什么是 Spring cloud stream ?
官方定义 Spring Cloud Stream 是一个构建消息驱动微服务的框架。
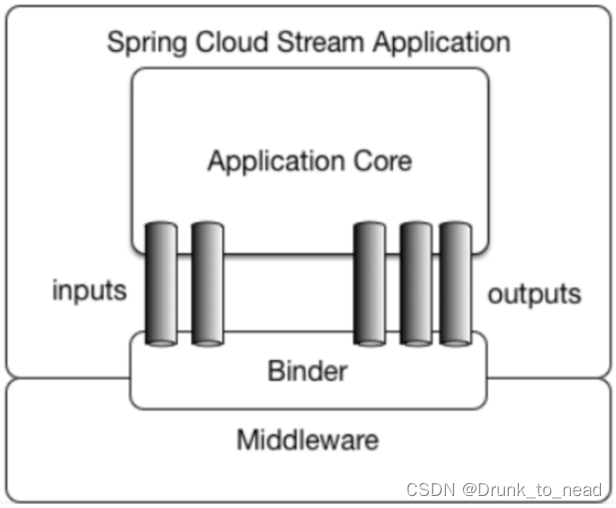
应用程序通过 inputs 或者 outputs 来与 Spring Cloud Stream 中binder 交互,通过我们配置来 binding ,而 Spring Cloud Stream 的 binder 负责与消息中间件交互。所以,我们只需要搞清楚如何与 Spring Cloud Stream 交互就可以方便使用消息驱动的方式。
通过使用Spring Integration来连接消息代理中间件以实现消息事件驱动。Spring Cloud Stream 为一些供应商的消息中间件产品提供了个性化的自动化配置实现,引用了发布-订阅、消费组、分区的三个核心概念。支持异常自动重试机制,并且可输入到dlq队列中。目前仅支持RabbitMQ、Kafka。
Stream解决了开发人员无感知的使用消息中间件的问题,因为Stream对消息中间件的进一步封装,可以做到代码层面对中间件的无感知,甚至于 动态的切换中间件 (rabbitmq切换为kafka),使得微服务开发的高度解耦,服务可以关注更多自己的业务流程
官方结构图:
常用注解:
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Input | 注解标识 输入 通道,通过该输入通道接收到的消息进入应用程序。 |
| @Output | 注解标识 输出 通道,发布的消息将通过该通道离开应用程序。 |
| @StreamListener | 监听队列,用于消费者的队列的 消息接收 |
| @EnableBinding | 指信道channel和exchange绑定在一起 |
根据Spring Boot 版本 找到相对应的 Spring Cloud Stream Kafka 版本 文档
官网文档:https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-stream#overview
demo
引入maven文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 或 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
定义一个Processor通道
public interface IProcessor {
String INPUT = "input";
String OUTPUT = "output";
/**
* 创建一个输入通道
*
* @return
*/
@Input(IProcessor.INPUT)
SubscribableChannel in();
/**
* 创建一个输出通道
*
* @return
*/
@Output(IProcessor.OUTPUT)
MessageChannel out();
}
实现消息输出通道
/**
* 消息发送
*/
@Service
public class SendService {
@Resource
private IProcessor processor;
/**
* 通过该方法发送一条记录
*/
public void raceCarSoreLikeOut(String msg){
// 发送一条记录
processor.out()
.send(
// 消息生成器转换
MessageBuilder.withPayload(msg)
// 可以设置 发送请求头 这里设置了 kafka_messageKey
.setHeader(
KafkaHeaders.MESSAGE_KEY,
msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
).build()
);
}
}
实现consume
/**
* 消费者
* 通过EnableBinding 绑定信道 可以输入多 @EnableBinding({a.class,b.class})
*/
@EnableBinding(IProcessor.class)
public class ConsumerService {
/**
* 实现方式 一
*/
@StreamListener(IProcessor.INPUT)
public void in(Message<String> payload) {
// 业务实现
// 获取消息体
payload.getPayload();
// 获取请求头
payload.getHeaders();
}
/**
* 实现方式 二 ......推荐使用 String 进行传输
*/
@StreamListener(IProcessor.INPUT)
public void in(@Payload String payload,@Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_MESSAGE_KEY) byte[] keymessageKey) {
// 业务实现
}
}
application.yml 文件
# spring cloud stream kafka config
spring:
cloud:
stream:
kafka:
binder:
# Kafka的消息中间件服务器 地址
brokers: ${kafka.bootstrap-servers}
# 开启自动分区
auto-add-partitions: true
# 关闭自动创建 topic
auto-create-topics: false
streams:
binder:
# 配置 处理 Binder 中的异常
# logAndContinue, 记录 并 继续
# logAndFail, 默认 记录 并 失败
# sendToDlq; 成功 并 加入死信队列
deserializationExceptionHandler: sendToDlq
bindings:
# 这里就是在 IProcessor 定义的 INPUT
input:
consumer:
# 是否开启 dlq 队列
enable-dlq: ${kafka.topic.A-topic.dlq}
# 默认开启 启动自平衡模式 可以轮询消费多台服务
auto-rebalance-enabled: true
# 指定 dlq 队列名称 默认为 error.<destination>.<group>
dlq-name: ${kafka.topic.A-topic.dlq-name}
# 是否开启自动提交 默认开启
auto-commit-offset: false
bindings:
output:
# 指定生产 topic
destination: ${kafka.topic.A-topic}
# 消息转换器 默认 application/json
content-type: text/plain
producer:
partition-key-expression: payload
input:
# 指定消费 topic
destination: ${kafka.topic.A-topic}
# 消息转换器 默认 application/json
content-type: text/plain
# 分组
group: ${kafka.topic.A-topic.group}
# 消费的一些设置参数 如 开启分区、重试次数... 具体看官网提供的文档
consumer:
partitioned: true





 Spring Cloud Stream是一个构建消息驱动微服务的框架,简化了与消息中间件的交互。它支持发布-订阅模型、消费组和分区等特性,并提供自动配置支持RabbitMQ和Kafka等中间件。本文介绍其核心概念、配置及示例代码。
Spring Cloud Stream是一个构建消息驱动微服务的框架,简化了与消息中间件的交互。它支持发布-订阅模型、消费组和分区等特性,并提供自动配置支持RabbitMQ和Kafka等中间件。本文介绍其核心概念、配置及示例代码。
















 860
860

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








