机器学习作业 西瓜书4.4(C)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#define LABLECOUNT 7 //特征数(包括类别)
#define SAMPLECOUNT 10 //样本集大小
#define VERTIFYCOUNT 7 //验证集大小
/*
色泽:青绿0 乌黑1 浅白2
根蒂:蜷缩0 稍蜷1 硬挺2
敲声:浊响0 沉闷1 清脆2
纹理:清晰0 稍糊1 模糊2
脐部:凹陷0 稍凹1 平坦2
触感:硬滑0 软粘1
好瓜:是1 否0
*/
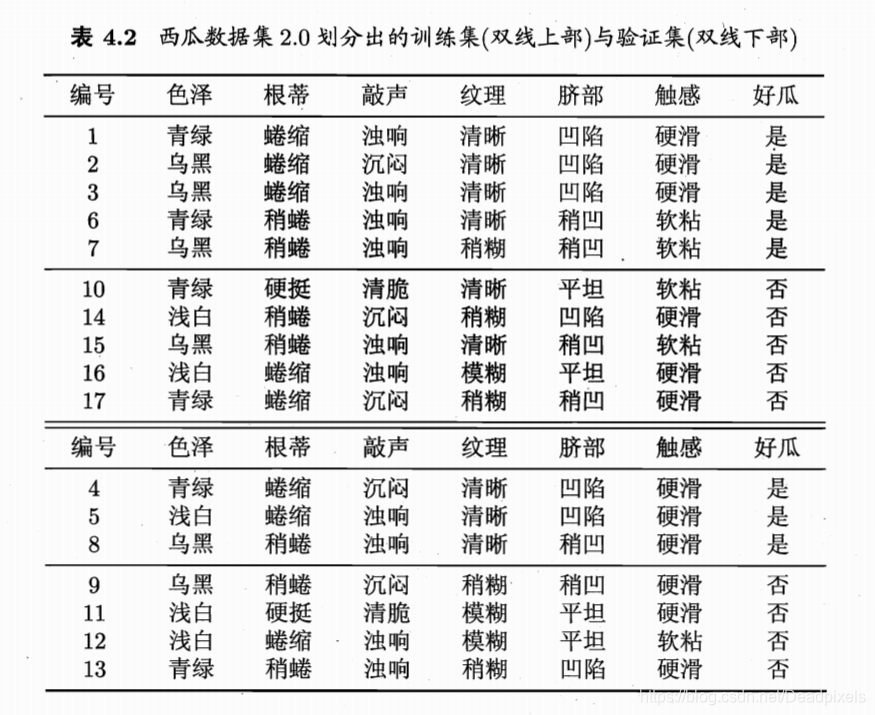
int datasets[SAMPLECOUNT][LABLECOUNT]={ //数据集,第一列是类别,后几列是特征
{1,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,1,0,0,1,1},
{1,1,1,0,1,1,1},
{0,0,2,2,0,2,1},
{0,2,1,1,1,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,0,1,1},
{0,2,0,0,2,2,0},
{0,0,0,1,1,1,0}
};
int datasets2[VERTIFYCOUNT][LABLECOUNT]={ //验证集
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0},
{1,2,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,2,2,2,2,2,0},
{0,2,0,0,2,2,1},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,0}
};
/*int datasets3[SAMPLECOUNT][LABLECOUNT]{
{1,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,1,0,0,1,1},
{1,1,1,0,1,1,1},
{0,0,2,2,0,2,1},
{0,2,1,1,1,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,0,1,1},
{0,2,0,0,2,2,0},
{0,0,0,1,1,1,0},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0},
{1,2,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,2,2,2,2,2,0},
{0,2,0,0,2,2,1},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,0}
};*/
typedef struct samplesets{
bool no[SAMPLECOUNT];
}ss;
typedef struct vertifysets{
bool no[VERTIFYCOUNT];
}vs;
typedef struct node{
int lable;
int data;
node *brother;
node *children;
ss nodess;
}node,*np;
typedef struct datalink{
int data;
int num;
int c1;
datalink *next;
}*dl;
int gain(ss ss0,bool lablemark[LABLECOUNT]) //计算信息增益最大特征
{
int count,count1,count2,result=0;
double D=0;
double H,G,C1=0,C2=0,GMAX=0;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)if(ss0.no[count]!=0)D++; //求D
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1)
{
if(datasets[count][0]==0) C1++;
else C2++;
}
}
H=-(C1/D)*log(C1/D)/log(2)-(C2/D)*log(C2/D)/log(2);
C1=0,C2=0;
dl head,current;
head=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink));
for(count=0;count<LABLECOUNT;count++,head=NULL)
{
if(lablemark[count]==1)
{
for(count1=0;count1<SAMPLECOUNT;count1++)
{
if(ss0.no[count1]==1)
{
head=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink));
head->data=datasets[count1][count];
head->num=1;
if(datasets[count1][0]==0)head->c1=1;
else head->c1=0;
head->next=NULL;
break;
}
}
for(count1++;count1<SAMPLECOUNT;count1++)
{
if(ss0.no[count1]==1)
{
for(current=head;current!=NULL;current=current->next)
{
if(current->data==datasets[count1][count])
{
current->num++;
if(datasets[count1][0]==0)current->c1++;
break;
}
if(current->next==NULL)
{
current->next=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink));
current=current->next;
current->data=datasets[count1][count];
current->num=1;
if(datasets[count1][0]==0)current->c1=1;
else current->c1=0;
current->next=NULL;
break;
}
}
}
}
for(current=head,G=H;current!=NULL;current=current->next)
{
if(current->num!=current->c1&¤t->c1!=0)G+=((double)current->num/D)*((double)current->c1/(double)current->num*log((double)current->c1/(double)current->num)/log(2)+(1-(double)current->c1/(double)current->num)*log(1-(double)current->c1/(double)current->num)/log(2));
