CFNetWork的概念
CFNetWork是一个底层次高性能的framework,可以让你对协议栈有更多更细的控制。它是对BSD socket的扩展,BSD socket是一个标准的socket抽象API,可以为你提供对象来简化诸如用FTP、HTTP或者解析DNS主机名之类的一些任务。CFNetWork是建立在BSD socket基础上的,无论是在硬件还是在技术上。
而NSURL(属于Cocoa层)是建立在CFNetWork技术上的。
When to Use CFNetwork /* 什么时候用CFNetWork */
CFNetwork has a number of advantages over BSD sockets. It provides run-loop integration, so if your application is run loop based you can use network protocols without implementing threads. CFNetwork also contains a number of objects to help you use network protocols without having to implement the details yourself. For example, you can use FTP protocols without having to implement all of the details with the CFFTP API. If you understand the networking protocols and need the low-level control they provide but don't want to implement them yourself, then CFNetwork is probably the right choice.
There are a number of advantages of using CFNetwork instead of Foundation-level networking APIs. CFNetwork is focused more on the network protocols, whereas the Foundation-level APIs are focused more on data access, such as transferring data over HTTP or FTP. Although Foundation APIs do provide some configurability, CFNetwork provides a lot more. For more information on Foundation networking classes, read URL Loading System Programming Guide.
Now that you understand how CFNetwork interacts with the other OS X networking APIs, you're ready to become familiar with the CFNetwork APIs along with two APIs that form the infrastructure for CFNetwork.
CFNetwork Infrastructure
Before learning about the CFNetwork APIs, you must first understand the APIs which are the foundation for the majority of CFNetwork. CFNetwork relies on two APIs that are part of the Core Foundation framework, CFSocket and CFStream. Understanding these APIs is essential to using CFNetwork.
在学习CF的API之前,你必须首先理解一些组成CF大部分的技术API。CF是依托于两大Core Foundation framework 的API:CFSocket and CFStream。学会这些API对使用CF是非常必要的
CFSocket API
Sockets are the most basic level of network communications. A socket acts in a similar manner to a telephone jack. It allows you to connect to another socket (either locally or over a network) and send data to that socket.
The most common socket abstraction is BSD sockets. CFSocket is an abstraction for BSD sockets. With very little overhead, CFSocket provides almost all the functionality of BSD sockets, and it integrates the socket into a run loop. CFSocket is not limited to stream-based sockets (for example, TCP), it can handle any type of socket.
You could create a CFSocket object from scratch using the CFSocketCreate function, or from a BSD socket using the CFSocketCreateWithNative function. Then, you could create a run-loop source using the function CFSocketCreateRunLoopSource and add it to a run loop with the functionCFRunLoopAddSource. This would allow your CFSocket callback function to be run whenever the CFSocket object receives a message.
Read CFSocket Reference for more information about the CFSocket API.
socket是网络交换中最基本的层。一个socket很像一个电话。它允许你与另一个socket(无论是本地的还是远端网络的)连接并且发送数据到那个socket。
最常见的socket是BSD socket。CF是BSD套接字的抽象。用很小的开销,CF提供的几乎所有BSD套接字的功能,并且它套接字与一个run-loop结合在一起。CF不局限于必须使用控制流的套接字,它可以处理任何类型的套接字。
CFStream API
Read and write streams provide an easy way to exchange data to and from a variety of media in a device-independent way. You can create streams for data located in memory, in a file, or on a network (using sockets), and you can use streams without loading all of the data into memory at once.
读写流可以提供一个简单的方法来交换数据,发送或者接受通过各种各样与设备无关的媒介方法。你可以为数据创建一个流无论数据是在缓存,文件,或者在网络上,你都可以用流不用一次性把数据装载到内存中。
A stream is a sequence of bytes transmitted serially over a communications path. Streams are one-way paths, so to communicate bidirectionally an input (read) stream and output (write) stream are necessary. Except for file-based streams, you cannot seek within a stream; once stream data has been provided or consumed, it cannot be retrieved again from the stream.
