|
Language:
Radar Installation
Description
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates. 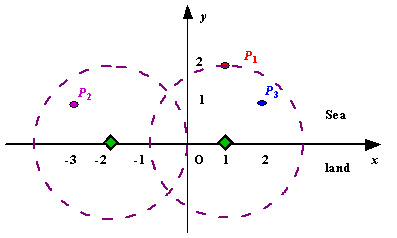
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros Output
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. "-1" installation means no solution for that case.
Sample Input 3 2 1 2 -3 1 2 1 1 2 0 2 0 0 Sample Output Case 1: 2 Case 2: 1 Source |
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
double x,y;
struct point
{
double x1;
double x2;
} p[1001];
int cmp(point a,point b)
{
return a.x1<b.x1;
}
int main()
{
int n,d;
//int ans=1;
int kase=0;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&d)&&n+d)
{
int ans=1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>x>>y;
p[i].x1=x-sqrt(d*d-y*y);
p[i].x2=x+sqrt(d*d-y*y);
if(y>d||y<0||d<=0)
ans=-1;
}
sort(p,p+n,cmp);
double xx=p[0].x2;
for(int i=1; i<n && ans!=-1; i++)
{
if(p[i].x1>xx)
{
ans++;
xx=p[i].x2;
}
else if(p[i].x2<xx)
{
xx=p[i].x2;
}
}
printf("Case %d: %d\n",++kase,ans);
}
}








 本文探讨了在无限海岸线上,通过雷达安装实现岛屿覆盖的最小数量问题。使用二维坐标系,通过输入岛屿的位置和雷达的覆盖距离,计算并输出所需雷达安装的数量。通过实例演示了解决此类问题的方法。
本文探讨了在无限海岸线上,通过雷达安装实现岛屿覆盖的最小数量问题。使用二维坐标系,通过输入岛屿的位置和雷达的覆盖距离,计算并输出所需雷达安装的数量。通过实例演示了解决此类问题的方法。
















 1186
1186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