}
if(G>GMAX||result==0)
{
GMAX=G;
result=count;
}
}
}
/*for(count=0,G=H;count<LABLECOUNT;count++,G=H)
{
if(lablemark[count]==1)
{
for(count1=0,C1=0,C2=0;count1<LABLENUM;count1++,C1=0,C2=0)
{
for(count2=0;count2<SAMPLECOUNT;count2++)
{
if(ss0.no[count2]==1&&datasets[count2][count]==count1)
{
if(datasets[count2][0]==0)C1++;
else C2++;
}
}
if(C1!=0&&C2!=0)G+=((C1+C2)/D)*(C1/(C1+C2)*log(C1/(C1+C2))/log(2)+C2/(C1+C2)*log(C2/(C1+C2))/log(2));
}
if(G>GMAX||result==0)
{
GMAX=G;
result=count;
}
}
}*/
return result;
}
int gini(ss ss0,bool lablemark[LABLECOUNT]) //计算基尼指数最小的特征
{
double G=0,V=0,Vc,min=-1;
int count,count1,count2;
int result;
dl head=NULL;
dl current;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1)V++;
}
for(count=0;count<LABLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(lablemark[count]==1)
{
head=NULL;
for(count1=0;count1<SAMPLECOUNT;count1++)
{
if(ss0.no[count1]==1)
{
for(current=head;;) //找到记录或者创建新纪录后跳出
{
if(current!=NULL)
{
if(current->data==datasets[count1][count]) //这个取值被记录过
{
current->num++;
if(datasets[count1][0]==0)current->c1++; //记录内部计数量处理
break;
}
else if(current->next==NULL) //已经找到最右端记录,应当创建新记录
{
current->next=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink));
current=current->next;
current->data=datasets[count1][count]; //记录新取值
current->next=NULL;
current->num=1;
if(datasets[count1][0]==0)current->c1=1;
else current->c1=0;
break;
}
else current=current->next; //继续向右寻找
}
else //head为空的情况
{
head=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink));
current=head;
current->data=datasets[count1][count]; //记录新取值
current->next=NULL;
current->num=1;
if(datasets[count1][0]==0)current->c1=1;
else current->c1=0;
break;
}
}
}
}
for(current=head,G=0;current!=NULL;current=current->next)
{
G+=(current->num/V)*2*current->c1/current->num*(1-current->c1/current->num); //计算当前特征的基尼指数
}
if(min==-1||G<min)
{
min=G;
result=count;
}
}
}
return result;
}
int c_rate(ss ss0,vs vs0,int lable) //正确率是否通过的函数
{
double c_rate1,c_rate2;
int temp1=0,temp2=0,count;
bool good;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1)
{
if(datasets[count][0]==0)temp1++;
else temp2++;
}
}
if(temp1>temp2)good=0; //判断是好瓜节点还是坏瓜节点
else good=1; //若好瓜坏瓜数目相同,判断为好瓜节点
for(count=0,temp1=0,temp2=0;count<VERTIFYCOUNT;count++)
{
if(vs0.no[count]==1)
{
if(datasets2[count][0]==good)temp1++;
temp2++;
}
}
c_rate1=(double)temp1/(double)temp2; //划分前的正确率
dl current;
dl head=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink)); //用datalink保存属性的所有取值
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1)
{
head->num=1;
head->data=datasets[count][lable];
if(datasets[count][0]==0)head->c1=1;
else head->c1=0;
head->next=NULL;
break;
}
}
count++;
for(;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1)
{
for(current=head;;current=current->next)
{
if(current->data==datasets[count][lable]) //找到记录
{
current->num++;
if(datasets[count][0]==0)current->c1++;
break;
}
else if(current->next==NULL) //没找到,创建新记录
{
current->next=(dl)malloc(sizeof(datalink));
current=current->next;
current->num=1;
current->data=datasets[count][lable];