一个流就是一连串的字节在一个交换路径上连续不断的传播。流是单向路径,所以为了双向交流的读入流和写出流是必须的。除了基于文件的数据流,你不能在流中检索;一旦数据流已提供或消耗时,它不能被再次从流中检索到。
CFStream is an API that provides an abstraction for these streams with two new CFType objects: CFReadStream and CFWriteStream. Both types of stream follow all of the usual Core Foundation API conventions. For more information about Core Foundation types, read Core Foundation Design Concepts.
CFStream 是一个API,用两个新的对象提供了对这种流的完美抽象,这两个新的对象是CFReadStream and CFWriteStream。
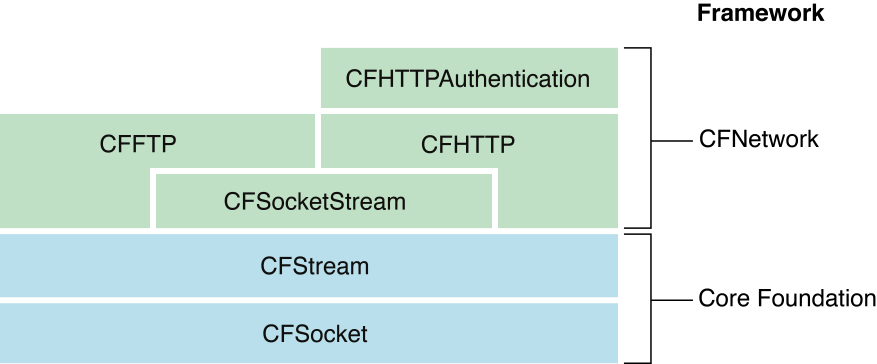
CFStream is built on top of CFSocket and is the foundation for CFHTTP and CFFTP. As you can see in Figure 1-2, even though CFStream is not officially part of CFNetwork, it is the basis for almost all of CFNetwork.
CFStream创建在CFSocket的上层,并且是CFHTTP and CFFTP的基础。
You can use read and write streams in much the same way as you do UNIX file descriptors. First, you instantiate the stream by specifying the stream type (memory, file, or socket) and set any options. Next, you open the stream and read or write any number of times. While the stream exists, you can get information about the stream by asking for its properties. A stream property is any information about the stream, such as its source or destination, that is not part of the actual data being read or written. When you no longer need the stream, close and dispose of it.
您可以使用读取和写入数据流中的大致相同的方式,就像你做的UNIX文件描述符。首先,通过指定的流类型(内存,文件或套接字),并设置任何选项实例化流。接着,在打开流和读取或写入任意次数。而流的存在,你可以通过询问其属性获取有关流的信息。一个流的属性是关于流,如它的源或目标,那是跟真正的数据区分的数据被读取或写入的一部分的任何信息。当你不再需要的数据流,关闭和处置。
CFStream functions that read or write a stream will suspend, or block, the current process until at least one byte of the data can be read or written. To avoid trying to read from or write to a stream when the stream would block, use the asynchronous version of the functions and schedule the stream on a run loop. Your callback function is called when it is possible to read and write without blocking.
该读或写一个流将暂停,或嵌段CFStream功能,当前的过程直到该数据中的至少一个字节可以被读取或写入。为了避免试图读取或写入时流将挡,使用功能的异步版本,并计划在运行循环流流。当它是可以读取和写入而不会阻塞你的回调函数被调用。
In addition, CFStream has built-in support for the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol. You can set up a dictionary containing the stream's SSL information, such as the security level desired or self-signed certificates. Then pass it to your stream as the kCFStreamPropertySSLSettings property to make the stream an SSL stream.
