc
# 反向检查
r, c = row - dr, col - dc
while 0 <= r < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= c < LINE_COUNT and self.board[r][c] == player:
count += 1
start_row, start_col = r, c
r -= dr
c -= dc
# 如果个数大于等于5,视作胜利
if count >= 5:
return True, (start_row, start_col, end_row, end_col)
return False, None
draw_game_info()和draw_mouse_hover()
draw_game_info()这个方法是五子棋游戏的信息显示函数,负责在屏幕上绘制当前游戏状态和结果信息。例如在屏幕左上角(20, 20)位置显示当前轮到哪位玩家下棋、在游戏结束时显示半透明背景显示赢家或者平局,同时提示按R去重启对局。
draw_game_info()这个方法用于显示鼠标悬停时的预览效果。通过读取鼠标的屏幕像素坐标(x, y),移去棋盘偏移量self.offset,除以格子的像素大小四舍五入可以得到最近的整数行列索引。同时确保再棋盘内,而且该位置没有棋子才可显示预览。透明效果需要用到pygame.SRCALPHA来启用透明通道,创建透明的Surface。
def draw_game_info(self):
# 显示当前玩家
player_text = "Now: " + ("Black" if self.current_player == 1 else "White")
player_color = BLACK if self.current_player == 1 else WHITE
text_surface = font.render(player_text, True, player_color)
screen.blit(text_surface, (20, 20))
# 获胜信息
if self.game_over:
if self.winner == 0:
message = "Round Draw!"
else:
message = f"{'Black' if self.winner == 1 else 'White'} Win!"
# 半透明背景
s = pygame.Surface((WIDTH, 100), pygame.SRCALPHA)
s.fill((0, 0, 0, 180))
screen.blit(s, (0, HEIGHT - 420))
# 显示消息
text_surface = font.render(message, True, RED)
screen.blit(text_surface, (WIDTH // 2 - text_surface.get_width() // 2, HEIGHT - 400))
# 显示重新开始提示
restart_text = "Press R to restart~"
restart_surface = font.render(restart_text, True, WHITE)
screen.blit(restart_surface, (WIDTH // 2 - restart_surface.get_width() // 2, HEIGHT - 360))
def draw_mouse_hover(self, pos):
if self.game_over:
return
# 将鼠标位置转换为棋盘坐标
x, y = pos
col = round((x - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
row = round((y - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
# 检查坐标是否在棋盘范围内
if 0 <= row < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= col < LINE_COUNT:
# 如果该位置为空,绘制半透明的棋子预览
if self.board[row][col] == 0:
color = BLACK if self.current_player == 1 else WHITE
s = pygame.Surface((GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE), pygame.SRCALPHA)
pygame.draw.circle(s, (*color, 150), (GRID_SIZE // 2, GRID_SIZE // 2), GRID_SIZE // 2 - 2)
screen.blit(s, (self.offset + col * GRID_SIZE - GRID_SIZE // 2,
self.offset + row * GRID_SIZE - GRID_SIZE // 2))
run()
该方法是五子棋游戏的核心控制循环,负责处理游戏的所有事件和渲染。主循环中不断获取待处理的事件,更新整个显示界面,例如窗口的关闭、左键点击时放置棋子、R键重新开始游戏。再循环中绘制棋盘和背景,绘制所有棋子以及游戏信息状态和鼠标悬停预览。
def run(self):
# 游戏主循环
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 退出游戏
pygame.quit()
# 鼠标点击事件
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN and not self.game_over:
if event.button == 1: # 左键点击
# 转换坐标并尝试放置棋子
x, y = event.pos
col = round((x - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
row = round((y - self.offset) / GRID_SIZE)
if 0 <= row < LINE_COUNT and 0 <= col < LINE_COUNT:
self.place_piece(row, col)
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
if event.key == pygame.K_r: # R键重新开始
self.reset_game()
# 游戏绘制
self.draw_board()
self.draw_pieces()
self.draw_mouse_hover(pygame.mouse.get_pos())
self.draw_game_info()
pygame.display.flip()




















 1454
1454

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