if(datasets[count][0]==0)current->c1=1;
else current->c1=0;
current->next=NULL;
break;
}
}
}
}
for(count=0,temp1=0;count<VERTIFYCOUNT;count++)
{
if(vs0.no[count]==1)
{
for(current=head;current!=NULL;current=current->next)
{
if(current->data==datasets2[count][lable])
{
if(datasets2[count][0]==((current->num-current->c1)>current->c1))temp1++;
break;
}
if(current->next==NULL)
{
temp2--; //如果没找到这种属性取值,则这个验证样例作废
break;
}
}
}
}
c_rate2=(double)temp1/(double)temp2; //划分后的正确率
if(c_rate2>c_rate1)return 1; //应当划分,不应当剪枝
else if(c_rate2==c_rate1)return 0; //不应当划分,不应当剪枝
else return -1; //不应当划分,应当剪枝
}
void post_pruning(np root,vs vs0)
{
int count;
np current,current1;
vs vsnext=vs0;
if(root->children==NULL)return;
for(current=root->children;current!=NULL;current=current->brother)
{
if(current->children!=NULL) //如果这个节点的当前孩子还有孩子,则当前孩子可能需要处理
{
for(count=0,vsnext=vs0;count<VERTIFYCOUNT;count++)if(datasets2[count][current->lable]!=current->data)vsnext.no[count]=0; //构造下一个vs
post_pruning(current,vsnext);
if(current->children!=NULL)return; //如果这个节点的当前孩子被处理完后仍有孩子,则这个节点已经无法处理了
}
}
//如果程序能走到这里,说明这个节点需要判断一下是否应该剪枝
if(c_rate(root->nodess,vs0,root->children->lable)<0)root->children=NULL; //如果这个节点分叉正确率判断未通过,则剪枝
return;
}
void process(np root,ss ss0,bool lablemark[LABLECOUNT],int lable) //普通的生成决策树
{
lablemark[lable]=0;
root->nodess=ss0;
int count,count1,count2,count3;
int temp=-1;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++) //检查所有实例是否同属一类
{
if(ss0.no[count]!=0)
{
if(temp==-1)temp=datasets[count][0];
else if(datasets[count][0]!=temp)goto ss0checkend;
}
}
root->nodess=ss0; //所有实例属同一类的操作
lablemark[lable]=1; //数组传入函数时如果改变数值,原数组数值会发生改变,这是我不希望发生的,所以在退出的时候将改变的值改回去
return;
ss0checkend:
for(count=0;count<LABLECOUNT;count++) //检查特征集是否为空
{
if(lablemark[count]!=0)goto lablemarkcheckend; //若有不为空的便可跳过
}
root->nodess=ss0; //特征集为空的操作
lablemark[lable]=1;
return;
lablemarkcheckend:
temp=gini(ss0,lablemark); //计算基尼指数最小的特征
//temp=gain(ss0,lablemark);
ss ssnext;
np current;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++) //遍历有几种取值
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1) //应当被检查的实例
{
for(current=root->children;;) //遍历root的孩子,看这个取值是否被记录
{
if(current==NULL) //未被记录
{
if(root->children==NULL)
{
root->children=(np)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); //创建新的孩子节点
current=root->children;
}
else
{
for(current=root->children;current->brother!=NULL;current=current->brother);
current->brother=(np)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
current=current->brother;
}
current->brother=NULL;
current->children=NULL;
current->lable=temp;
current->data=datasets[count][temp];
for(count3=0,ssnext=ss0;count3<SAMPLECOUNT||count3<VERTIFYCOUNT;count3++)
{
if(datasets[count3][temp]!=datasets[count][temp])ssnext.no[count3]=0; //构造下一个样本组
}
process(current,ssnext,lablemark,temp);
current=root->children;
}
else if(datasets[count][temp]==current->data)break; //这个取值已经记录在案
else current=current->brother; //与当前记录不符,查看下一个记录
}
}
}
}
void pre_pruning_process(np root,ss ss0,vs vs0,bool lablemark[LABLECOUNT],int lable)//带预剪枝的决策树生成
{
lablemark[lable]=0;
root->nodess=ss0;
int count,count1,count2,count3;