此外, CFStream还内置了安全套接字层( SSL )协议的支持。你可以建立一个包含流的SSL信息,字典等所需的安全级别或自签名证书。然后将它传递给你的流作为kCFStreamPropertySSLSettings属性,以使数据流成为SSL流。
CFNetwork API Concepts /* CFNetwork API 的概要 */
To understand the CFNetwork framework, you need to be familiar with the building blocks that compose it. The CFNetwork framework is broken up into separate APIs, each covering a specific network protocol. These APIs can be used in combination, or separately, depending on your application. Most of the programming conventions are common among the APIs, so it's important to comprehend each of them.
为了理解这个协议框架,你需要熟悉构成它的每一块。这个框架可以划分为几方面的API,每一个包含了特殊的网络协议。这些API可以被用来组合或者分离使用,这取决于你的应用。大多数程序中都可以见到这些API,所以理解他们每一部分是非常重要的。
CFFTP API
Communicating with an FTP server is made easier with CFFTP. Using the CFFTP API, you can create FTP read streams (for downloading) and FTP write streams (for uploading). Using FTP read and write streams you can perform functions such as:
CFFTP协议使得与FTP通信变得非常简单。可以轻松创建读取流(下载)、写入流(上传)。可以做一下工作:
Download a file from an FTP server /* 从FTP服务器下载一个文件 */
Upload a file to an FTP server /* 上传一个文件到FTP服务器 */
Download a directory listing from an FTP server /* 下载一个文件夹列表从一个FTP服务器 */
Create directories on an FTP server /* 创建一个文件夹在服务器上 */
An FTP stream works like all other CFNetwork streams. For example, you can create an FTP read stream by calling the function CFReadStreamCreateWithFTPURL function. Then, you can call the function CFReadStreamGetError at any time to check the status of the stream.
一个FTP流就像其他所有CFNetwork的流。例如,您可以创建一个FTP通过调用函数CFReadStreamCreateWithFTPURL函数读取流。然后,您可以调用函数CFReadStreamGetError随时检查流的状态。
By setting properties on FTP streams, you can adapt your stream for its particular application. For example, if the server that the stream is connecting to requires a user name and password, you need to set the appropriate properties so the stream can work properly. For more information about the different properties available to FTP streams read Setting up the Streams.
通过FTP数据流设置属性,可以适应您的流其特定的应用程序。例如,如果流连接到该服务器需要用户名和密码,您需要设置相应的属性,使数据流能够正常工作。有关可用的FTP数据流的不同属性的更多信息,请阅读设置流。
A CFFTP stream can be used synchronously or asynchronously. To open the connection with the FTP server that was specified when the FTP read stream was created, call the function CFReadStreamOpen. To read from the stream, use the CFReadStreamRead function and provide the read stream reference, CFReadStreamRef, that was returned when the FTP read stream was created. The CFReadStreamRead function fills a buffer with the output from the FTP server.
一个CFFTP流可以同步或异步使用。要打开与指定当FTP读取数据流创建FTP服务器的连接,调用函数CFReadStreamOpen 。从流中读取,使用CFReadStreamRead功能,并提供读取数据流参考, CFReadStreamRef ,即返回时读取FTP创建流。该CFReadStreamRead函数填充与FTP服务器的输出缓冲区。
CFHTTP API
To send and receive HTTP messages, use the CFHTTP API. Just as CFFTP is an abstraction for FTP protocols, CFHTTP is an abstraction for HTTP protocols.
发送和接收HTTP消息,使用CFHTTP API。正如CFFTP是FTP协议的一个抽象, CFHTTP是HTTP协议的抽象。
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a request/response protocol between a client and a server. The client creates a request message. This message is then serialized, a process that converts the message into a raw byte stream. Messages cannot be transmitted until they are serialized first. Then the request message is sent to the server. The request typically asks for a file, such as a webpage. The server responds, sending back a string followed by a message. This process is repeated as many times as is necessary.
超文本传输协议(HTTP )是一个客户机和一个服务器之间的请求/响应协议。客户端创建一个请求消息。此消息随后被序列化,这一过程将消息转换成原始的字节流。不能被发送的消息,直到它们被第一序列化。然后将请求消息发送到服务器。该请求典型地请求一个文件,如网页。服务器的响应,回送一个字符串后跟一个消息。如需要此过程重复多次。
To create an HTTP request message, you specify the following:
The request method, which can be one of the request methods defined by the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, such as OPTIONS, GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE, TRACE, and CONNECT
The URL, such as http://www.apple.com
The HTTP version, such as version 1.0 or 1.1
The message’s headers, by specifying the header name, such as User-Agent, and its value, such as MyUserAgent
The message’s body
After the message has been constructed, you serialize it. Following serialization, a request might look like this:
GET / HTTP/1.0\r\nUser-Agent: UserAgent\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n
Deserialization is the opposite of serialization. With deserialization, a raw byte stream received from a client or server is restored to its native representation. CFNetwork provides all of the functions needed to get the message type (request or response), HTTP version, URL, headers, and body from an incoming, serialized message.
反序列化是序列化的对立面。与反序列化,接受来自客户端的原始字节流或服务器恢复到其原始的代表性。 CFNetwork框架提供了所有需要得到的消息类型(请求或响应)的功能, HTTP版本, URL ,标题和正文的传入,序列化消息。
CFHTTPAuthentication API
If you send an HTTP request to an authentication server without credentials (or with incorrect credentials), the server returns an authorization challenge (more commonly known as a 401 or 407 response). The CFHTTPAuthentication API applies authentication credentials to challenged HTTP messages. CFHTTPAuthentication supports the following authentication schemes:
如果你发送一个HTTP请求到认证服务器,而没有凭证(或不正确的凭据) ,服务器返回授权挑战(俗称401或407响应) 。该CFHTTPAuthentication的API适用于身份验证凭据的挑战HTTP消息。 CFHTTPAuthentication的支持以下身份验证方案:
Basic /* 基本的 */
Digest /* 摘要 */
NT LAN Manager (NTLM)
Simple and Protected GSS-API Negotiation Mechanism (SPNEGO)
New in OS X v10.4 is the ability to carry persistency across requests. In OS X v10.3 each time a request was challenged, you had to start the authentication dialog from scratch. **Now, you maintain a set of CFHTTPAuthentication objects for each server. When you receive a 401 or 407 response, you find the correct object and credentials for that server and apply them. CFNetwork uses the information stored in that object to process the request as efficiently as possible.
现在,你在每个服务器上拥有一个CFHTTPAuthentication的对象的集合。当你收到一个401或407的反应,你会发现该服务器的正确的对象和凭证,并应用它们。 CFNetwork会使用存储在该对象来处理该请求,尽可能有效的信息。
By carrying persistency across request, this new version of CFHTTPAuthentication provides much better performance. More information about how to use CFHTTPAuthentication is available in Communicating with Authenticating HTTP Servers.
通过开展持续性跨越的要求, CFHTTPAuthentication的这个新版本提供了更好的性能。有关如何使用CFHTTPAuthentication的是与认证HTTP服务器通讯提供更多的信息。
CFHost API
You use the CFHost API to acquire host information, including names, addresses, and reachability information. The process of acquiring information about a host is known as resolution.
您可以使用CFHost API来获取主机信息,包括姓名,地址和可达性信息。获取关于主机的信息的过程被称为分解析。
CFHost is used just like CFStream:
Create a CFHost object.
Start resolving the CFHost object.
Retrieve either the addresses, host names, or reachability information.
Destroy the CFHost object when you are done with it.
Like all of CFNetwork, CFHost is IPv4 and IPv6 compatible. Using CFHost, you could write code that handles IPv4 and IPv6 completely transparently.
CFHost is integrated closely with the rest of CFNetwork. For example, there is a CFStream function called CFStreamCreatePairWithSocketToCFHost that will create a CFStream object directly from a CFHost object. For more information about the CFHost object functions, see CFHost Reference.