int temp=-1;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++) //检查所有实例是否同属一类
{
if(ss0.no[count]!=0)
{
if(temp==-1)temp=datasets[count][0];
else if(datasets[count][0]!=temp)goto ss0checkend;
}
}
root->nodess=ss0; //所有实例属同一类,判为叶节点
lablemark[lable]=1; //数组传入函数时如果改变数值,原数组数值会发生改变,所以在退出的时候将改变的值改回去
return;
ss0checkend:
for(count=0;count<LABLECOUNT;count++) //检查特征集是否为空
{
if(lablemark[count]!=0)goto lablemarkcheckend; //若有不为空的便可跳过
}
root->nodess=ss0; //特征集为空,判为叶节点
lablemark[lable]=1;
return;
lablemarkcheckend:
temp=gini(ss0,lablemark); //计算基尼指数最小的特征
//temp=gain(ss0,lablemark);
if(c_rate(ss0,vs0,temp)<=0) //预剪枝正确率判断没有通过,则不划分
{
root->nodess=ss0;
lablemark[lable]=1;
return;
}
ss ssnext;
vs vsnext;
np current;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++) //遍历有几种取值
{
if(ss0.no[count]==1) //应当被检查的实例
{
for(current=root->children;;) //遍历root的孩子,看这个取值是否被记录
{
if(current==NULL) //未被记录
{
if(root->children==NULL)
{
root->children=(np)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); //创建新的孩子节点
current=root->children;
}
else
{
for(current=root->children;current->brother!=NULL;current=current->brother);
current->brother=(np)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
current=current->brother;
}
current->brother=NULL;
current->children=NULL;
current->lable=temp;
current->data=datasets[count][temp];
for(count3=0,ssnext=ss0,vsnext=vs0;count3<SAMPLECOUNT||count3<VERTIFYCOUNT;count3++) //构造下一个样本组
{
if(count3<SAMPLECOUNT&&datasets[count3][temp]!=datasets[count][temp])ssnext.no[count3]=0;
if(count3<VERTIFYCOUNT&&datasets2[count3][temp]!=datasets[count][temp])vsnext.no[count3]=0;
}
pre_pruning_process(current,ssnext,vsnext,lablemark,temp);
current=root->children;
}
else if(datasets[count][temp]==current->data)break; //这个取值已经记录在案
else current=current->brother; //与当前记录不符,查看下一个记录
}
}
}
}
void print(np root,int depth) //中序遍历,输出图形
{
if(root==NULL)return;
np current;
int count;
current=root->children;
print(current,depth+1);
for(count=0;count<depth;count++)printf("\t");
if(root->lable==-1)
{
printf("ROOT");
}
else
{
printf("L%dD%d",root->lable,root->data);
}
if(root->children==NULL)
{
printf(":");
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)
{
if(root->nodess.no[count]==1)printf(" %d",count+1);
}
}
printf("\n");
while(current!=NULL)
{
current=current->brother;
print(current,depth+1);
}
}
int main(void)
{
int count;
ss ss0;
vs vs0;
bool lablemark[LABLECOUNT];
for(count=0;count<LABLECOUNT;count++)lablemark[count]=1;
np root=(np)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
root->children=NULL;
root->brother=NULL;
root->data=-1;
root->lable=-1;
for(count=0;count<SAMPLECOUNT;count++)ss0.no[count]=1;
for(count=0;count<VERTIFYCOUNT;count++)vs0.no[count]=1;
//process(root,ss0,lablemark,0);
pre_pruning_process(root,ss0,vs0,lablemark,0);
//post_pruning(root,vs0);
print(root,0);
system("pause");
}
完成草率,可能有误,欢迎指正




 本文详细介绍了一种基于机器学习的决策树算法实现过程,包括信息增益计算、基尼指数计算、预剪枝和后剪枝等关键步骤。通过具体的代码示例,展示了如何从数据集中构建决策树,并评估其在验证集上的表现。
本文详细介绍了一种基于机器学习的决策树算法实现过程,包括信息增益计算、基尼指数计算、预剪枝和后剪枝等关键步骤。通过具体的代码示例,展示了如何从数据集中构建决策树,并评估其在验证集上的表现。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