CFHost与CFNetwork的其他地方紧密结合起来。例如,有一个名为CFStreamCreatePairWithSocketToCFHost一个CFStream函数,将直接从CFHost对象创建一个CFStream对象。有关CFHost对象功能的详细信息,请参阅CFHost参考。
CFNetServices API
If you want your application to use Bonjour to register a service or to discover services, use the CFNetServices API. Bonjour is Apple's implementation of zero-configuration networking (ZEROCONF), which allows you to publish, discover, and resolve network services.
如果你希望你的应用程序使用Bonjour来注册一个服务或者发现服务,请使用CFNetServices API。 Bonjour是苹果的实施零配置网络( ZEROCONF ) ,它允许你发布,发现和解决网络服务。
To implement Bonjour the CFNetServices API defines three object types: CFNetService, CFNetServiceBrowser, and CFNetServiceMonitor. A CFNetService object represents a single network service, such as a printer or a file server. It contains all the information needed for another computer to resolve that server, such as name, type, domain and port number. A CFNetServiceBrowser is an object used to discover domains and network services within domains. And a CFNetServiceMonitor object is used to monitor a CFNetService object for changes, such as a status message in iChat.
为了实现卓悦的CFNetServices API定义了三种类型的对象: CFNetService , CFNetServiceBrowser和CFNetServiceMonitor 。甲CFNetService对象表示一个单一的网络服务,诸如打印机或文件服务器。它包含所有解决该服务器例如名称,类型,域和端口号所需的另一台计算机中的信息。甲CFNetServiceBrowser是用来发现域内的域和网络服务的对象。和一个CFNetServiceMonitor对象用于监视更改,如在iChat中的状态消息一CFNetService对象。
For a full description of Bonjour, see Bonjour Overview. For more information about using CFNetServices and implementing Bonjour, see NSNetServices and CFNetServices Programming Guide.
CFNetDiagnostics API
Applications that connect to networks depend on a stable connection. If the network goes down, this causes problems with the application. By adopting the CFNetDiagnostics API, the user can self-diagnose network issues such as:
连接到网络的应用程序依赖于一个稳定的连接。如果网络出现故障,这会导致问题的应用程序。通过采用CFNetDiagnostics API时,用户可以自诊断网络问题,如:
Physical connection failures (for example, a cable is unplugged)
Network failures (for example, DNS or DHCP server no longer responds)
Configuration failures (for example, the proxy configuration is incorrect)
Once the network failure has been diagnosed, CFNetDiagnostics guides the user to fix the problem. You may have seen CFNetDiagnostics in action if Safari failed to connect to a website. The CFNetDiagnostics assistant can be seen in Figure 1-3.
Figure 1-3 Network diagnostics assistant
CFNetDiagnostics Assistant
By providing CFNetDiagnostics with the context of the network failure, you can call the CFNetDiagnosticDiagnoseProblemInteractively function to lead the user through the prompts to find a solution. Additionally, you can use CFNetDiagnostics to query for connectivity status and provide uniform error messages to the user.
To see how to integrate CFNetDiagnotics into your application read Using Network Diagnostics. CFNetDiagnostics is a new API in OS X v10.4.





 本文深入介绍了CFNetwork框架,包括其核心组件CFNetWork的概念、优势及应用场景,以及构成CFNetWork基础设施的重要API如CFSocket和CFStream。此外,文章还详细阐述了CFNetWork中的关键API概念,如CFFTPAPI、CFHTTPAPI、CFHostAPI等。
本文深入介绍了CFNetwork框架,包括其核心组件CFNetWork的概念、优势及应用场景,以及构成CFNetWork基础设施的重要API如CFSocket和CFStream。此外,文章还详细阐述了CFNetWork中的关键API概念,如CFFTPAPI、CFHTTPAPI、CFHostAPI等。
















 3285
3285

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








